- Graph:
- A graph consists of:
- a set of
vertices
(or nodes)
- a list (collection) of edges (or links) between two vertices of the graph
- a set of
vertices
(or nodes)
- A graph consists of:
- Example:
- Graph G =
{V, E}
where:
- V = {A, B, C, D}
- E = {(A,B), (B,C), (C,D), (A,D)}
Graphical representation:
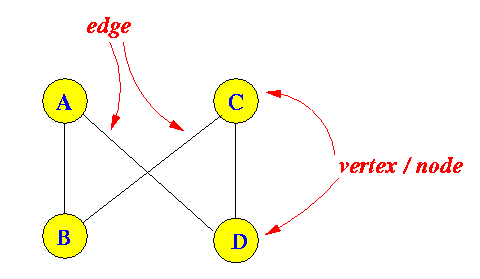
- Graph G =
{V, E}
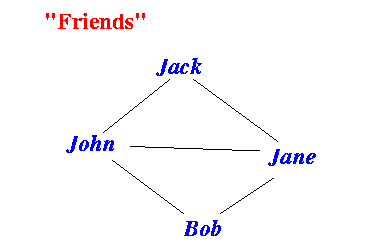
- Graphs are often used to
represent relationship information
- Example: "friendship" relationship
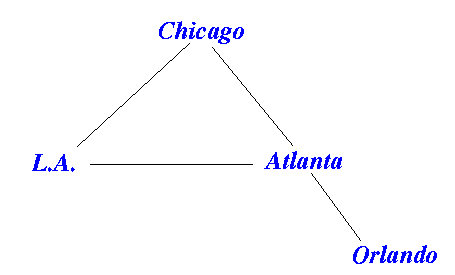
- Example: flight database
- Vertex set
- Vertex set V(G) = the set of vertices of graph G
- Edge-list
- Edge-list E(G) = the list (collection) of edges of graph G
- Notes:
- The collection of vertices is a
set
There are no duplicate elements in a set
- The collection of edges is
a list
There can be duplicate elements in a list
- The collection of vertices is a
set
- Some examples of
"extreme" graphs:
- Multiple edges between
vertices:
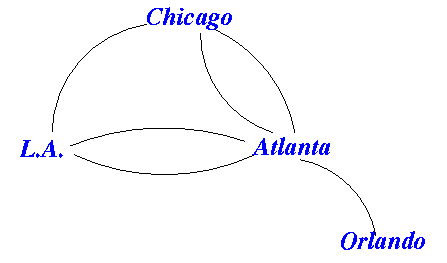
(Each edge represents a way to travel between 2 locations)
- Self-loops
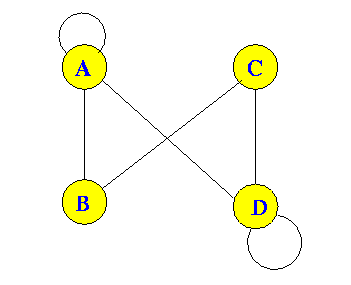
(An edge represents an equivalence relationship between 2 structures; some structures are "self-equivalent" while others and not)
- Multiple edges between
vertices:
- Simple graph:
- A graph
that does not have:
- Multiple edges between vertices
- Self-loops
- A graph
that does not have:
- Property of simple graphs:
- The list of edges is a set (no duplicate elements)
- Adjacent vertices:
- The vertices u and v are adjacent is they are connected by an edge in graph G
- Incident edge:
- An edge that connects the vertices u and v is said to be incident with u and v
- Degree of a node:
- Degree of a node v = number of incident edges to node v
Example:

The degree of each node = 2
- Walk:
- Walk between u and z
= a seccession of
edges of the form:
- uv, vw, wx, ...., yz
Example:
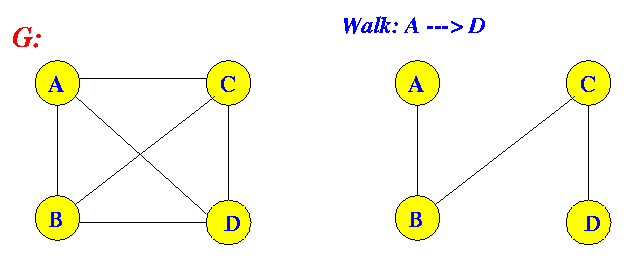
Walk = (A,B), (B,C), (C,D)
- Walk between u and z
= a seccession of
edges of the form:
- Trail:
- Trail = a
walk where
each edge is
different
Example:
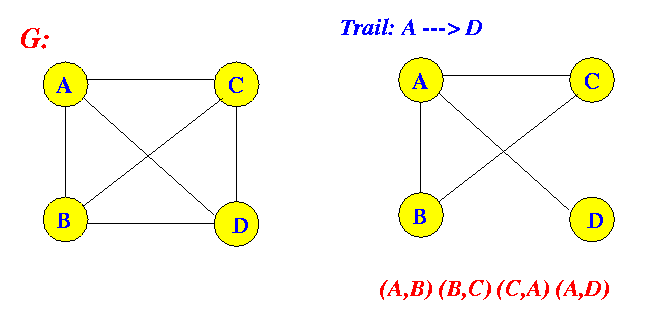
I.e.: trail = use an edge at most once
- Trail = a
walk where
each edge is
different
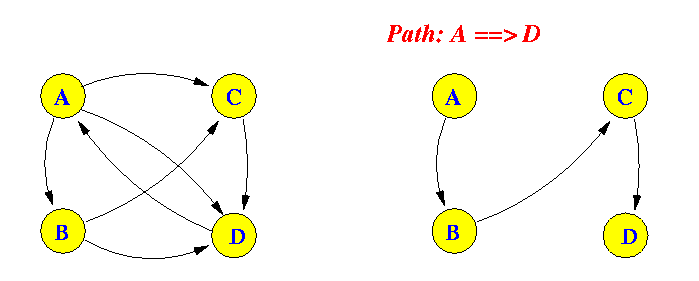
- Path:
- Path = a
walk where
each edge
and
each vertex is
different
Example:
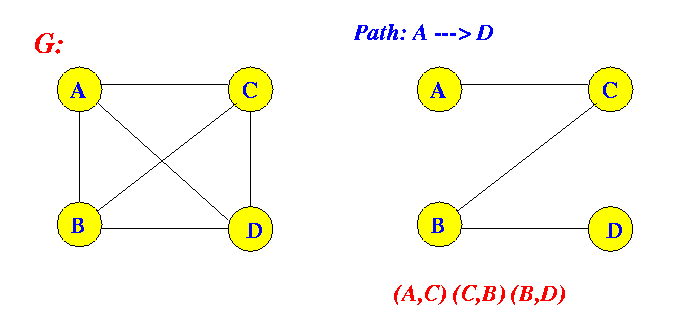
I.e.: path = visit a vertex at most once
- Path = a
walk where
each edge
and
each vertex is
different
- Cycle:
- Cycle = a
"path" where
starting vertex is
equal to the
ending vertex
(I put "path" in quotes because the starting vertex is repeated)
Example:
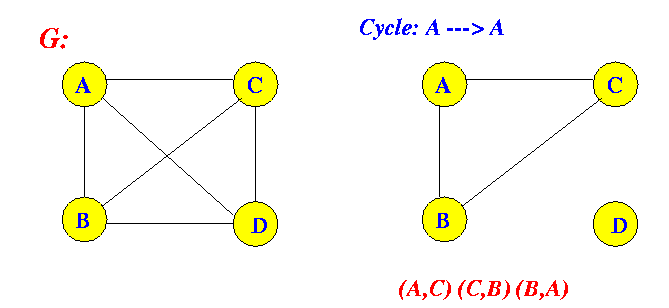
- Cycle = a
"path" where
starting vertex is
equal to the
ending vertex
- Complete graph:
- Complete graph =
a graph where
every vertex is
adjacent to
every other vertex
- Kn = the complete graph containing n vertices
Example:
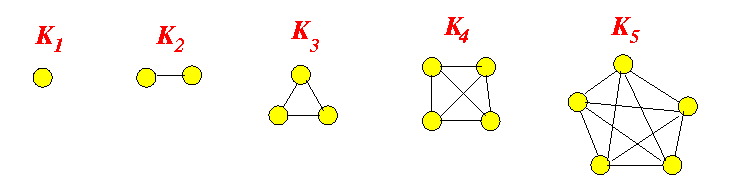
- Complete graph =
a graph where
every vertex is
adjacent to
every other vertex
- Edges:
- Edges of a graph can be:
- directed, or
- undirected
- Edges of a graph can be:
- Undirected edges:
- Undirected edges is like
a two-way street
- You can traverse an
undirected edge (u,v) as:
- u ⇒ v, or as
- v ⇒ u
- Undirect edges are sometimes denoted as {u,v}
- Undirected edges is like
a two-way street
- Direct edges:
- Undirected edges is like
a one-way street
- You can only traverse an
directed edge (u,v) as:
- u ⇒ v
- Undirected edges is like
a one-way street
- Directed graph:
- Directed graph = a graph with directed edges
Example:
- Property 1:
- If a (undirected) graph G has
m edges then:
∑ deg(v) = 2m v ∈ G - Proof:
- Each edge is
incident to
2 nodes
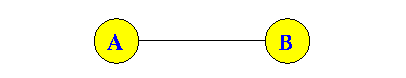
- Therefore, each edge contributes
2 to the
total sum
- There are m edges
Each edge contributes 2 to the total sum
Therefore: The total sum = 2 × m
Example:
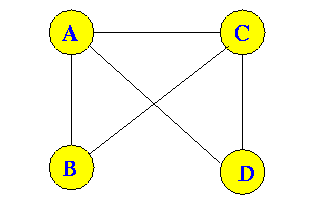
There are 5 edges
And: deg(A) + deg(B) + deg(C) + deg(D) = 3 + 2 + 3 + 2 = 10
- Each edge is
incident to
2 nodes
- If a (undirected) graph G has
m edges then:
- Property 2:
- If a directed graph G has
m edges then:
∑ indeg(v) = ∑ outdeg(v) = m v ∈ G v ∈ G - Proof:
- Each directed edge is
incident to
2 nodes:
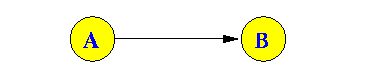
directed edge:
- once as an outgoing edge
- once as an incoming edge
- Therefore, each directed edge
contributes:
- 1 to the total sum of "indeg(v)"
- 1 to the total sum of "outdeg(v)"
- There are m edges
Each edge contributes 1 to each of the total sum
Therefore:
- The total sum "indeg(v)" = m
- The total sum "outdeg(v)" = m
Example:
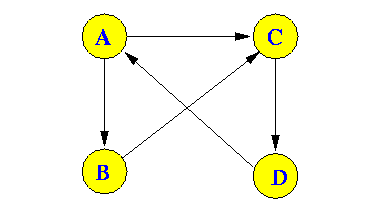
There are 5 edges
And: indeg(A) + indeg(B) + indeg(C) + indeg(D) = 1 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 5
outdeg(A) + outdeg(B) + outdeg(C) + outdeg(D) = 2 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 5
- Each directed edge is
incident to
2 nodes:
- If a directed graph G has
m edges then:
- Property 3:
- Let G be a
simple undirected graph
with n vertices and
m edges
Then:
n(n-1) m ≤ ------- 2Proof:
- One edge
connects 2 vertices
- There are n different vertices
- The maximum
number of ways to
select
2 different vertices is
(according to combinatorics):
n! Choose(n, 2) = ----------- (n-2)! 2! n (n-1) (n-2) (n-3).... 1 = --------------------------- [(n-2) (n-3) ... 1] [2] n(n-1) = -------- 2
- Therefore: the
maximum number of
(distinct) edges in a
graph with n vertices =
(n × (n-1))/2
Since this number is the maximum, it follows that:
m = a possible number of edges in a graph ≤ maximum number of edges in a graph n (n-1) ≤ --------- 2
- One edge
connects 2 vertices
- Example: graphs with
the maximum # edges
are complete graphs

Kn has (n×(n−1))/2 edges
- Let G be a
simple undirected graph
with n vertices and
m edges
- Subgraph:
- Graph S = {V(S), E(S)} is
a subgraph of
graph G = {V(G), E(G)}
if:
- V(S) ⊆ V(G)
- E(S) ⊆ E(G)
Example:
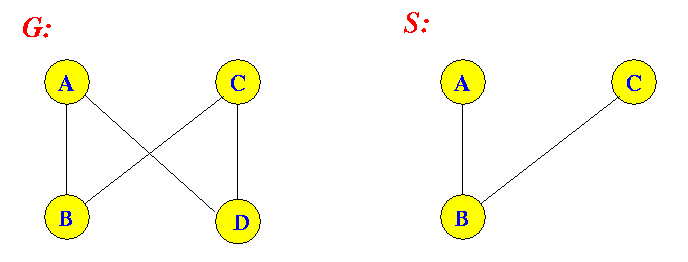
- Graph S = {V(S), E(S)} is
a subgraph of
graph G = {V(G), E(G)}
if:
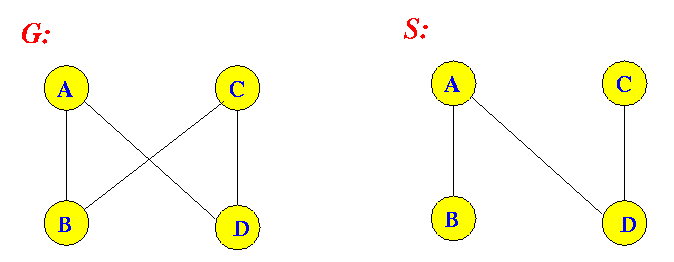
- Spanning subgraph:
- Graph S = {V(S), E(S)} is
a spanning subgraph of
graph G = {V(G), E(G)}
if:
- S
is a subgraph of
G, and
- V(S) = V(G)
Example:
- S
is a subgraph of
G, and
- Graph S = {V(S), E(S)} is
a spanning subgraph of
graph G = {V(G), E(G)}
if:
- Connected graph:
- Connected graph =
a graph where
for every pair of
nodes (u,v),
there exists a
path connecting
the nodes u and v
Example:
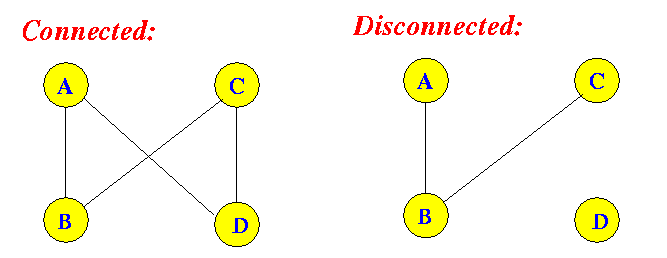
- Connected graph =
a graph where
for every pair of
nodes (u,v),
there exists a
path connecting
the nodes u and v
- Connected component:
- Connected component =
a maximally connected subgraph
Example:
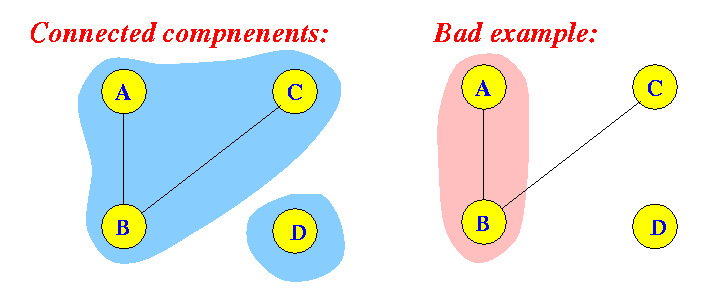
- Connected component =
a maximally connected subgraph
- Tree:
- Tree = a
connected graph
that does not have
any cycle
Example:
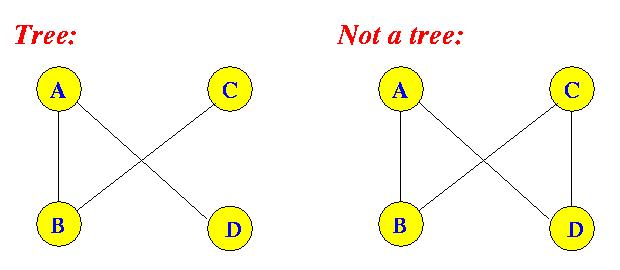
- Tree = a
connected graph
that does not have
any cycle
- Forest:
- Forest = a
(not necessaily connected) graph
that does not have
any cycle
Example:
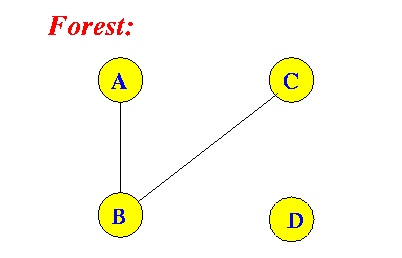
- Forest = a
(not necessaily connected) graph
that does not have
any cycle
- Spanning tree:
- Spanning tree = a
spanning subgraph
that is a tree
Example:
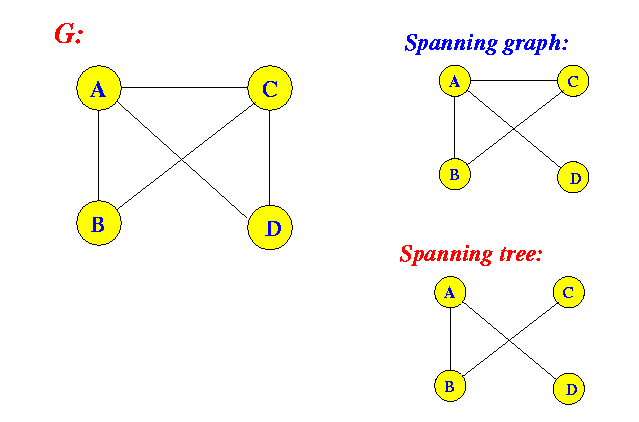
- Spanning tree = a
spanning subgraph
that is a tree
- # edges in some graphs:
- Let G be a
tree with
n vertices and
m edges
Then:
m = n -1
- Let G be a
forest with
n vertices and
m edges
Then:
m ≤ n -1
- Let G be a
connected graph with
n vertices and
m edges
Then:
m ≥ n -1
- Let G be a
tree with
n vertices and
m edges