- Scientific calculations
often involve
Mathematical functions,
such as
sin,
cos,
tan,
log, and so on.
Examples: sin and ln functions on a calculator
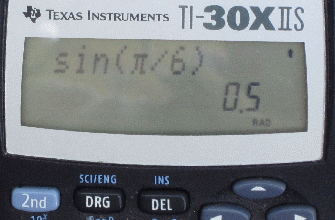

- Programming languages
allow you to embed
Mathematical functions
within a
arithmetic expression.
Furthermore, a computer allows you to use variables as arguments to a Mathematical function
In other words:
- Suppose you have define a
variable x as follows:
double x = 2.0; - You can write
expressions like these:
sin(x) computes the sin of x sin(2*x) computes the sin of 2*x
- Suppose you have define a
variable x as follows:
- Note:
- The names of the
sin, cos, tan, ln, and other
Mathematical functions in
Java is
a little bit
different
than what you are used to.
- They are given below
- The names of the
sin, cos, tan, ln, and other
Mathematical functions in
Java is
a little bit
different
than what you are used to.
- The Java programming language
has an extensive collection
of functions (methods) organized in various
libraries
Note: a bit of history
- In Mathematics, the
sin() operation is called
a function
- In Java, the
sin() operation is implemented
by a Java method
- In fact, we used the words
"function" and
"method"
interchangeably in
Computer Science.
- Before the word
method became popular,
other words used were:
-
subroutine,
procedure and
function
- In Mathematics, the
sin() operation is called
a function
- The documentation of
the
Java methods (functions)
are online at the following
website:
click here
- We will now look at the
Mathematical functions
which are documented
on this
webpage:
click here
- Here are some of the names of
Java's Mathematical functions (methods):
Java's method name Corresponding Mathematical function Math.sin(x) Sine function of value x Math.cos(x) Cosine function of value x Math.tan(x) Tangent function of value x Math.asin(x) Arc sine (inverse of sine) function of value x Math.acos(x) Arc cosine function of value x Math.atan(x) Acr tangent function of value x Math.exp(x) ex Math.log(x) Natural log function of value x Math.log10(x) 10-based log function of value x Math.pow(a, b) ab Math.sqrt(x) Squared root of the number x
- Example: compute √2
Math.sqrt(2.0) = √2
- You can apply a Mathematical function
on a floating point variable
Examples:
double a; Math.sqrt(a) will compute the squared root on the value that is current stored in the variable a Math.sqrt(a+1) will compute the squared root on the value a+1
- We just learned how to compute √2
Consider the following Java program:
public class CompVal { public static void main(String[] args) { Math.sqrt(2.0); // Computes √2 } }Interesting result:
- When you compile and run this program, you will see .... absolutely nothing !!!
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac CompVal.java
- To run: java CompVal
- The reason is:
- Unlike a
calculator that
always shows
the result of a computation
on its display....
A computer will only show the result of a computation when it is told !!!
Example:
public class CompVal2 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println( Math.sqrt(2.0) ); // Print !! } }This program will print: 1.4142135623730951 (which is the decimal value of √2)
- Unlike a
calculator that
always shows
the result of a computation
on its display....
- Programming facts:
- A computed value is
not printed
If you want to print a computed value, use a print statement
- A computed value is
not stored
If you want to store (save) a computed value, use an assignment statement
Example: storing a computed value
public class CompVal3 { public static void main(String[] args) { double a; a = Math.sqrt(2.0); // Save computed value in variable System.out.println(a); // You can print the saved value later } } - A computed value is
not printed
- Quadratic equation:
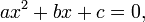
Solutions:
x1 = 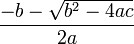
x2 = 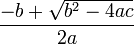
- The Mathematical expressions
are written in
Java as follows:
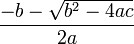 written as:
( -b - Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a)
written as:
( -b - Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a)
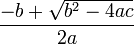 written as:
( -b + Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a)
written as:
( -b + Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a)
- Here is a Java program to compute the
famous a,b,c-formula:
public class Abc { public static void main(String[] args) { double a, b, c, x1, x2; // Define 5 variable a = 1.0; b = 0.0; c = -4.0; x1 = ( -b - Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); x2 = ( -b + Math.sqrt( b*b - 4*a*c ) ) / (2*a); System.out.print("a = "); System.out.println(a); System.out.print("b = "); System.out.println(b); System.out.print("c = "); System.out.println(c); System.out.print("x1 = "); System.out.println(x1); System.out.print("x2 = "); System.out.println(x2); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Abc.java
- To run: java Abc