- Integer operators:
- An integer operator is a operator that operates on two integer values
Emphasis:
- An integer operator must use 2 integer value
- Integer operators are
arithmetic operators that
manipulate (operate on)
integer values
- A integer operator
only operates on
integer values
- Specifically:
An integer operator
cannot operate on
floating point values
(Nor can a floating point operator operate on integer values)
- Specifically:
An integer operator
cannot operate on
floating point values
- The result of an
integer operator is
always an integer value
(And the result of an floating point operator is always a floating point value)
Most of the integer (arithmetic) operators should look familiar to you...
(Except for the % operator)
- A integer operator
only operates on
integer values
- Integer arithmetic operators:
Operator symbol Operation Note + addition Binary operator, e.g.: 9 + 4 = 13 − subtraction Binary operator, e.g.: 9 − 4 = 5 * multiplication Binary operator, e.g.: 9 * 4 = 36 / division (= quotient) Binary operator, e.g.: 9 / 4 = 2 % modulus (= remainder) Binary operator, e.g.: 9 % 4 = 1 ( ... ) brackets Changes order of computation − negation Changes the sign of the value: − 4 = (−4)
(Read as: − 4 = negative 4)
- From elementary school:
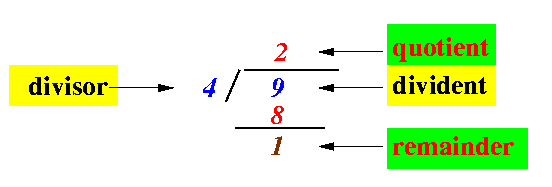
- The / integer operator
computes the quotient
of a divisio
The / integer operator will always produce an integer result
Examples:
9 / 4 = (floating point result = 2.25) = 2 -9 / 4 = (floating point result = -2.25) = -2 9 / -4 = (floating point result = -2.25) = -2 -9 / -4 = (floating point result = 2.25) = 2
- The % operator
(remainder) will also
produce an integer result
The sign of the result is always equal to the sign of the dividend
Examples:
9 % 4 = (floating point result = 2.25) = 1 -9 % 4 = (floating point result = -2.25) = -1 9 % -4 = (floating point result = -2.25) = 1 -9 % -4 = (floating point result = 2.25) = -1
- Property of integer division:
dividend = quotient × divisor + remainderExample:
9 / 4 = 2 9 % 4 = 1 9 = 2 * 4 + 1 -9 / 4 = -2 -9 % 4 = -1 -9 = (-2)* 4 + (-1) 9 / -4 = -2 9 % -4 = 1 9 = (-2)*(-4) + 1 -9 / -4 = 2 -9 % -4 = -1 -9 = 2 *(-4) + (-1)
- You must have noticed that
the "+", "-", "*"
and "/" can represent:
- a floating point operation, or
- an integer operation
Special emphasis:
-
The Java compiler (and you also) can tell the
difference between
integer division and
floating point division by
the operands used.
Example 1:
9 / 5 (Operands are 2 integers ⇒ / is integer division) 9.0 / 5.0 (Operands are 2 floating point numbers ⇒ / floating point division)Example 2:
int a, b; double x, y; a / b (Operands are 2 integers ⇒ / is integer division) x / y (Operands are 2 floating point numbers ⇒ / floating point division)
- The computer does
not have any instructions
that operates on
operands of different types.
Example: this operations cannot be performed directly:
Computer cannot calculate this directly: 9 / 5.0 (2 types of operands: integer and floating point)One of the operands must be converted into the other type before the operation can be performed.
We focus on integer-only operations in this webnote.
We will delay this discussion of mixed types operations for the next webnote.
- Each arithmetic operator
in Java has
a priority and an
associativity
- Operator priority was discussed in:
click here
- Operator associativity was discussed in: click here
- Operator priority was discussed in:
click here
- Priority of the
integer arithmetic operators:
Operator Priority Note ( .... ) Highest − (negation) Higher Unary operator, e.g.: −3 * / % High Binary operator, e.g.: 4 * 5 + − Lowest Binary operator, e.g.: 4 + 5
- Associativity of the
integer arithmetic operators:
Operator Associativity Example ( .... ) "inside out" ((3 + 4) * 5 ) = (7 * 5) − (negation) Right − − 3 = − (−3) = 3 (from right to left) * / % Left 4 * 5 % 7 / 4 = 20 % 7 / 4 = 6 / 4 = 1 + − Left 4 − 6 + 4 − 7 = (−2) + 4 − 7 = 2 − 7 = −5
- Example 1:
Integer expression: 72 / 10 + 72 % 10 Evaluated as follows: 72 / 10 + 72 % 10 = 7 + 72 % 10 = 7 + 2 = 9(This is how you compute the sum of the digits in the number 72 !!!)
- Example 2: using the
negation operator
Integer expression: 22 - - 3 * - 4 + - - 1 Evaluated as follows: 22 - - 3 * - 4 + - - 1 = 22 - (-3) * - 4 + - - 1 = 22 - (-3) * (-4) + - - 1 = 22 - (-3) * (-4) + - (-1) = 22 - (-3) * (-4) + (+1) = 22 - 12 + 1 (Use associativity rule) = 10 + 1 = 11
- Example 3: using brackets
Integer expression: (22 - - 3) * - (4 + - - 1) Evaluated as follows: (22 - - 3) * - (4 + - - 1) = (22 - (-3)) * - (4 + - - 1) = (22 - (-3)) * - (4 + - (-1)) = (22 - (-3)) * - (4 + 1) = 25 * - (4 + 1) = 25 * - 5 = 25 * (-5) = -125
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Priority02.java
- To run: java Priority02
- What is the output of the following program
public class Exercise1 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 15; int b = 24; System.out.println(b - a + 7); System.out.println(b - a - 4); System.out.println(b % a / 2); System.out.println(b % (a / 2)); System.out.println(b * a / 2); System.out.println(b * (a / 2)); System.out.println(b / 2 * a); System.out.println(b / (2 * a)); } }
- Answers:
16 5 4 3 180 168 180 0
- Example Program:
(You can use the Java compiler to teach yourself Java)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Exercise1.java
- To run: java Exercise1
- Fact:
- If a number x is divisible by the number d, then the remainder of the division of x by d is equal to zero
- Examples:
12 is divisible by 2 ⇔ 12 % 2 = 0 12 is divisible by 3 ⇔ 12 % 3 = 0 12 is divisible by 4 ⇔ 12 % 4 = 0 12 is not divisible by 5 ⇔ 12 % 5 = 2 12 is divisible by 6 ⇔ 12 % 6 = 0 12 is not divisible by 7 ⇔ 12 % 7 = 5
- Later in the course, we will use this property to find all divisors of a number.