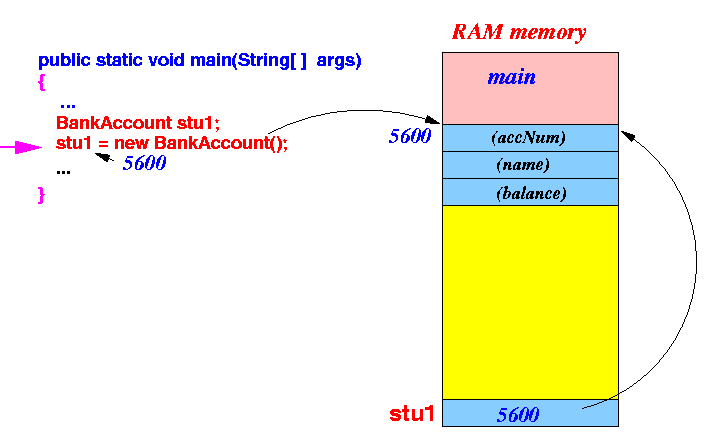
- Object
(= group of variables defined inside some class)
is created using
the new operation
Example:
- Topic discussed in
this webpage:
- How do we create an object containing some initialized values ???
- Constructor method:
- Constructor method =
an instance method
(defined inside some class)
that is
invoked when
an object of that class
is created
(by the new operation)
- Object creation rule in the Java:
- When an object is created, one of the constructor method in the class must be invoked (to initialize the instance variables in the object)
Purpose of constructor methods:
- Constructor methods are used to initialize the instance variables inside the newly created object
- Constructor method =
an instance method
(defined inside some class)
that is
invoked when
an object of that class
is created
(by the new operation)
- How to recognize a
constructor method:
- A constructor method of
a class has the
same name as that class
- A constructor method of
a class does
not have a return type
- As a rule:
- A constructor method
is often defined using the
public access specifier
so that it can be used by methods inside
other classes
(You can define constructor method with other specifiers, e.g., private - but such construction can only be used by methods inside the same class)
- A constructor method
is often defined using the
public access specifier
so that it can be used by methods inside
other classes
Example:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Instance variables private String name; // private double balance; // public BankAccount( .... ) // This is a constructor method { ... used to initialize the instance variables } public void deposit( .... ) // This is NOT a constructor method { ... } }
- A constructor method of
a class has the
same name as that class
- Note:
- Because a constructor method is an instance method, it has the implicit parameter this !!!!
- A constructor method is
defined just like an
ordinary method,
except:
- You must use
the name of the
enclosing class as
the name for
a constructor method
- You cannot have
a return type
(And therefore, you cannot return any value from inside the constructor method)
- You must use
the name of the
enclosing class as
the name for
a constructor method
- Example:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Private access private String name; // -- limit to ONLY inside private double balance; // the class "BankAccount" /* ==================================================== Constructor 1: initialize all 3 instance variables ==================================================== */ public BankAccount(int a, String n, double amount) { System.out.println("Test message: invoking Constructor 1"); // For demo only ! accNum = a; name = n; balance = amount; } /* ==================================================== Constructor 2: initialize all 2 instance variables (opens an account with balance = 0) ==================================================== */ public BankAccount(int a, String n) { System.out.println("Test message: invoking Constructor 2"); // For demo only ! accNum = a; name = n; balance = 0.0; } /* ============================================== convToString(): return a String containing information of BankAccount ============================================== */ public String convToString( ) { return( "Account number: " + this.accNum + ", Name: " + this.name + ", Balance: " + this.balance); } /* ============================================== deposit(amount): Add "amount" to balance ============================================== */ public void deposit( double amount ) { this.balance += amount; } /* ====================================================== withdraw(amount): Subtract "amount" from balance ====================================================== */ public void withdraw( double amount ) { if ( this.balance >= amount ) this.balance -= amount; // Subtract "amount" from balance } }
- How and when is a
constructor method used:
- A constructor method is invoked by the new operation (to initialize the instance variables in the newly created object)
There can be many different constructors...
Which one will be used ???
- Selection of the constructor methods:
- Which constructor
method will be
invoked depends
on the number and type of
parameters specified in the
new operation
- If a constructor method is
found that have the
exact match
for the number and type of
parameters specified in the
new operation,
this constructor method
will be used.
- Otherwise, the Java compiler will search for a suitable constructor through widening conversion (casting) operations
- If a constructor method is
found that have the
exact match
for the number and type of
parameters specified in the
new operation,
this constructor method
will be used.
- Which constructor
method will be
invoked depends
on the number and type of
parameters specified in the
new operation
- Examples:
- new BankAccount(
123, "John", 1000.0 )
will invoke
the constructor:
BankAccount(int a, String n, double amount)
because the given parameters matches exactly the parameters specified in the constructor
-
new BankAccount( 123, "John" )
will invoke
the constructor:
BankAccount(int a, String n)
because the given parameters matches exactly the parameters specified in the constructor
-
new BankAccount( 123, "John", 1000 )
will invoke
the constructor:
BankAccount(int a, String n, double amount)
because after converting 1000 to 1000.0, the given parameters matches the parameters specified in the constructor
- new BankAccount(
123, "John", 1000.0 )
will invoke
the constructor:
- Example Java program:
public class Class07 { public static void main(String[] args) { String x; BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount(123, "John", 1000.0); // Use constructor 1 x = stu1.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu1: " + x); BankAccount stu2 = new BankAccount(456, "Mary"); // Use constructor 2 x = stu2.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu2: " + x); BankAccount stu3 = new BankAccount(123, "James", 1000); // Use constructor 1 x = stu3.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu1: " + x); } }Output:
Test message: invoking Constructor 1 stu1: Account number: 123, Name: John, Balance: 1000.0 Test message: invoking Constructor 2 stu2: Account number: 456, Name: Mary, Balance: 0.0 Test message: invoking Constructor 1 stu3: Account number: 123, Name: James, Balance: 1000.0
Note:
- Normally,
you do not put
print statements (System.out.println(...))
inside a constructor method
- I did it in this example to make the program show you that a particular constructor was executed
- Normally,
you do not put
print statements (System.out.println(...))
inside a constructor method
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BankAccount.java Prog file: click here
- The Class07.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Class07.java
- To run: java Class07
- Object creation and constructor:
- When a object
is created (by the new
operation),
(exactly) one of the
(possibly many)
constructor methods
defined inside the class
must be invoked by the
Java compiler.
- That means:
- Every class definition must contain at least one constructor method inside the class definition
- When a object
is created (by the new
operation),
(exactly) one of the
(possibly many)
constructor methods
defined inside the class
must be invoked by the
Java compiler.
- Enforcing the fact that
every class definition
must contain
at least one
constructor method:
- IF
the class definition
contains
one or more constructor method:
- The Java compiler does
not do anything
to the class definition
(Because the class definition satisfies the at least one constructor requirement)
- The Java compiler does
not do anything
to the class definition
- IF
the class definition
does not contain
any constructor method:
- The Java compiler will
automatically add
the following constructor method
to the
class definition:
NameOfTheEnclosingClass() { // No statements }
- The Java compiler will
automatically add
the following constructor method
to the
class definition:
- IF
the class definition
contains
one or more constructor method:
- Consider the following BankAccount class
without any constructor methods:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Private access private String name; // -- limit to ONLY inside private double balance; // the class "BankAccount" // Does NOT contain any constructor method ! /* ============================================== convToString(): return a String containing information of BankAccount ============================================== */ public String convToString( ) { return( "Account number: " + accNum + ", Name: " + name + ", Balance: " + balance); } /* ============================================== deposit(amount): Add "amount" to balance ============================================== */ public void deposit( double amount ) { balance += amount; } /* ====================================================== withdraw(amount): Subtract "amount" from balance ====================================================== */ public void withdraw( double amount ) { if ( balance >= amount ) balance -= amount; // Subtract "amount" from balance } }
-
The Java compiler will
automatically include
the following constructor method:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Private access private String name; // -- limit to ONLY inside private double balance; // the class "BankAccount" // Automatically inserted ! public BankAccount() { // No statements ! } /* ============================================== convToString(): return a String containing information of BankAccount ============================================== */ public String convToString( ) { return( "Account number: " + accNum + ", Name: " + name + ", Balance: " + balance); } /* ============================================== deposit(amount): Add "amount" to balance ============================================== */ public void deposit( double amount ) { balance += amount; } /* ====================================================== withdraw(amount): Subtract "amount" from balance ====================================================== */ public void withdraw( double amount ) { if ( balance >= amount ) balance -= amount; // Subtract "amount" from balance } }
- Consequently, we
can use the following
new operation
new BankAccount()We saw this before in this example: (See: click here)
public class Class06 { public static void main(String[] args) { BankAccount stu1; stu1 = new BankAccount(); // Create one BankAccount object with // 3 data fields: // stu1.studID, stu1.name, stu1.major stu1.accNum = 12345; stu1.name = "Mary"; stu1.balance = 1000.0; String x; x = stu1.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu1: " + x); stu1.deposit( 450 ); x = stu1.convToString( ); System.out.println("After depositing $450: " + x); stu1.withdraw( 100 ); x = stu1.convToString( ); System.out.println("After withdraw $100: " + x); } }
- On the other hand, we
cannot use this
new operation:
new BankAccount( 123, "John", 1000.0)because there is no constructor with matching parameters
- Example:
public class Class08 { public static void main(String[] args) { String x; BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount(123, "John", 1000.0); // Error BankAccount stu2 = new BankAccount(456, "Mary"); // Error } }Compiler output:
Class08.java:7: cannot find symbol symbol : constructor BankAccount(int,java.lang.String,double) location: class BankAccount BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount(123, "John", 1000.0); ^ Class08.java:10: cannot find symbol symbol : constructor BankAccount(int,java.lang.String) location: class BankAccount BankAccount stu2 = new BankAccount(456, "Mary"); ^ 2 errors
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BankAccount class file: click here
- the Class08.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Class08.java
- To run: java Class08
- Consider the following BankAccount class
with (2) constructor methods:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Private access private String name; // -- limit to ONLY inside private double balance; // the class "BankAccount" /* ==================================================== Constructor 1: initialize all 3 instance variables ==================================================== */ public BankAccount(int a, String n, double amount) { System.out.println("Test message: invoking Constructor 1"); // For demo only ! accNum = a; name = n; balance = amount; } /* ==================================================== Constructor 2: initialize all 2 instance variables (opens an account with balance = 0) ==================================================== */ public BankAccount(int a, String n) { System.out.println("Test message: invoking Constructor 2"); // For demo only ! accNum = a; name = n; balance = 0.0; } /* ============================================== convToString(): return a String containing information of BankAccount ============================================== */ public String convToString( ) { return( "Account number: " + accNum + ", Name: " + name + ", Balance: " + balance); } /* ============================================== deposit(amount): Add "amount" to balance ============================================== */ public void deposit( double amount ) { balance += amount; } /* ====================================================== withdraw(amount): Subtract "amount" from balance ====================================================== */ public void withdraw( double amount ) { if ( balance >= amount ) balance -= amount; // Subtract "amount" from balance } }The Java compiler will not include any more constructor method in the class.
- Consequently, we
can use the following
new operation
new BankAccount(123, "John", 1000.0) and new BankAccount(456, "Mary")We saw this before in the above example: (See: click here)
public class Class07 { public static void main(String[] args) { String x; BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount(123, "John", 1000.0); // Use constructor 1 x = stu1.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu1: " + x); BankAccount stu2 = new BankAccount(456, "Mary"); // Use constructor 2 x = stu2.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu2: " + x); BankAccount stu3 = new BankAccount(123, "James", 1000); // Use constructor 1 x = stu3.convToString( ); System.out.println("stu1: " + x); } }
- On the other hand, we
cannot use this
new operation:
new BankAccount( )because there is no constructor with matching parameters !!!!!
- Example:
public class Class09 { public static void main(String[] args) { BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount( ); // Error !!! } }Compiler output:
Class09.java:6: cannot find symbol symbol : constructor BankAccount() location: class BankAccount BankAccount stu1 = new BankAccount( ); ^ 1 error
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BankAccount class file: click here
- the Class09.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Class08.java
- To run: java Class08
- Computer jargon:
default constructor
- Default constructor =
the
default constructor method
in the
Java programming language
is a constructor method
that
has no input parameters
(Apparently, the term default constructor has a very different meaning in C++)
- Default constructor =
the
default constructor method
in the
Java programming language
is a constructor method
that
has no input parameters
- Answer:
- It ultimately depends on how you want to initialize the instance variables inside your object
- A typical class definition
will contain
- A constructor that
let you initial
all the necessary variables
- A default constructor that
initial
the variables to some
pre-defined default values.
- A copy constructor that initial the variables to the values inside another (existing) object.
- A constructor that
let you initial
all the necessary variables
- Example:
public class BankAccount { private int accNum; // Private access private String name; // -- limit to ONLY inside private double balance; // the class "BankAccount" /* ==================================================== Constructor 1: initialize all 3 instance variables ==================================================== */ public BankAccount(int a, String n, double amount) { accNum = a; name = n; balance = amount; } /* ==================================================== Constructor 2: initialize all instance variables to some chosen default values (The default constructor) ==================================================== */ public BankAccount( ) { accNum = -1; name = "Nobody"; balance = 0.0; } /* ==================================================== Constructor 3: initialize all instance variables to values in an existing object (The copy constructor) ==================================================== */ **** This method will be discussed in the next webpage **** .... other methods .... }
- There is
also
a requirement in Java
that
every constructor method
must invoke
a constructor method in its
Super class
- Although the
Java-supplied default constructor contains
no statements:
nameOfTheEnclosingClass { }the Java compiler will automatically insert a call to the default constructor of its Super class
nameOfTheEnclosingClass { super(); }
- You will learn more about this in CS171 in the inheritance topic.
|
|