- In Mathematics,
simultaneous equations
are a set of equations
containing multiple variables.
This set of equations is often referred to as a system of equations.
Wikipedia page: click here
- Example 1:
2 simultaneous equations
(with 2 unknowns
x1 and x2
)
3 x1 + 7 x2 = 78 8 x1 + 5 x2 = 45
Example 2: 3 simultaneous equations (with 3 unknowns x1, x2 and x3 )
5 x1 + 6 x2 - 3 x3 = 23 3 x1 - 4 x2 + 8 x3 = 25 -6 x1 + x2 - 2 x3 = 19
- From High School, you should
have learned about matrices
(if not, here is the definition):
- Matrix = a 2-dimensional grid of number
Example:
+- -+ | 5 6 -3 | A = | 3 -4 8 | | -6 1 -2 | +- -+
- The elements in a
matrix are
numbered as follows:
+- -+ | a11 a12 a13 | A = | a21 a22 a23 | | a31 a32 a33 | +- -+
- From High School, you should
also
have learned about vectors
(if not, here is the definition):
- Column vector = a column of number
- Row vector = a row of number
Example: column vector
+- -+ | 2 | x = | 5 | | -1 | +- -+
- The elements in a
vector are
numbered as follows:
+- -+ | x1 | x = | x2 | | x3 | +- -+
- From High School, you should
also
have learned about
Matrix-vector multiplication
(if not, here is the definition):
+- -+ +- -+ | a11 a12 a13 | | x1 | A×x = | a21 a22 a23 | × | x2 | | a31 a32 a33 | | x3 | +- -+ +- -+ +- -+ def | a11x1 + a12x2 + a13x3 | = | a21x1 + a22x2 + a23x3 | | a31x1 + a32x2 + a33x3 | +- -+The product A×x is a vector !
- Writing simultaneous equations in
matrix/vector form
Example:
5 x1 + 6 x2 - 3 x3 = 23 3 x1 - 4 x2 + 8 x3 = 25 -6 x1 + x2 - 2 x3 = 19
View it as a column vector (of 3 elements): +- -+ +- -+ | 5 x1 + 6 x2 - 3 x3 | | 23 | ==> | 3 x1 - 4 x2 + 8 x3 | = | 25 | | -6 x1 + x2 - 2 x3 | | 19 | +- -+ +- -+
The left column vector can be written as a Matrix-vector product: +- -+ +- -+ +- -+ | 5 6 -3 | | x1 | | 23 | <==> | 3 -4 8 | × | x2 | = | 25 | | -6 1 -2 | | x3 | | 19 | +- -+ +- -+ +- -+ Matrix column column vector vector
- A very well-known technique used
to solve
simultaneous equations is the
Gaussian Elimination Method
Wikipedia page: click here
- In this webpage, we will study:
- The elementary row operations
used in the Gaussian elemination method
- A basic
Gaussian elmination method
to solve
systems of simultaneous equations
(There are more advanced variants to select pivots to maximize computational accuracy)
- A computer program that
using a two-dimensional array
to implement the
Gaussian elmination method.
You can use this program to solve homework problems in you Linear Algebra class :-)
- The elementary row operations
used in the Gaussian elemination method
- Consider the following system of equations:
2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12
The solution is:
x1 = 2 x1 = 3 Because: 2 × 2 + 4 × 3 = 4 + 12 = 16 3 × 2 + 2 × 3 = 6 + 6 = 12
- Equality of the
Left hand Side (LHS) and
the Right hand Size (RHS):
- The equality (=)
of the LHS and
the RHS
means that:
- the values in the LHS and RHS of the equal "=" sign are in balance.
- The equality (=)
of the LHS and
the RHS
means that:
- The equations can be
represented
intuitively in the following manner:
2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12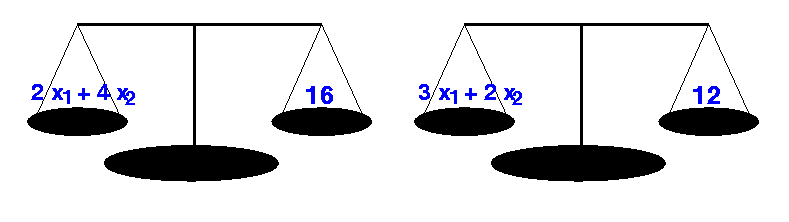
- Operations that can
maintain
the equality of
LHS and RHS:
- Equality maintaining operation #1:
- If we multiply (or divide) the LHS and the RHS with the same factor, the equality will still hold.
Example: multiplying first equation by 0.5
0.5 × (2 x1 + 4 x2) = 0.5 × 16 ==> x1 + 2 x2 = 8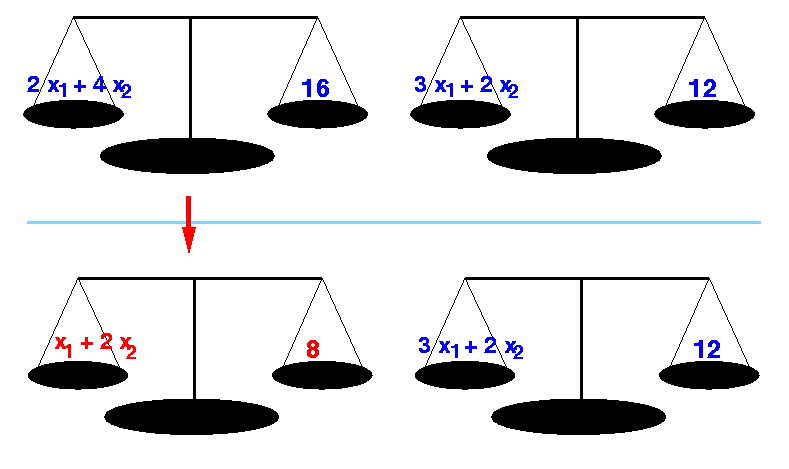
(This makes perfect sense: because take away half from both sides of the scale will keep the scale in balance)
- Equality maintaining operation #2:
- We can add (or subtract) any factor of one equation to another equation, and the resulting equality will still hold
Example:
x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq 1) 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12 (eq 2) (eq 2) ===> 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12 3 x (eq 1) ===> 3 x1 + 6 x2 = 24 − --------------------------- 0 x1 − 4 x2 = −12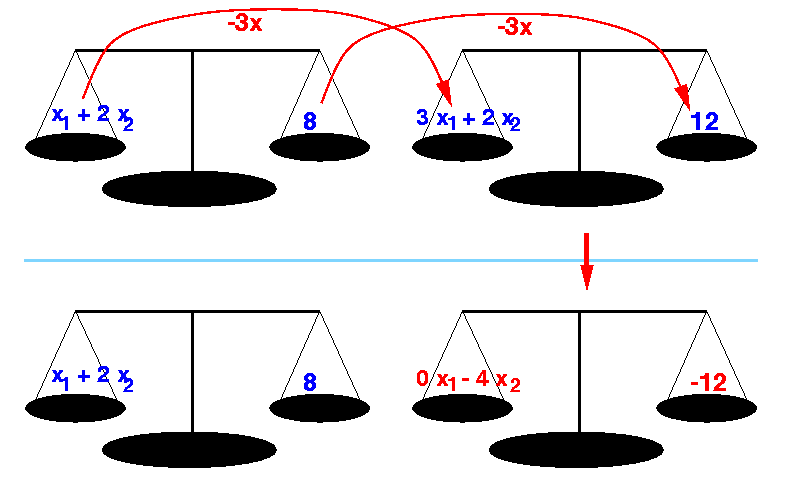
(This makes perfect sense: because if both scales are in balance, then adding the stuff from the left side of one scale to the left side of the other scale, and simultaneously adding the stuff from the left side of one scale to the left side of the other scale will keep the scale in balance.
We can do this any number of times, even with fractional amounts)
- Equality maintaining operation #1:
- Elementary row operations:
operations that
maintain equality
- Row multiplication:
- Each element in a row can be multiplied by a non-zero constant.
Example:
If: 2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 Then: x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (multiply each element in the row by 0.5)
- Row addition:
- A row can be replaced by the sum of that row and a multiple of another row.
Example:
If: x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq 1) 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12 (eq 2) Then: we can replace (eq2) with (eq2 - 3×eq1): x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq 1) -4 x2 = -12 (eq 2 - 3×eq1)
- Row multiplication:
- Overview:
- The Gaussian elimination method use the two elementary row operations to transform the original system of simultaneous equations into a trivial system of of simultaneous equations
- Trivial system of simultaneous equations:
- The trivial system of
simultaneous equations is the following
set of equations:
x1 + 0 × x2 = value1 0 × x1 + x2 = value2
It's called "trivial" because solving this system requires no effort at all...
The solution is:
x1 = value1 x2 = value2 - The trivial system of
simultaneous equations is the following
set of equations:
- Solve:
2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12
- Step 1A:
make the first coefficient of
the first row equal to
1
- Original equations:
2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12
- Multiply
first equation
by 0.5 (or divide by 2):
1 x1 + 2 x2 = 8 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12
Step 1B: make all other coefficients in the first column equal to ZERO (by adding a multiple of the first row to the other rows)
- Original equations:
1 x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq1) 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12 (eq2)
- Subtract
3× equation
eq1 from
equation eq2
1 x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq1) 0 x1 - 4 x2 = -12 (eq2 - 3×eq1)
Repeat
- Original equations:
- Step 2A:
make the second coefficient of
the second row equal to
1
- Original equations:
x1 + 2 x2 = 8 -4 x2 = -12(Note: the second coefficient of the equation is −4... I did not show the first coefficient (0x1) because it is ZERO)
- Multiply
first equation
by −0.25 (or divide by
−4):
x1 + 2 x2 = 8 1 x2 = 3
Step 2B: make all other coefficients in the second column equal to ZERO (by adding a multiple of the second row to the other rows)
- Original equations:
x1 + 2 x2 = 8 (eq3) 1 x2 = 3 (eq4) - Subtract
2× equation
eq4 from
equation eq3
x1 + 0 x2 = 2 (eq3 - 2×eq4) 1 x2 = 3 (eq4)
Resulting trivial system of simultaneous equations:
x1 = 2 x2 = 3
Which also give the solution...
- Original equations:
- Dictionary definition of pivot:
- Pivot =
the center point
of any rotational system
- To pivot = to cause to rotate
- Pivot =
the center point
of any rotational system
- Computer Science definition:
- Pivot (a.k.a. pivot element) = the coefficient in the set of equations used to make all other coefficients in a column to be equal to ZERO (0)
- Example 1: the
pivot element
in Step 1 (A/B) above is
the coefficient of a11
Simultaneous equations: 2 x1 + 4 x2 = 16 3 x1 + 2 x2 = 12In matrix/vector form: +- -+ +- -+ +- -+ | 2 4 | | x1 | = | 16 | | 3 2 | | x2 | | 12 | +- -+ +- -+ +- -+The element 2 in the matrix is coefficient a11
- Example 2: the
pivot element
in Step 2 (A/B) above is
the coefficient of a22
Simultaneous equations: x1 + 2 x2 = 8 -4 x2 = -12In matrix/vector form: +- -+ +- -+ +- -+ | 1 2 | | x1 | = | 8 | | 0 -4 | | x2 | | -12 | +- -+ +- -+ +- -+The element −4 in the matrix is coefficient a22
- Selecting the pivot in
the Gaussian Elimination Algorithm:
- There are sophisticated ways to
select pivots in
the Gaussian Elimination Algorithm
to reduce computational errors
made by the algorithm
- We will only discussed the
basic
Gaussian Elimination Algorithm
using a
very simple pivot selection algorithm
- There are sophisticated ways to
select pivots in
the Gaussian Elimination Algorithm
to reduce computational errors
made by the algorithm
- The basic
pivot selection algorithm:
- Pivot used in iteration 1: coefficient a11
- Pivot used in iteration 2: coefficient a22
- And so on...
- Pivot used in iteration n: coefficient ann
- Solve:
2 x1 + 4 x2 + 6 x3 = 14 x1 + 4 x2 + 3 x3 = 3 3 x1 + 5 x2 + 2 x3 = 2
We do not need to write out the variable x1, x2 and x3
We can represent these simulatneous equation by the following shorter form:
+- -+ | 2 4 6 | 14 | | 1 4 3 | 3 | | 3 5 2 | 2 | +- -+Note:
- This is not
a matrix
- It is a short hand used
to execute
elementary row operations
- We must remember that column i in this short hand form corresponds to the variable xi.
- This is not
a matrix
- The Gaussian Elimination Algorithm
on the short hand form:
- Iteration 1:
- Step 1A: select pivot
a11
+- -+ | 2 4 6 | 14 | | 1 4 3 | 3 | | 3 5 2 | 2 | +- -+
- Step 1B: divide the
entire pivot row by the
pivot a11
+- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | | 1 4 3 | 3 | | 3 5 2 | 2 | +- -+This step is a.k.a.: normalizing the pivot row
- Step 1C: make
all other coefficient
under the pivot element
ZERO.
+- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | | 1 4 3 | 3 | - 1×(Pivot row) | 3 5 2 | 2 | - 3×(Pivot row) +- -+
Result: +- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | | 0 2 0 | -4 | | 0 -1 -7 | -19 | +- -+This step is a.k.a.: sweeping the pivot column
- Step 1A: select pivot
a11
- Iteration 2:
- Step 2A: select pivot
a22
+- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | | 0 2 0 | -4 | | 0 -1 -7 | -19 | +- -+
- Step 2B: normalizing
the pivot row
by divide the
entire pivot row by the
pivot a22
+- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 -1 -7 | -19 | +- -+
- Step 2C:
sweep the
pivot column
+- -+ | 1 2 3 | 7 | - 2×(Pivot row) | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 -1 -7 | -19 | -(-1)×(Pivot row) +- -+ Note: - (-1)×(Pivot row) <==> + 1×(Pivot row)
Result: +- -+ | 1 0 3 | 11 | | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 0 -7 | -21 | +- -+
- Step 2A: select pivot
a22
- Iteration 3:
- Step 3A: select pivot
a33
+- -+ | 1 0 3 | 11 | | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 0 -7 | -21 | +- -+
- Step 3B: normalizing
the pivot row
by divide the
entire pivot row by the
pivot a33
+- -+ | 1 0 3 | 11 | | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 0 1 | 3 | +- -+
- Step 3C:
sweep the
pivot column
+- -+ | 1 0 3 | 11 | - 3×(Pivot row) | 0 1 0 | -2 | - 0×(Pivot row) | 0 0 1 | 3 | +- -+
Result: +- -+ | 1 0 0 | 2 | | 0 1 0 | -2 | | 0 0 1 | 3 | +- -+
- Step 3A: select pivot
a33
- Iteration 1:
- The trivial system's solution:
x1 = 2 x2 = -2 x3 = 3
- Variables used to store
information
used by the
Gaussian Elimination Algorithm:
double[][] A; // The Coefficient "matrix" double[] b; // The right hand side "vector" int n; // number of unknowns (and size of A and b) - Example:
Simultaneous equations: 2 x1 + 4 x2 + 6 x3 = 14 x1 + 4 x2 + 3 x3 = 3 3 x1 + 5 x2 + 2 x3 = 2Representation: n = 3; double[][] A = new double[n][n]; double[] b = new double[n]; A[0][0] = 2; A[0][1] = 4; A[0][2] = 6; b[0] = 14; A[1][0] = 1; A[1][1] = 4; A[1][2] = 3; b[0] = 3; A[2][0] = 3; A[2][1] = 5; A[2][2] = 2; b[0] = 2;
- Important note:
- In Mathematics, the
indices begin
with 1 (ONE):
- a11, a12 and so on...
- However, in
Computer Scoence,
the array indices
begin with 0 (ZERO)
- A[0][0] = a11
- A[0][1] = a12
- And so on !!!
- In Mathematics, the
indices begin
with 1 (ONE):
- From the above discussion,
we have the following
high level description of the
Gaussian Elimination algorithm:
Read in n, A and b; for ( each row i from 0 to n-1 ) do { (Step i A): Select pivot pivot = A[i][i]; (Step i B): Normalize row i for ( each element in row i ) divide element by the pivot; (Step i C): Sweep column i; for row k from 0 to n-1, except row i do { factor = A[k][i]; Subtract "factor" × (row i) from (row k) } }
- Refining (Step B) Normalize row i
- Description:
for ( each element in row i ) divide element by the pivot;
- Refinement:
for ( j = 0; j < n; j++ ) a[i][j] = a[i][j] / pivot; // elements in A b[i] = b[i] / pivot; // element in the RHS
- Description:
- Refining (Step C): Sweep column i
- Description:
(Row i is the pivot row) for row k from 0 to n-1, except row i do { factor = A[k][i]; Subtract "factor" × (row i) from (row k) }
- Refinement:
(Row i is the pivot row) for ( k = 0, 1, 2, ...., n-1, except when k=i ) { factor = A[k][i]; /* -------------------------------- Go through ALL elements in row k --------------------------------- */ for ( j = 0; j < n; j++ ) { Subtract (factor×a[i][j]) from a[k][j] } Subtract (factor×b[i]) from b[k] }
- Description:
- Java program:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Gauss1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); double[][] A; // The coefficients double[] b; // The RHS double pivot, factor; int n; // Number of variables int i, j, k; System.out.print("Number of unknows: "); n = in.nextInt(); // Read in problem size A = new double[n][n]; // Reserve space for coefficient matrix b = new double[n]; // Reserve space for RHS vector /* -------------------------------------- Read in the rows, one row at a time -------------------------------------- */ for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Read in row i's coefficients for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.print("A["+i+"]["+j+"] = "); A[i][j] = in.nextDouble(); } // Read in row i's RHS System.out.print("b["+i+"] = "); b[i] = in.nextDouble(); } /* ------------------------------------ The Gaussian elimination method ------------------------------------ */ for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Process row i /* --------------------- (A) Select pivot --------------------- */ pivot = A[i][i]; /* --------------------- (B) Normalize row i --------------------- */ for (j = 0; j < n; j++) A[i][j] = A[i][j]/pivot; b[i] = b[i]/pivot; /* --------------------- (C) Sweep using row i --------------------- */ for (k = 0; k < n; k++) { if ( k != i ) { factor = A[k][i]; for (j = 0; j < n; j++) A[k][j] = A[k][j] - factor*A[i][j]; b[k] = b[k] - factor*b[i]; } } } System.out.println("======================"); System.out.println("Solution:"); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) System.out.println("x" + (i+1) + " = " + b[i]); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Gauss1.java
- To run: java Gauss1
- Inputs of the Gaussian Elimination Algorithm:
- The coefficient matrix (double[][] A)
- The RHS (double[] b)
- Output of the Gaussian Elimination Algorithm:
- The solution (vector)
Note:
- We can return the solution stored inside the input parameter double[] b
- The solution (vector)
- The Gaussian Elimination Algorithm written as
a method:
public class MathTools { public static double[] GaussianElim(double[][] A, double[] b) { double pivot, factor; int i, j, k; int n = b.length; // # unknowns /* ----------------------------- Gaussian elimination method ----------------------------- */ for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Process row i /* --------------------- (A) Select pivot --------------------- */ pivot = A[i][i]; /* --------------------- (B) Normalize row i --------------------- */ for (j = 0; j < n; j++) A[i][j] = A[i][j]/pivot; b[i] = b[i]/pivot; /* --------------------- (C) Sweep using row i --------------------- */ for (k = 0; k < n; k++) { if ( k != i ) { factor = A[k][i]; for (j = 0; j < n; j++) A[k][j] = A[k][j] - factor*A[i][j]; b[k] = b[k] - factor*b[i]; } } } return(b); // The answer is in double[] b } }
- How to use the GaussianElim()
method:
public class Gauss2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); double[][] A; double[] b, x; double pivot, factor; int n; // Number of variables int i, j, k; System.out.print("Number of unknows: "); n = in.nextInt(); // Read in problem size A = new double[n][n]; // Reserve space for coefficient matrix b = new double[n]; // Reserve space for RHS vector // Read in the rows, one row at a time for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Read in row i's coefficients for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { System.out.print("A["+i+"]["+j+"] = "); A[i][j] = in.nextDouble(); } // Read in row i's RHS System.out.print("b["+i+"] = "); b[i] = in.nextDouble(); } x = MathTools.GaussianElim(A, b); System.out.println("Solution:"); for (i = 0; i < n; i++) System.out.println("x[" + (i+1) + "] = " + x[i]); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The MathTools.java class file: click here
- The Gauss2.java test prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Gauss2.java
- To run: java Gauss2
Here's a sysem of 7 equations input file: click here
How to use the input:
- Run program using: java Gauss2 < Gauss.inp
-
Right click on link and
save the
Gauss.inp file in the same scratch directory
- The MathTools.GaussianElim()
will
modify the actual input parameters
because
as you know:
- Array elements in the input parameters
can be modified by
method
through the
array reference input parameter
See: click here
- Array elements in the input parameters
can be modified by
method
through the
array reference input parameter
- If you do not
want a method to
modify an array parameter,
then you must do the following:
- Inside the method, create a
new array of the
same size and dimension
as the array that you want to
preserve
- Copy the elements of
the input array into
the created array
- Modify the copy
- Inside the method, create a
new array of the
same size and dimension
as the array that you want to
preserve