- Look only
at the public things
in the Card class:
public class Card { public static final int SPADE = 4; public static final int HEART = 3; public static final int CLUB = 2; public static final int DIAMOND = 1; public Card( int suit, int rank ) ... public int suit() ... public String suitStr() ... public int rank() ... public String rankStr() ... public String toString() ... }From the definitions of the public methods, we can tell how to use them
- The constant value SPADE:
- Because the definition
contains the keyword static:
public static final int SPADE ....
it is a class constant and the syntax used to refer to SPACE is:
Card.SPADE
Other constants are used in a similar fashion.
- Because the definition
contains the keyword static:
- The constructor
Card( int suit, int rank):
- We know that a constructor is
used to initialized a
newly created Card object
- From its definition,
we know this particular constructor takes
2 int parameters
- Example usage:
Card x; x = new Card( Card.CLUB, 1 ); // Ace of club
- Note:
- In order to use a method
effectively,
we need to know the
meaning
of each parameter
I.e., you need to know the card encoding method discussed above.
- In order to use a method
effectively,
we need to know the
meaning
of each parameter
- We know that a constructor is
used to initialized a
newly created Card object
- The method
int suit()
- We know that it is
an instance method
(Because it does not have the keyword static
- Therefore, the
suit() method
must be invoked
using an
object variable, like this:
Card x; x = new Card( Card.CLUB , 1 ); x.suit() // (suit() has no parameters)
- Because the method suit()
returns an
int value,
we need to stored the
return value in an
int typed variable:
Card x; int r; x = new Card( Card.CLUB , 1 ); r = x.suit() // (suit() has no parameters)
The above discussion also applies to the other instance methods (because they are similar).
- We know that it is
an instance method
- Example Java program showing
how to use the
Card class:
public class TestCard1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Card x; int r; String s; x = new Card( Card.CLUB, 1); // Create a card r = x.suit(); // Get the suit of a card System.out.println("x.suit() = " + r); r = x.rank(); // Get the rank of a card System.out.println("x.rank() = " + r); s = x.suitStr(); // Get the suit of a card (Str) System.out.println("x.suitStr() = " + s); s = x.rankStr(); // Get the rank of a card (Str) System.out.println("x.rankStr() = " + s); System.out.println(x.toString()); // Convert a card into a String System.out.println(x); // toString() invoked automatically // by Java to convert object to String!!! } }Output:
x.suit() = 2 (2 = club) x.rank() = 14 (rank of Ace) x.suitStr() = c (club) x.rankStr() = A (Ace) Ac Ac
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Card.java Prog file: click here
- The TestCard1.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestCard1.java
- To run: java TestCard1
- This is what is going on behind the scene:
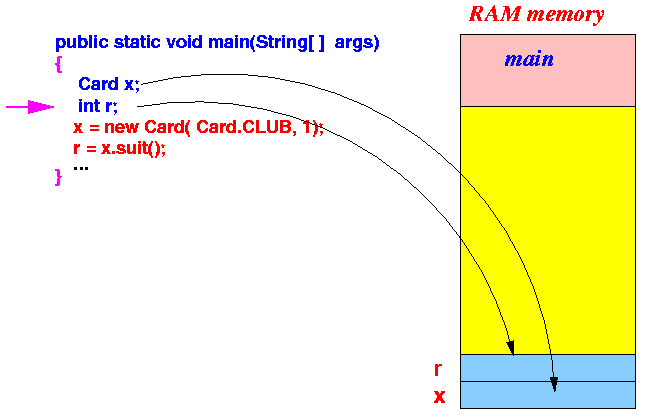
- The variable definitions in
main() first
create the local variables:
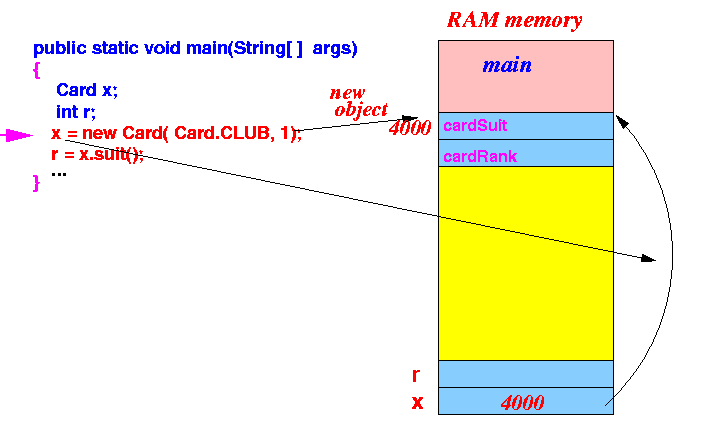
- The new Card
operator
first
create a Card object
and
returns a
object reference to
the local variable x:
- Immediately,
the execuition will
invoke the constructor
using the
newly created object
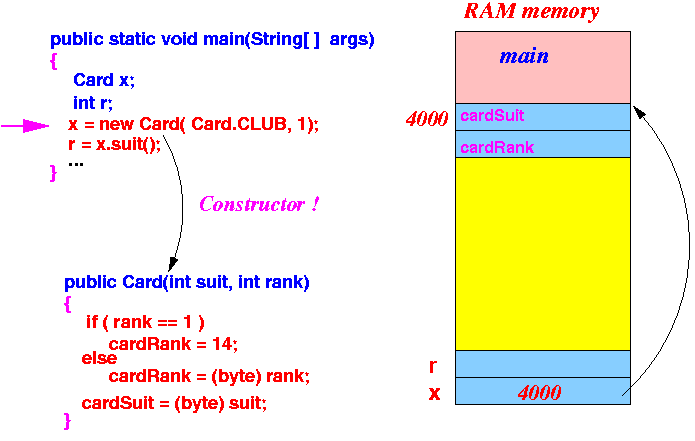
In other words:
- The object x is passed to the constructor (along with the other parameters)
- This is what happens inside the execution of the
constructor method:
- The parameters
(x,
Card.CLUB and
1) are
passed to the
constructor method:
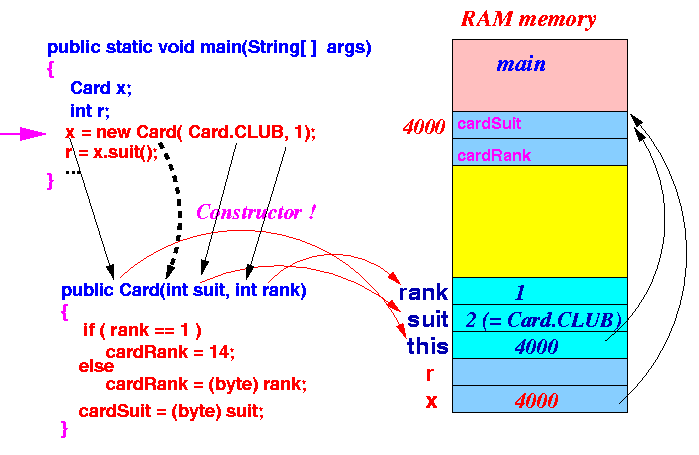
- The assignment cardRank = 14
(is short hand for
this.cardRank = 14),
will store the value 14 into the
instance variable
cardRank:
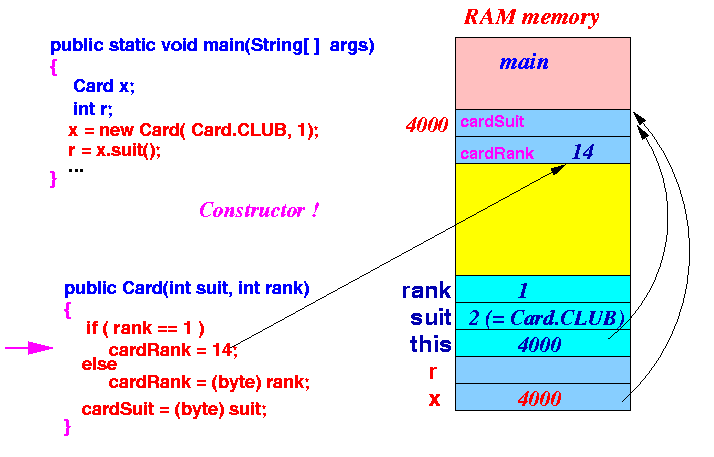
- The assignment cardSuit = suit
(is short hand for
this.cardSuit = suit),
will store the value 2 into the
instance variable
cardSuit:
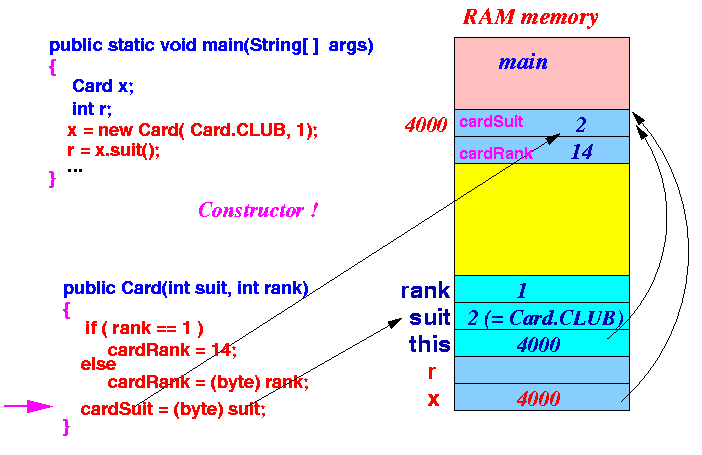
- When the
constructor exits,
we have initialized
the newly created object:
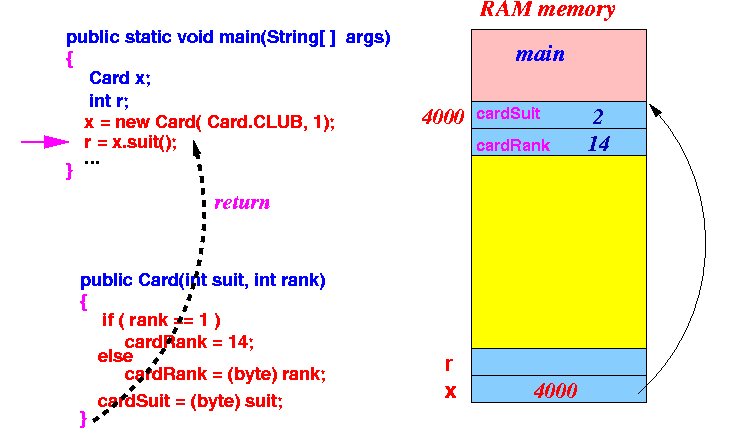
- The parameters
(x,
Card.CLUB and
1) are
passed to the
constructor method:
- Invoking of the instance method
x.suit() is executed as follows:
- The invocation will
pass x
as the
implicit parameter this:
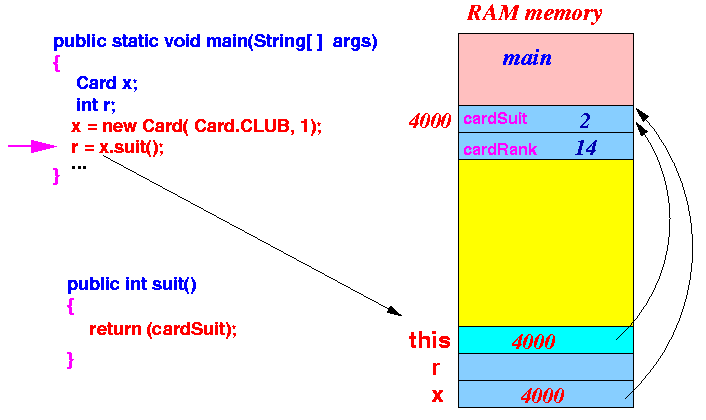
- The instance method will
now use the implicit parameter
this to return
the cardSuit (= 2) value:
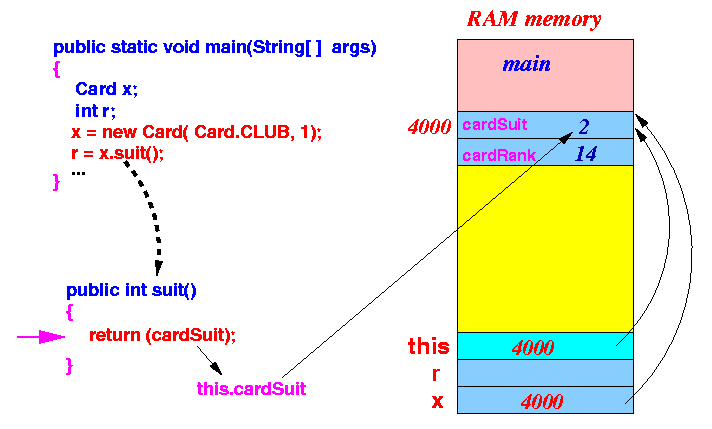
because return(cardSuit) is the short hand for return(this.cardSuit)
- The invocation will
pass x
as the
implicit parameter this:
- The variable definitions in
main() first
create the local variables: