- The Java compiler (translator)
consider white space characters
(i.e., SPACE, TAB and New line)
as insignificant
(See:
click here )
- All that the Java compiler cares about is syntactical correctness
- Ambiguous syntax
- A language allows ambiguous syntax is the same sentence can be read in more than one way
- Example:
English (in fact, all human languages)
- An American History professor
can mean:
- a History professor
who is an American citizen
(i.e.: American
History professor)
- a professor of American History. (i.e.: American History professor)
- How humans deal with
ambiguity:
- Humans can often
use additional information
to resolve the
ambiguity
(E.g., we have additional information about the specific professor)
- If we cannot resolve the ambiguity, we (humans) can ask further questions to resolve it.
- Humans can often
use additional information
to resolve the
ambiguity
- Difference between
natural language and
programming language:
- A natural language
evolves through
usage
It's evolution is not controlled
- A programming language
is designed by
one or a group of humans
It's design is completely controlled
- A natural language
evolves through
usage
- Commonly held goal in the design
of a programming language:
- A programming language
should have an
unambiguous syntax
- In other words:
- There is exactly one way to interpret each program statement syntactically
- A programming language
should have an
unambiguous syntax
- Historical facts
about programming languages:
- Older programming languages
does have
ambiguous syntax
These languages include:
- Algol 60
- Pascal
- C
- Modern programming languages are
unambiguous
Examples:
- Algol 68
- Ada
- Modula
- Older programming languages
does have
ambiguous syntax
- However:
- Because Java
(and C++) are
derived from
the older programming language
C
(and C
has an
ambiguous syntax):
- Java has inherited the ambiguous syntax in C...
(This is very unfortunate for a modern language like Java and C++, but the designers want to keep C's syntax extremely badly)
- Because Java
(and C++) are
derived from
the older programming language
C
(and C
has an
ambiguous syntax):
- The dangling else ambiguity
was first discovered in the
programming language Algol 60
- I will use a
concrete example to
illustrate this
famous ambiguity
- Programming problem:
shipping cost
- Country code for US
= 1
Cost to ship to a package to a destination in the US = $5.00, except for Hawaii which cost $10.00
The state code for Hawaii = 50
- The shipping cost for
a destination outside the US
is $20.00
- Write a Java program than reads in:
- A country code (integer)
- A state code (integer)
and prints the shipping cost
- Country code for US
= 1
- Algorithm:
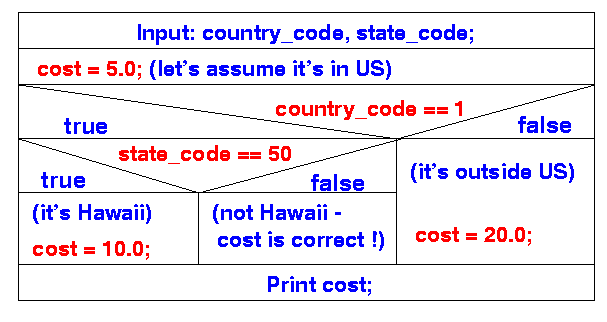
Note:
- There is no ambiguity in
the algorithm given as a
structure diagram
- The ambiguity will be
introduced when we
write the
algorithm in the
Java programming language !!!
cost = 5.0; if ( country_code == 1 ) if ( state_code == 50 ) cost = 10.0; // Hawaii else cost = 20.0; // Outside US
(The algorithm is unnecessarily confusing because I want to show the ambiguous syntax....)
- There is no ambiguity in
the algorithm given as a
structure diagram
- There are 2 different
yet syntactically correct ways
to read the if-statements:
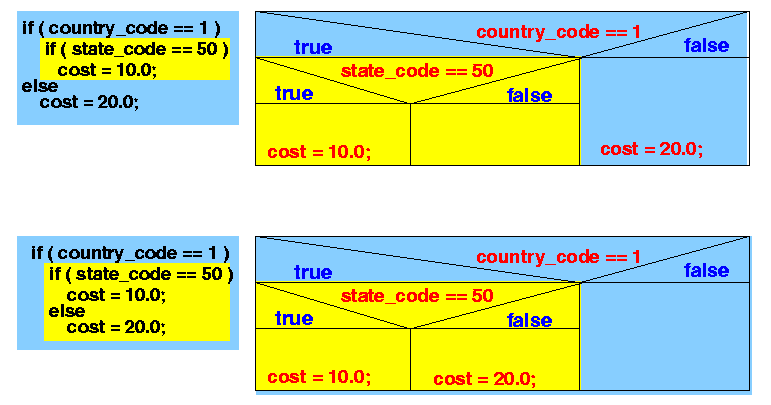
Explanation:
- The first way is to
associate the keyword
else with the
first keyword if
- The first if is
an if-else-statement
- The second if is an if-statement that comprises the then-part of the (first) if-else-statement
See the corresponding structure diagram
- The first if is
an if-else-statement
- The second way is to
associate the keyword
else with the
second keyword if
- The first if is
an if-statement
- The second if is an if-else-statement that comprises the then-part of the (first) if-statement
See the corresponding structure diagram
- The first if is
an if-statement
(This is the only ambiguous syntax in the Java programming language which it had inherited from C)
- The first way is to
associate the keyword
else with the
first keyword if
- Note:
- Syntactically speaking,
both interpretations are
equally correct
- For our algorithm
to be correct,
we
need
the first interpretation
However, it is conceivable that for another algorithm to be correct, the second interpretation is needed.
- It is not possible to interpret the same syntactical construct differently in a computer language (because a computer is a dumb machine)
- Syntactically speaking,
both interpretations are
equally correct
- Resolving the
dangling-else ambiguity
syntactically:
- Java (and C, C++)
imposes the following syntax rule:
- The keyword else is associated to the nearest keyword if that makes a syntactically correct statement
Result:
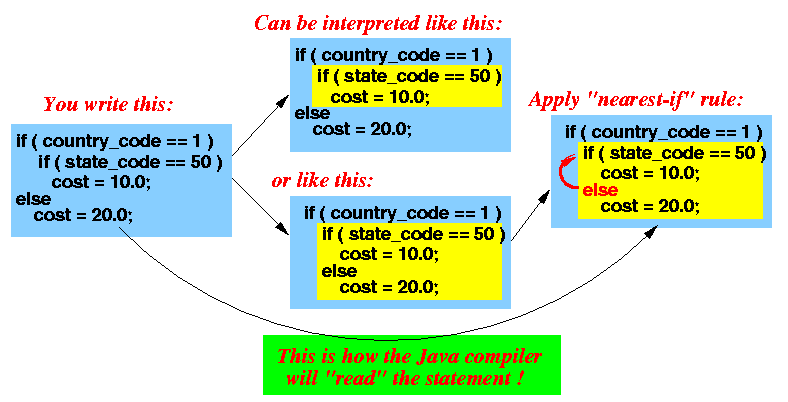
- Java (and C, C++)
imposes the following syntax rule:
- Java program:
import java.util.Scanner; public class DanglingElse01 { public static void main(String[] args) { int country_code, state_code; double cost; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); // Construct Scanner object System.out.print("Enter country code: "); country_code = in.nextInt(); // Read in integer System.out.print("Enter state code: "); state_code = in.nextInt(); // Read in integer cost = 5.0; if ( country_code == 1 ) if ( state_code == 50 ) cost = 10.0; // Hawaii else cost = 20.0; // Outside US System.out.println("Shipping cost = " + cost); } }Sample execution:
Enter country code: 1 (code for US) Enter state code: 40 (not Hawaii) Shipping cost = 20.0 (should be $5 !)
The reason is that the Java program is executed as follows:
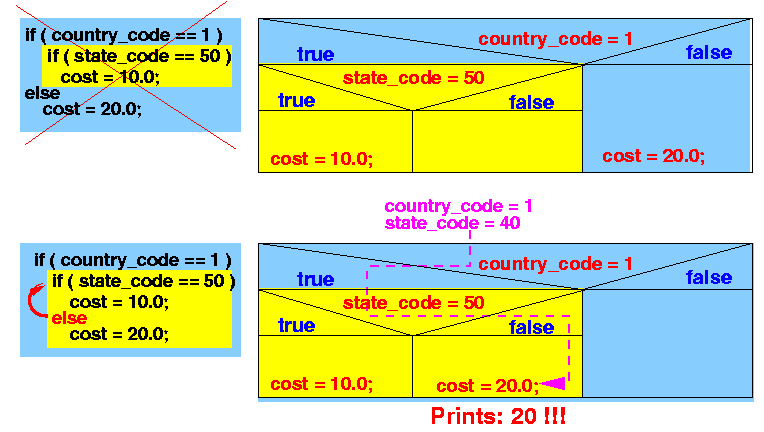
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac DanglingElse01.java
- To run: java DanglingElse01
- It is very easy to
avoid the dangling-else
ambiguity:
- Always use statement blocks in the then-part and else-part of conditional statements
- Example:
if ( country_code == 1 ) { if ( state_code == 50 ) { cost = 10.0; // Hawaii } } else { cost = 20.0; // Outside US }
- There is no ambiguity in this
program because:
- It is not syntactically possible to associate the keyword else with the second keyword if.
If we try, we will get a syntax error:
if ( country_code == 1 ) { if ( state_code == 50 ) { cost = 10.0; // Hawaii } } <--- This extraneous } will cause a syntax error else { cost = 20.0; // Outside US }
- Example Program:
(fixing the
dangling-else ambiguity)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac DanglingElse02.java
- To run: java DanglingElse02
Sample execution:
Enter country code: 1 (code for US) Enter state code: 40 (not Hawaii) Shipping cost = 5.0 (correct !!!)