- What is converting between
user-defined types
- Suppose we define 2 variables
of different user-defined types:
ClassA x = new ClassA(); // User-defined type 1: ClassA ClassB y = new ClassB(); // User-defined type 2: ClassB
- Suppose we define 2 variables
of different user-defined types:
- Facts:
- The variable x is of the (user-defined) type CLassA
- The variable y is of the (user-defined) type CLassB
- The following casting operator
convert a value of
the type ClassA into
the type CLassB:
(ClassB) x // x contains a value of type ClassA
- The following statement will store the
converted into
a type CLassB variable:
y = (ClassB) x; // x contains a value of type ClassA
- Note:
- I showed you the syntax to
perform the conversion from
a value of type ClassA
to another type ClassB
- The conversion may be illegal if the types are incompatible !!!
- I showed you the syntax to
perform the conversion from
a value of type ClassA
to another type ClassB
- Fact:
- In general,
2 (different) user-defined types
(i.e., classes) are
incomptatible
- In other words:
- In general, it is not allowed to convert between different user-defined types (classes)
- In general,
2 (different) user-defined types
(i.e., classes) are
incomptatible
- Example:
- Suppose we have 2 user-defined types
(classes)
ClassA and
ClassB as follows:
public class ClassA { int A; double B; }public class ClassB { double X; int Y; double Z; }(I left the access specifiers out because they don't play any role in the placement of the variables)
Notice that:
-
2 different classes
(e.g., CLassA and
ClassB)
in general contain
different numbers
and different types of
variables
Example:
- ClassA has 2 variables
- ClassB has 3 variables
In other words:
- The structure of different objects are in general different
- Therefore, the following is -
generally speaking - not allowed:
public class Demo { public static void main( String[] args ) { ClassA x = new ClassA(); ClassB y = new ClassB(); x = (ClassA) y; // Illegal y = (ClassB) x; // Illegal } }Because 2 different classes have - in general - different structure
We call classes with different structures incompatible data types
- Suppose we have 2 user-defined types
(classes)
ClassA and
ClassB as follows:
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- ClassB.java Prog file: click here
- Demo.java Prog file: click here
How to compile the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Demo.java
You will see the following error messages:
Demo.java:8: inconvertible types found : ClassB required: ClassA x = (ClassA) y; ^ Demo.java:9: inconvertible types found : ClassA required: ClassB y = (ClassB) x; ^ 2 errors
- The Java compiler uses the type
of an object variable to
determine the locations
of the different instance variables
- Example:
- When we define a ClassA
object:
ClassA x = new ClassA();the computer will not only create the object:
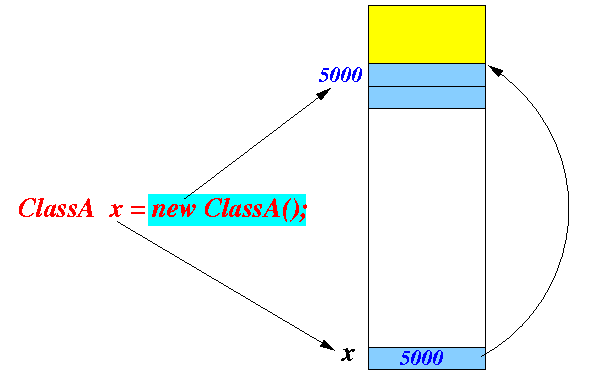
but it will also use the structure (the ordering of the variables) of the type definitopn to locate (find) the variables (x.A and x.B):
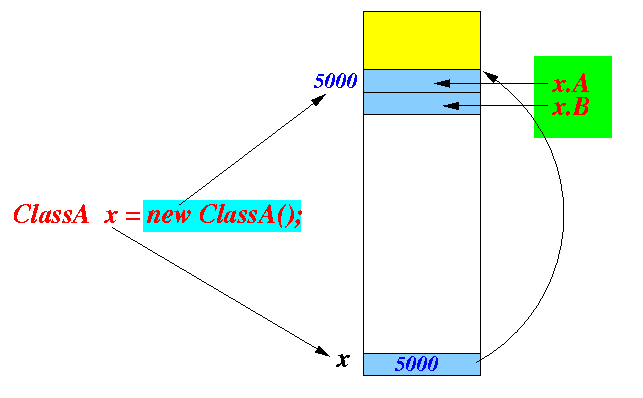
- When we define a ClassA
object:
- The conversion of
incompatible types will
result in
complete and utter chaos
Example:
-
if Java would allow you to
do:
ClassA x = new ClassA(); ClassB y = ...; y = (ClassB) x; // Put the value of x into yThe result is not only making y points to an ClassA object:
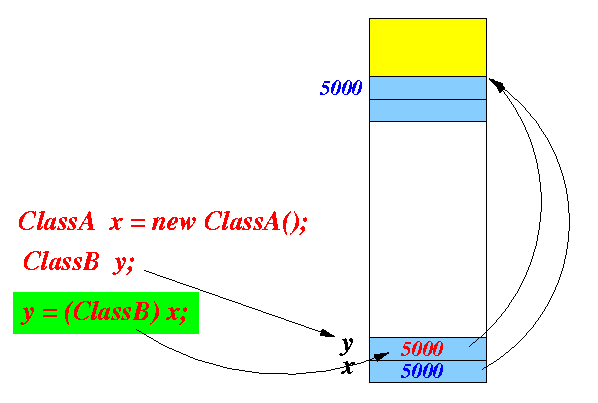
But also allowing the user to access the memory cells using the structure specified by ClassB:
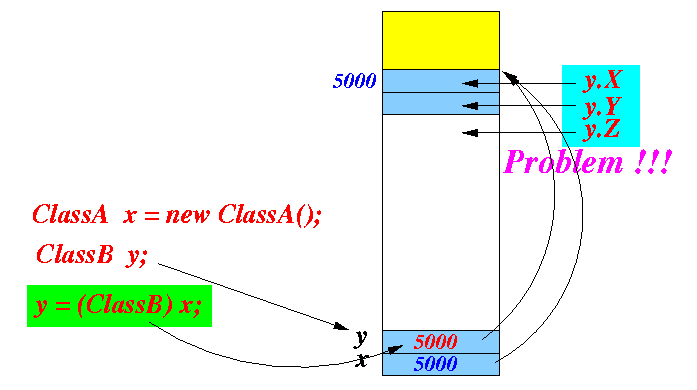
-
if Java would allow you to
do:
- Fact:
- The structure of
2 different user-defined types are
completely unrelated
It makes no sense to use the structure of one type to access memory cells used to store information of another type.
- That's why conversion between user-defined types are in general not allowed
- The structure of
2 different user-defined types are
completely unrelated
- There is one case in
user-defined types where
2 different user-defined types
are compatible:
- The base class and its derived class are compatible types
- The Java compiler allows conversion between values of the base class and derived class !!!
- Upcasting conversion (upcasting):
- Upcasting is converting a value of the derived class to a value of the base class
Example:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... ... } }
ClassB b = new ClassB(); ClassA a; a = (ClassA) b; // Upcasting // Convert a value from child class to parent class
- Downcasting conversion (downcasting):
- Downcasting is the
inverse of
upcasting:
Downcasting is converting a value of the base class to a value of a derived class
Example:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... ... } }
ClassA a = new ClassA(); ClassB b; b = (ClassB) a; // Upcasting // Convert a value from parent class to child class
- Downcasting is the
inverse of
upcasting:
- Here is a simple tool to remember these terms:
base class (parent class) - parent preceeds any child ^ | | | upcasting | | downcasting | v derived class (child class)
- Example Program:
(Demo upcasting and
downcasting)

- ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- ClassB.java Prog file: click here
- Demo.java Prog file: click here
How to compile the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Demo.java
Notes:
- You will not see any errors when you compile.
- Safe conversion:
- A conversion operation is safe if the user cannot perform an invalid access operation after the conversion operation
- Unsafe conversion:
- A conversion operation is unsafe if the user can perform an invalid access operation after the conversion operation
- Recall the upcasting
conversion:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... var1; // Receives ALL variables and methods ... var2; // defined in ClassA } ... var3; ... var4; }
ClassB b = new ClassB(); legal variable names through b: var1 var2 var3 var4 ClassA a; a = (ClassA) b; // Upcasting // Convert a value from child class to parent class
- After the upcasting conversion,
the user can use the following
variable names through
a:
var1 var2 (Because a is of type ClassA and ClassA has the variable var1 and var2)Now the variable a is pointing to a ClassB object:
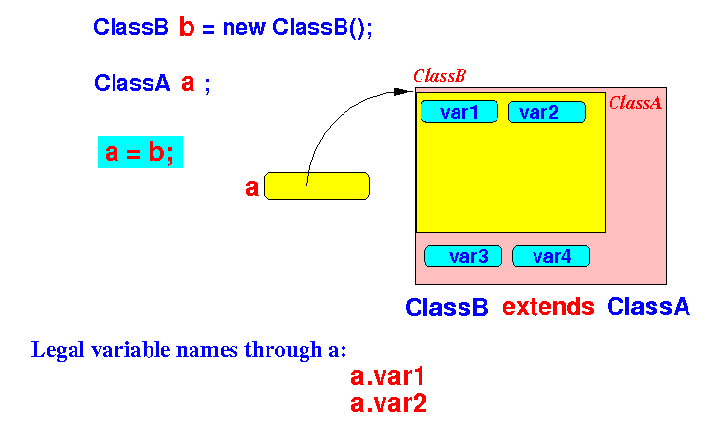
Notice that:
- The variables var1 and
var2
exists
in the object pointed to by
a
- Therefore:
- The user cannot perform an invalid access operation after the conversion operation
Thus:
- Upcasting is a safe conversion operation.
- The variables var1 and
var2
exists
in the object pointed to by
a
- Automatic conversion operation:
- An automatic conversion operation is an assignment operation without using a cast operator
- Example: automatic conversion from
int to
double
int b = 3; double a; a = b; // You do not need to use a = (double) b;
- Rule in Java:
- When an assignment operation requires a safe conversion operation, the Java compiler will perform an automatic conversion
Example with primitive types:
int b = 3; double a; a = b; // Conversin of int ⇒ double is safe. // Java performs this automatic conversion: // a = (double) b;Example with user-defined types:
ClassB b = new ClassB(); // ClassB is a derived class of ClassA ClassA a; a = b; // Conversin of ClassB ⇒ ClassA is safe. // Java performs this automatic conversion: // a = (ClassA) b;
- Example Program:
(Demo automatic upcasting)

- ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- ClassB.java Prog file: click here
- Demo.java Prog file: click here
How to compile the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Demo.java
Notes:
- You will not see any errors when you compile.
- Recall the downcasting
conversion:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... var1; // Receives ALL variables and methods ... var2; // defined in ClassA } ... var3; ... var4; }
ClassA a = new ClassA(); legal variable names through a: var1 var2 illegal variable names var3 var4 ClassB b; b = (ClassB) a; // Downcasting // Convert a value from parent class to child class
- After the downcasting conversion,
the user can use the following
variable names through
b:
var1 var2 var3 var4 (Because b is of type ClassB and ClassB has all 4 variables)Now the variable b is pointing to a ClassA object:
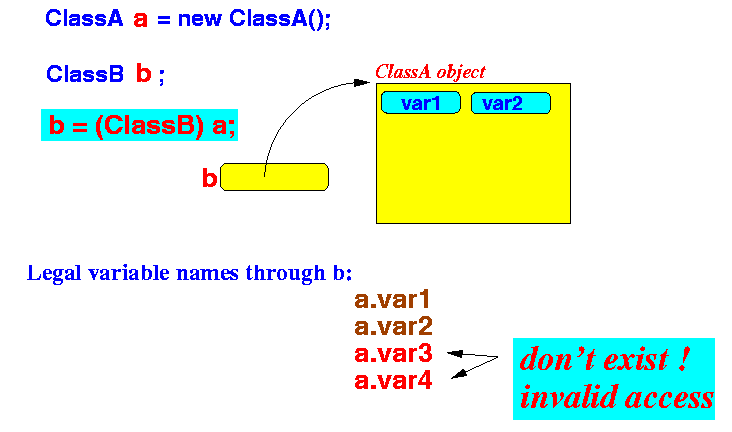
Notice that:
- The variables var3 and
var4
do not exists
in the object pointed to by
b !!!
- Therefore:
- The user can perform an invalid access operation after the conversion operation !!!!
Thus:
- Upcasting is a unsafe conversion operation.
- The variables var3 and
var4
do not exists
in the object pointed to by
b !!!
- Although a downcasting conversion
is unsafe,
it can be useful
- The proper usage of a
downcasting conversion:
- The proper usage of a downcasting conversion is to undo a previous upcasting conversion
Example:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... var1; // Receives ALL variables and methods ... var2; // defined in ClassA } ... var3; ... var4; }
ClassB b = new ClassB(); ClassA a; a = (ClassA) b; // Upcasting /* ================================= Undoing the upcasting operation: ================================= */ ClassB b2; b2 = (ClassB) a; // Downcasting that undo the // previous upcasting operation
- Example Program:
(Demo proper downcasting)

- ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- ClassB.java Prog file: click here
- Demo.java Prog file: click here
How to compile the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile:
javac Demo.java
- Run the program with: java Demo
Notes:
- You will not see any errors when you run the program.
- The improper usage of a
downcasting conversion:
- Do not use the downcasting conversion for anything other than undoing a previous upcasting conversion
Common mistake:
- A common mistake is using the downcasting conversion on a base class object
Example:
public class ClassA public class ClassB extends ClassA { { ... var1; // Receives ALL variables and methods ... var2; // defined in ClassA } ... var3; ... var4; }
ClassB a = new ClassA(); ClassB b; b = (ClassB) a; // Downcasting conversion on a base class objectResult:
- The Java compiler cannot detect
any error
(too complex to explain)
- However, when the program is run,
the Java runtime system will
detect that the
ClassB typed variable
b will
point to a
base class ClassA typed
object.
As discussed previously, this will result in
- potential invalid access operations (see: click here )
- The Java runtime system will prevent the potential invalid access operations from happening and will cause a run time error
- Example Program:
(Demo improper downcasting)

- ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- ClassB.java Prog file: click here
- Demo.java Prog file: click here
How to compile the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile:
javac Demo.java
- Run the program with: java Demo
Notes:
- You will see this
run time error:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: ClassA at Demo.main(Demo.java:9)