- Every computer program written in
a high level programming language
has a starting point of execution
- Each programming language has
its own
convention on
where a program will
start execution
- Example starting point in some popular programming languages:
Programming language Starting point of a program Java main() method C/C++ main() method Python First line in the program
- How a computer program is executed:
- The execution will start
at the statement
at the starting point of
the execution
(In Java, this will be the first statement in main())
- After a statement is executed, the next statement executed depends on the flow of control
- The execution will start
at the statement
at the starting point of
the execution
- Flow of control:
- Normal flow of control is:
- After executing a statement, the next statement that will be executed is the statement following the last executed statement
- There are control statements in a programming language that can change the normal flow of control
- Normal flow of control is:
- Recall the Euclid Algorithm:
As long as one of the number is not zero (0) do { if ( number on A ≥ number on B ) replace the number on A by the value (A - B) otherwise replace the number on B by the value (B - A) } The Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) = BWe saw the execution of the Euclid algorithm using 2 pieces of paper: click here
- We have also seen a Java program
that implements the
Euclid algorithm:
public class Euclid { public static void main(String args[]) { int A; // Memory cell named "A" int B; // Memory cell named "B" // These memory cells are like the 2 pieces of paper // we used above. They can store and recall a value A = 28; // Write "28" on the piece of paper named "A" B = 36; // Write "36" on the piece of paper named "B" // ================================ // This is the Euclid Algorithm: // ================================ while ( A != 0 && B != 0 ) { if ( A >= B ) A = A - B; // Replace the number on A by (A-B) else B = B - A; // Replace the number on B by (B-A) } System.out.println("GCD = " + B); } }When the Java program is run on a computer, the computer will be doing pretty much the same thing as the execution on 2 pieces of paper that we saw here: click here
-
I will illustrate how a computer executes the
Euclid algorithm with a series of diagram:
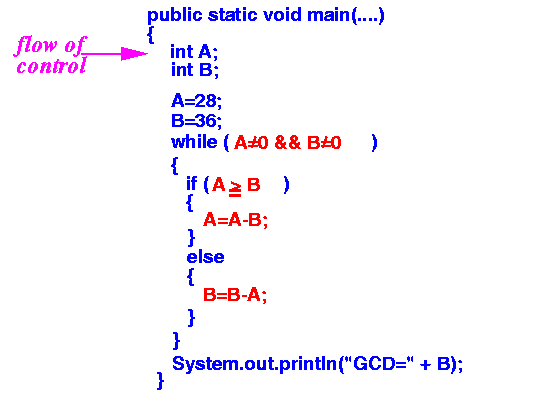
- The program execution
of a Java program starts
at beginning of main(...)
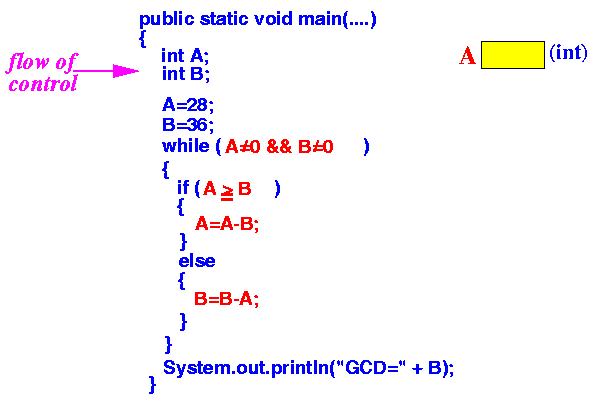
- Executing the
line "int A;"
tells the computer to
create a new variable name A
This is like getting a new sheet of paper and tag it with the name A
Result:
The flow of control goes to the next line
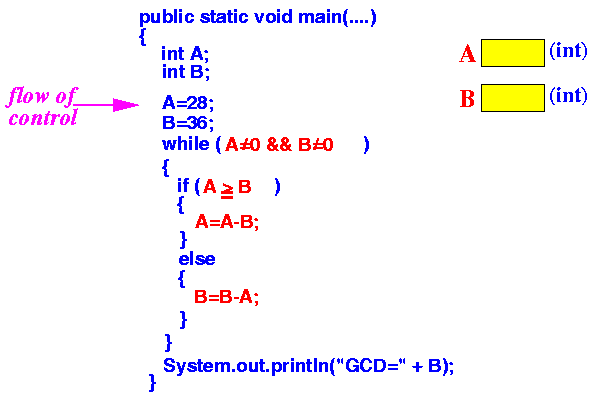
- Executing the
line "int B;"
tells the computer to
create a new variable name B
This is like getting a new sheet of paper and tag it with the name B
Result:
The flow of control goes to the next line
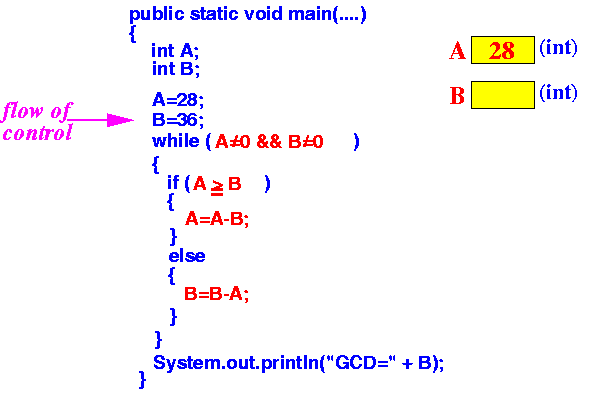
- Executing the
line "A=28;"
tells the computer to
put the number 28 in the variable A
This is like writing "28" on the sheet of paper tagged with the name A
Result:
- Executing the
line "B=36;"
tells the computer to
put the number 36 in the variable B
This is like writing "36" on the sheet of paper tagged with the name B
Result:
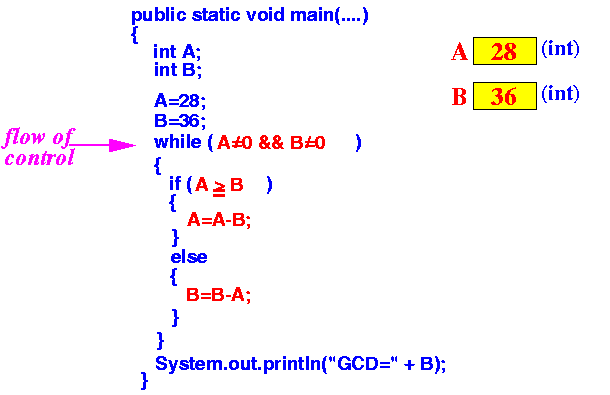
- Executing the
line "while (A≠0 && B≠0)"
tells the computer
only continue
inside the statements inside {...}
if the condition is true.
The symbol && means "and".
Since 28 (A) ≠ 0 and 36 (B) ≠ 0, the condition is true and the execution continues inside {...}
Result:
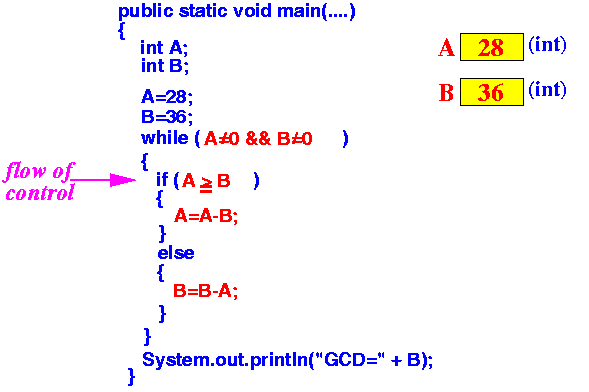
- Executing the
line "if (A≥B)"
tells the computer to:
continue
inside the first {...}
if the condition is true and
continue
inside the second {...}
if the condition is false
Since 28 (A) < 36 (B), the condition is false and the execution continues inside the second {...} (after the word else)
Result:
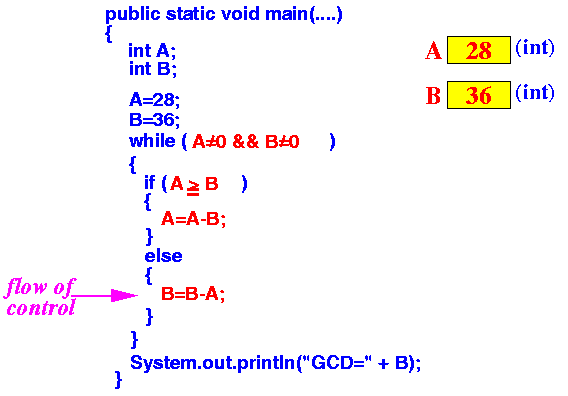
- Executing the
line "B=B−A;"
tells the computer to
put the difference (36−28)
in the variable B
This is like writing the difference (36−28) on the sheet of paper tagged with the name B
Result:
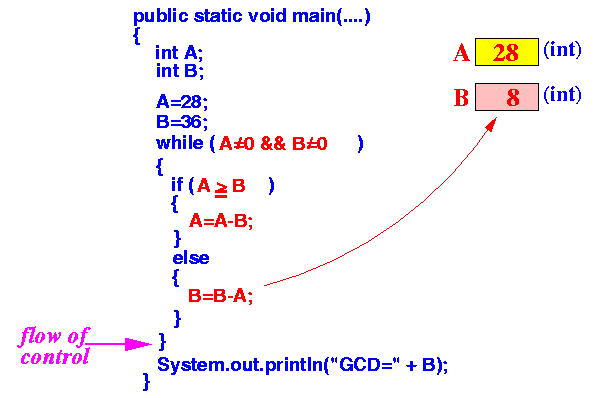
When the execution reaches the line "}", the flow of control will go back to up to the while line and execute the steps all over again !!!
In other words:
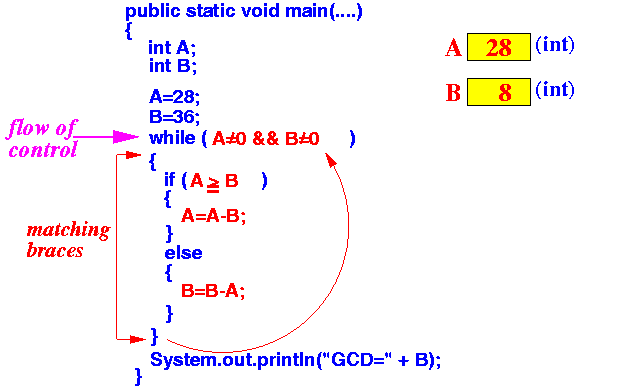
- The program execution
of a Java program starts
at beginning of main(...)
- Conclusion:
- The computer executing the
Euclid algorithm written in
the Java programming language
is doing the exact same steps
as what a human would do using
2 pieces of paper.
- A computer program is nothing more than a precise sequence of steps (that a human would use) to solve a problem that is expressed in a programming language
- The computer executing the
Euclid algorithm written in
the Java programming language
is doing the exact same steps
as what a human would do using
2 pieces of paper.
- It is important to
realize that a
programming language is
like any of the human languages
- Important facts about programming languages:
- A programming language has
syntax rules
that govern the
correctness
of the "sentences"
- The compiler (translator)
is extremely inflexible
on the syntax rules:
- If the compiler finds any syntax error in a program, it will not compile (translate) the entire program
- A programming language has
syntax rules
that govern the
correctness
of the "sentences"
- Important advice:
- Remember the syntax rules of the programming language carefully
(Don't worry, the syntax rules are very simple; still, you need to remember them well !)