- Problem description:
- Write a method to
computer the factorial of the input number
n
- In other words, the method should
have the following header:
public static int fac( int n ) { .... }The input parameter n is an integer
The output value (= n!) is also an integer value
- Write a method to
computer the factorial of the input number
n
- From Mathematics:
n! = n × (n−1)! with: 0! = 1
- The factorial(n) problem has the
recursive property
- We saw in the preious webpage, that
the factorial n (n!) problem has the
recursive property:
- The problem factorial(n) can be
solved
using the
solution of
one
smaller problem
factorial(n−1)
(i.e.: m1 = n−1)
- The
base (simple) case n = 0 of the
factorial problem can be
solved readily:
factorial(0) = 1
- The problem factorial(n) can be
solved
using the
solution of
one
smaller problem
factorial(n−1)
- We saw in the preious webpage, that
the factorial n (n!) problem has the
recursive property:
- So we can apply the
recursive algorithm technique to
compute n!:
- Which smaller problem do
we use to solve
factorial(n):
sol1 = factorial(n-1)
- How do we
use the
solution sol1
to solve factorial(n):
factorial(n) = n × sol1
- Because we used
factorial(n−1),
we will need the solution for
1 base case:
factorial(0) = 1
- Which smaller problem do
we use to solve
factorial(n):
- The recursive algorithm to solve
factorial(n):
int factorial( int n ) { if ( n == 0 /* the base cases */ ) { return 1; // The readily available solution for the base case } else { /* ---------------------------------- Delegate the problem: hire someone to solve (n-1)! ---------------------------------- */ sol1 = factorial ( n−1 ); /* ------------------------------------------- Use the solutions of the smaller (n-1)! to solve my problem: ------------------------------------------- */ mySol = n * sol1; return mySol; } }
- The algorithm written in
Java:
public class Recurse1 { public static int factorial( int n ) { int sol1, mySol; // Define variable... if ( n == 0 /* the base cases */ ) { return 1; // The readily available solution for the base case } else { sol1 = factorial ( n-1 ); // Let "someone else" (= factorial(n-1) ) // solve the smaller problem mySol = n * sol1; // Use the solution of the smaller problem // to solve my own problem return mySol; // Return my solution } } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Recurse1.java
- To run: java Recurse1
- Definition:
- Recursive method =
a method that
invokes itself
during the execution of that method.
- Types of
recursive methods:
- Direct recursion:
the method
invokes itself
inside the method.
- Indirect recursion: the method invokes another method which will invoke the original method.
- Direct recursion:
the method
invokes itself
inside the method.
- Recursive method =
a method that
invokes itself
during the execution of that method.
- Example - direct recursion:
factorial()
public class Recurse1 { public static int factorial( int n ) { int sol1, solution; // Define variable... if ( n == 0 /* the base cases */ ) { return 1; // The readily available solution for the base case } else { // factorial(n) is solved using solutions of // the smaller problem factorial(n-1)... sol1 = factorial ( n-1 ); // Solve a smaller problem solution = n * sol1; // Use the solution of the smaller problem // to solve the original problem return solution; } } }
- Consider the following recursive call:
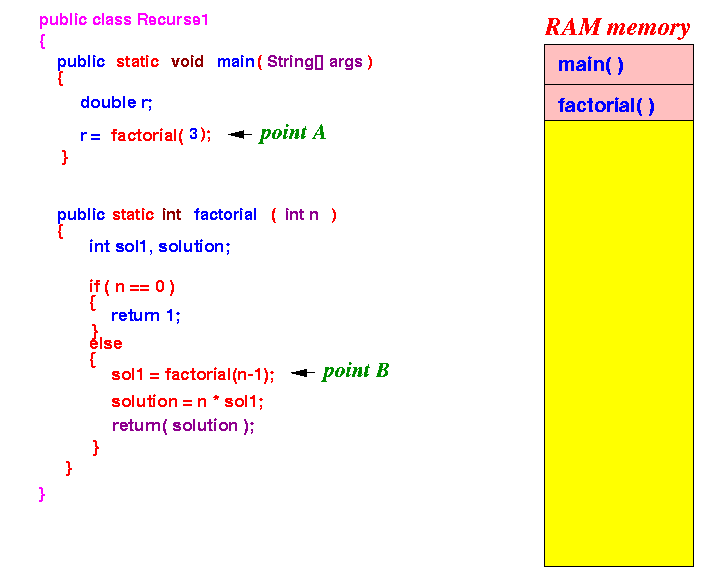
- This is what happens inside the computer
when
the method invocation
factorial(3)
is executed:
- Execution starts in main():
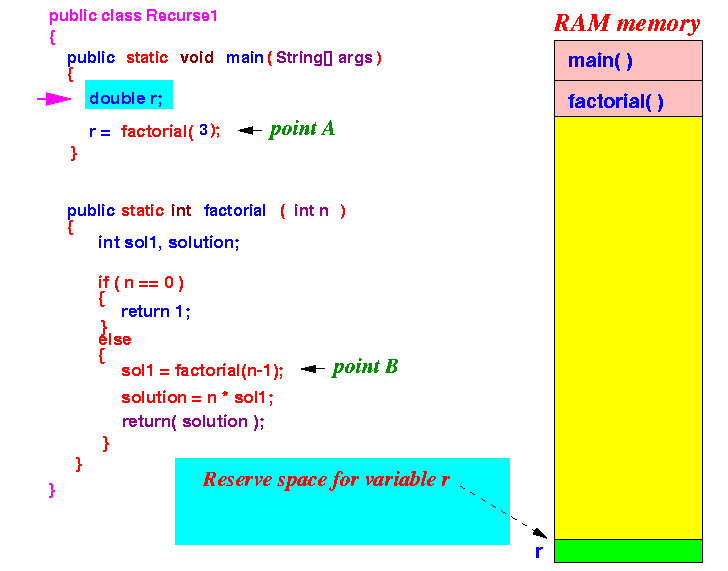
Reserves space for local variable r of main()
- Execution starts in main():

Reserves space for local variable r of main()
- main()
calls factorial(3)
- passes parameter 3
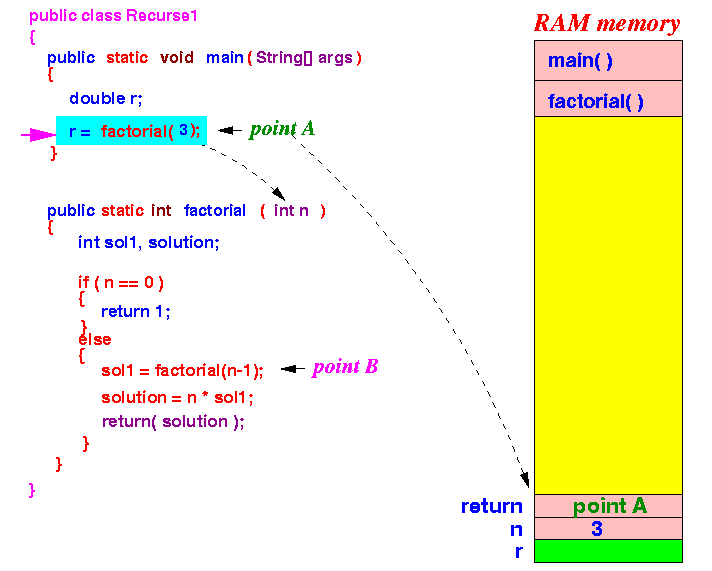
Note:
- I have color-coded the parameter variables and local variable of each factorial method invocation
(This will help you see what is going on).
Now the execution continues inside the factorial method
- factorial() will
create the
local variables:
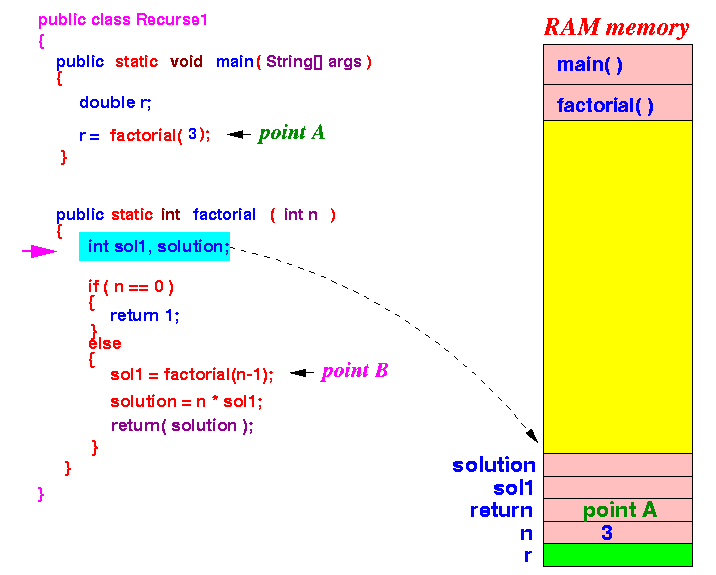
Because n = 3, the execution will proceed to the else-part of the if-else-statement.
- factorial(3)
calls factorial(n-1 (2))
- passes parameter 2
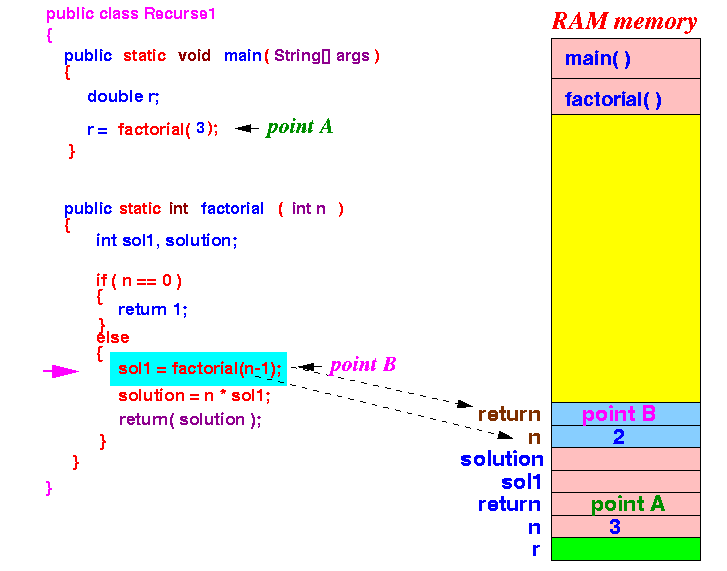
Notice that a new copy of the parameter variable n is created.
Now the execution again goes to the factorial method
- factorial(2) will
create the
local variables:
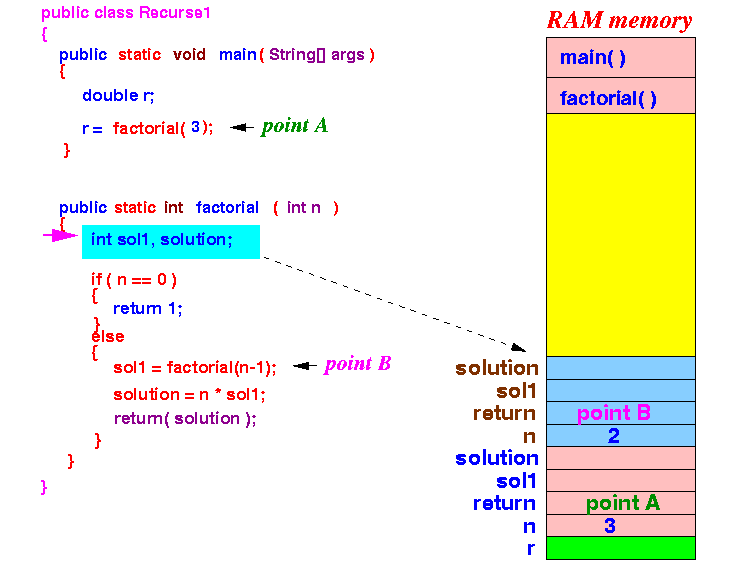
Notice that each factorial method will use it's own parameter and local variables !!!
Because n = 2, the execution will proceed to the else-part of the if-else-statement.
- factorial(2)
calls factorial(n-1 (1))
- passes parameter 1
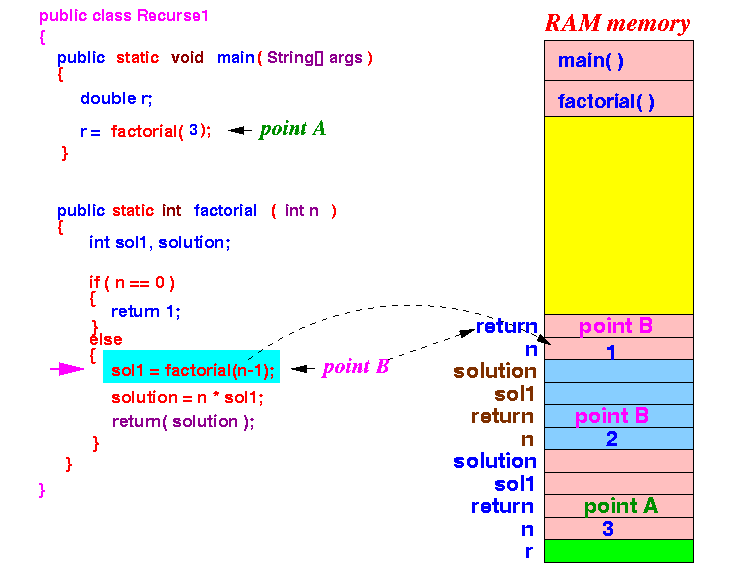
Notice that yet another new copy of the parameter variable n is created.
Now the execution again goes to the factorial method !!!
- factorial(1) will
create the
local variables:
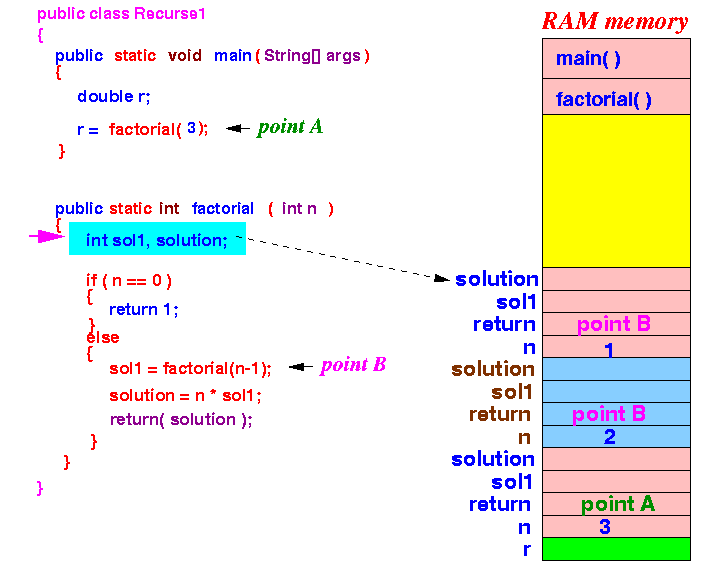
Because n = 1, the execution will proceed to the else-part of the if-else-statement.
- factorial(1)
calls factorial(n-1 (0))
- passes parameter 0
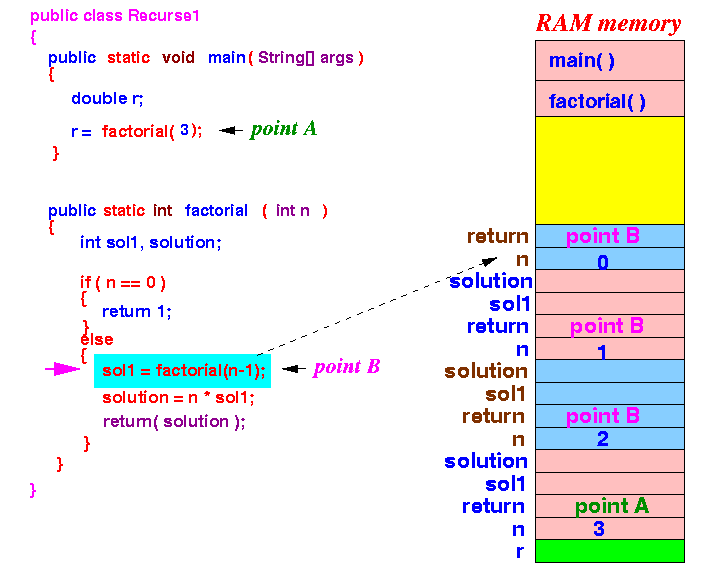
Notice that yet another new copy of the parameter variable n is created.
Now the execution again goes to the factorial method !!!
- factorial(0) will
create the
local variables:
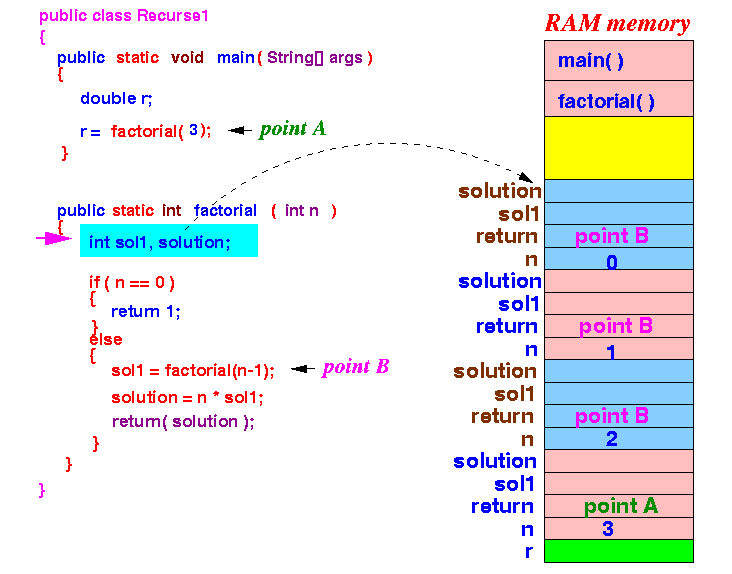
Now:
- Because n = 0, the execution will proceed to the then-part of the if-else-statement.
- factorial(0)
will return the value 1:
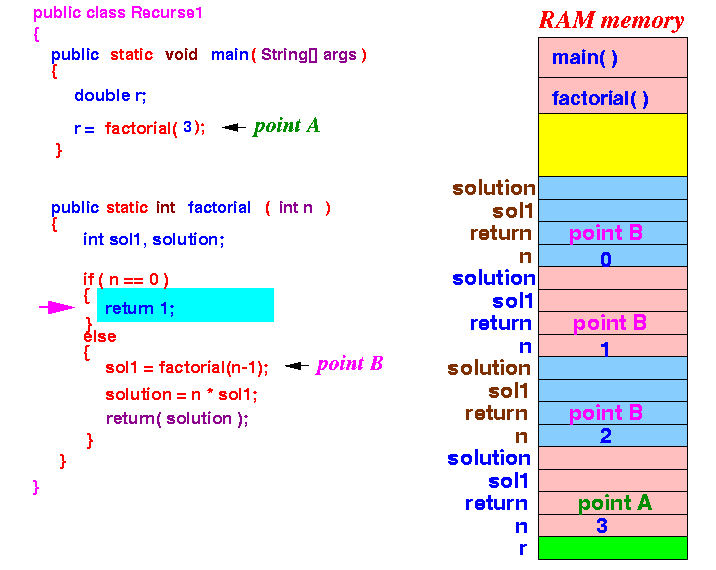
factorial(0) will terminate.
- The local and parameter variables (the blue section at the top of the stack) of factorial(0) will be destroyed.
The execution will return to point B inside factorial(1) !!!
- Execution
returns
to point B
in factorial(2):
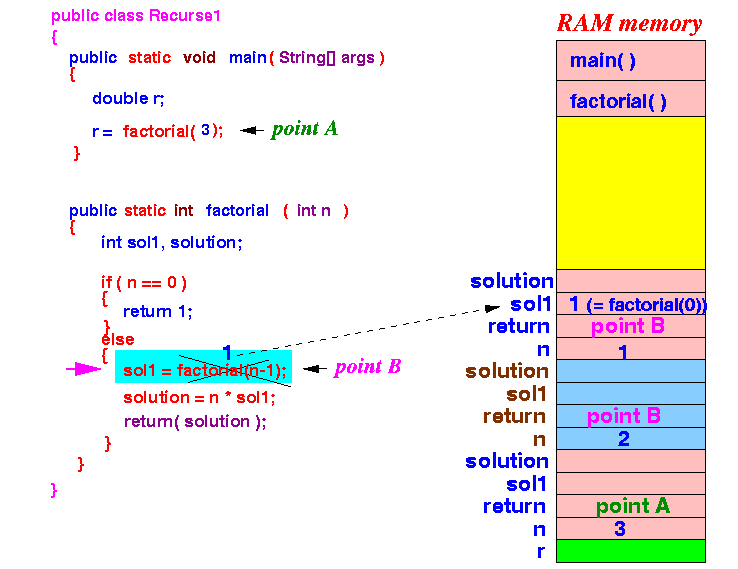
factorial(1) will use the solution sol1 and return solution = 1 × 1 = 1
- factorial(1)
will return the value 1:
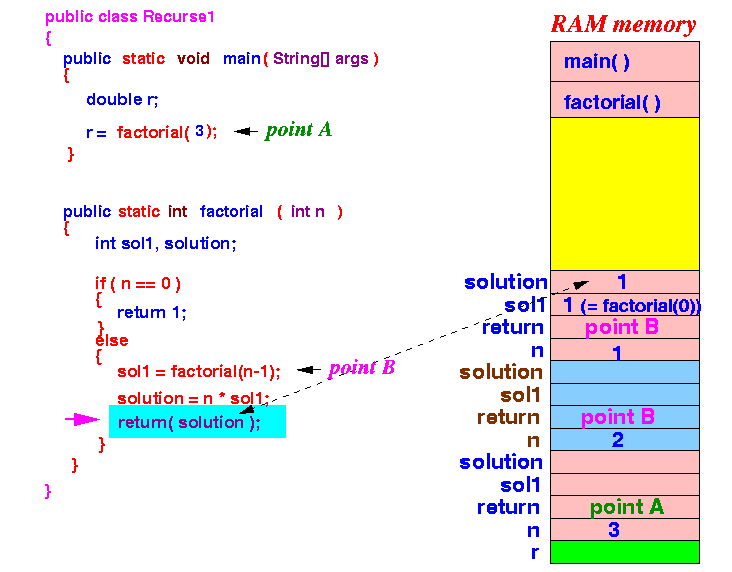
factorial(1) will now terminate.
- The local and parameter variables (the pinkish section at the top of the stack) of factorial(1) will be destroyed.
The execution will return to point B inside factorial(2) !!!
- Execution
returns
to point B
in factorial(2):
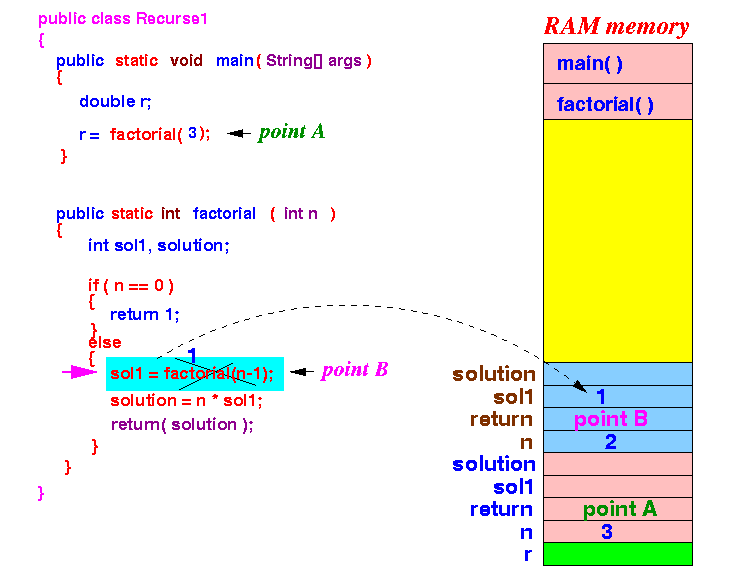
factorial(2) will use the solution sol1 (= 1) and return solution = 2 × 1 = 2
- factorial(2)
will return the value 2:
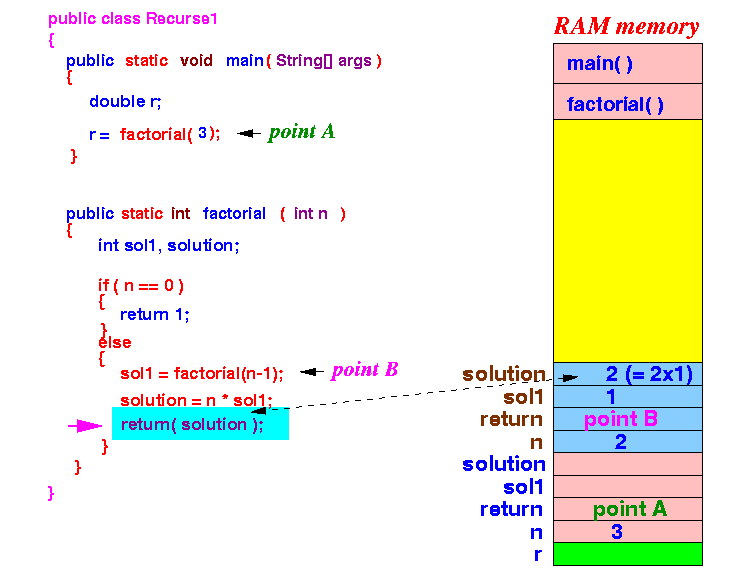
factorial(2) will now terminate.
- The local and parameter variables (the blue section at the top of the stack) of factorial(2) will be destroyed.
The execution will return to point B inside factorial(3) !!!
- Execution
returns
to point B
in factorial(3):
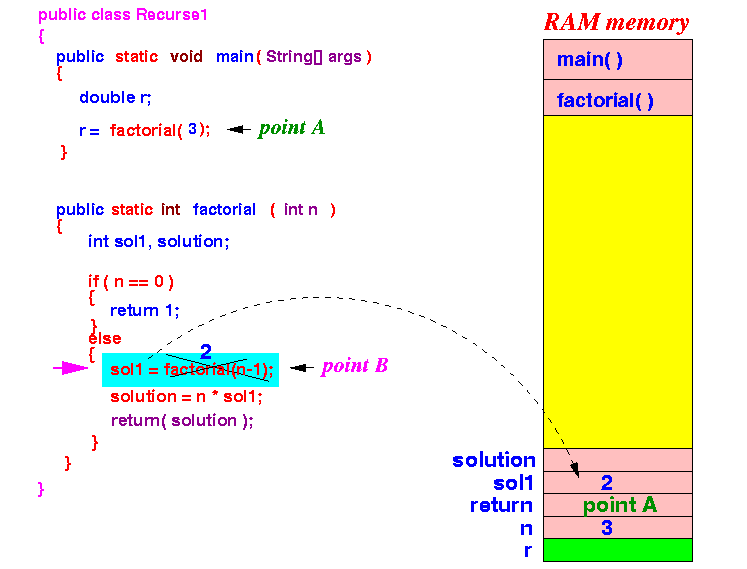
factorial(3) will use the solution sol1 (= 2) and return solution = 3 × 2 = 6
- Finally... the original call of
factorial(3)
will return the value 26:
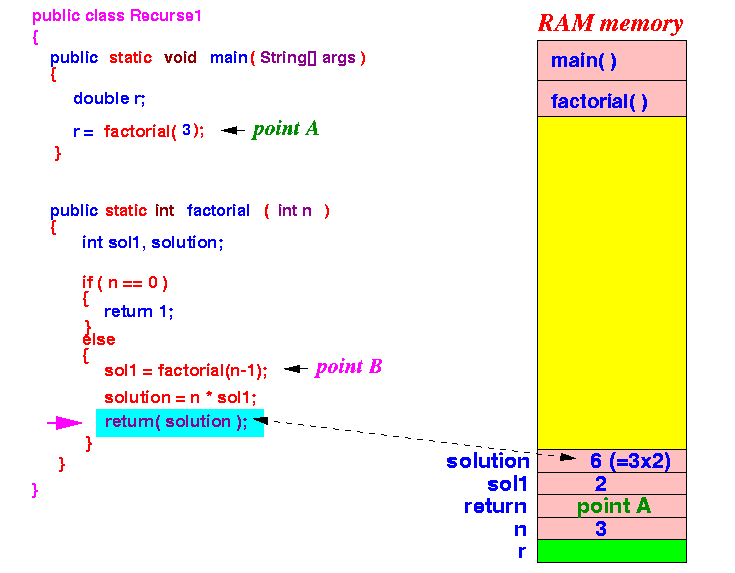
factorial(3) will now terminate.
- The local and parameter variables (the pinkish section at the top of the stack) of factorial(3) will be destroyed.
The execution will return to point A inside main() --- we are finally back !!!
- Execution
returns
to point A
in main():
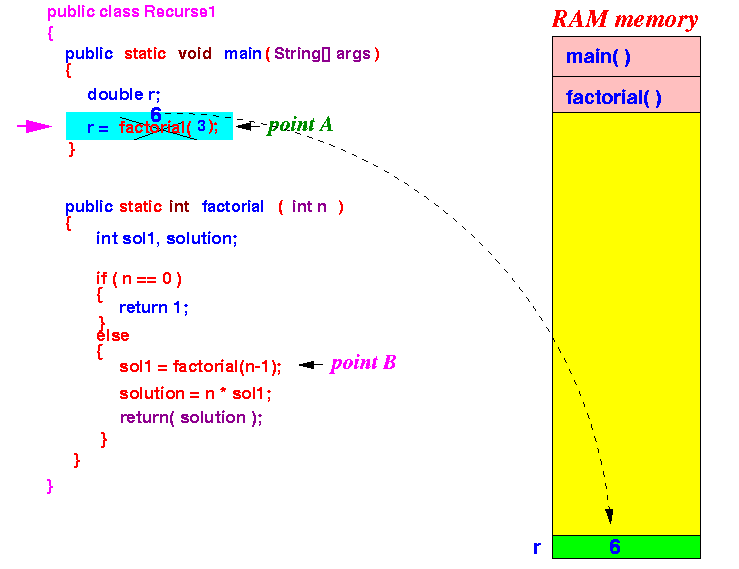
We are finally done !!!
- Execution starts in main():