- The recursive LCS algorithm:
/* ---------------------------------- Meaning of the input parameters x = x0 x1 x2 .... x(i-1) y = y0 y1 y2 .... y(j-1) ---------------------------------- */ int LCS( int i, int j, String x, String y ) { int sol1, sol2, sol3; /* ============================== Base cases ============================== */ if ( i == 0 || j == 0 ) { /* ------------------------------------------ One of the strings has 0 character => no match possible Longest common subsequence = 0 characters ------------------------------------------- */ return(0); } if ( x[i-1] == y[i-1] ) { sol1 = LCS(i-1, j-1, x, y); return( sol1 + 1 ); } else { sol2 = LCS(i-1, j, x, y); sol3 = LCS(i, j-1, x, y); if ( sol2 >= sol3 ) { return(sol2); } else { return(sol3); } } }
- Fact:
- A recursive solver (= recursive problem solving method) will often solve the same problem multiple times
Example:
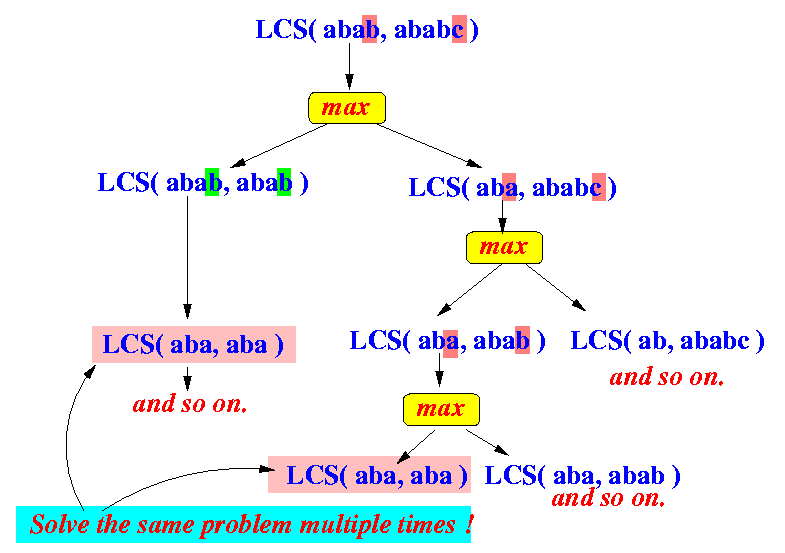
- Memoization:
- Store the solution
for LCS(i.j, x, y)
in an array:
L[i][j] = solution of LCS(i, j, x, y) (L[i][j] = -1 means: don't have the solution)
- When we need to solve LCS(i, j, x, y), we will first check if we already have the solution stored in L[i][j]
LCS with memoization:
/* ---------------------------------- Meaning of the input parameters x = x0 x1 x2 .... x(i-1) y = y0 y1 y2 .... y(j-1) ---------------------------------- */ int L[][]; // L[i][j] = Saved output of LCS(i,j) ********** int LCS( int i, int j, String x, String y ) { int sol1, sol2, sol3; if ( i == 0 || j == 0 ) { /* ------------------------------------------ One of the strings has 0 character => no match possible Longest common subsequence = 0 characters ------------------------------------------- */ return(0); } /* ------------------------------------------------- Check if we have a Memoized solution ********* ------------------------------------------------- */ if ( L[i][j] >= 0 ) { return( L[i][j] ); // Return stored solution !!! } /* ------------------------------------------------------ We will only run the recursive solver if we don't have the solution LCS(i,j) stored... ------------------------------------------------------ */ if ( x[i-1] == y[i-1] ) { sol1 = LCS(i-1, j-1, x, y); L[i][j] = sol1 + 1; // Memoize the solution ******** return( sol1 + 1 ); } else { sol2 = LCS(i-1, j, x, y); sol3 = LCS(i, j-1, x, y); if ( sol2 >= sol3 ) { L[i][j] = sol2; // SAVE the solution ******** return(sol2); } else { L[i][j] = sol3; // SAVE the solution ******** return(sol3); } } }
- Store the solution
for LCS(i.j, x, y)
in an array:
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file:
click here
- Sample input:
X = BAA Y = BBAB
- Prog file:
click here
- Note:
- Memoization is considered an inferior way to use Dynamic Programming
- Short coming of
memoization:
- It uses recursion (which can be very expensive because we need to store variables on the stack)
- The "standard"
dynamic programming technique
does
not use
recursive
- The "standard" dynamic programming technique compute a solution iteratively, starting from the base (smallest problem) cases and working towards larger problems
The standard dynamic programming technique looks like this:
for ( i = 0; i < m; i++ ) for ( j = 0; j < n; j++ ) L[i][j] = .... (uses L[i-..][j], L[i][j-..] or L[i-..][j-..])
- Fact:
- If you are not very skilled in
dynamic programming,
you will have a hard time
finding the
tabular solution
directly...
- It is often easier to:
- First: find a
recursive solution
- Then:
use the memoization technique
to store the solution in a
table (array) form
- Final: convert the memoization into an iterative program
- First: find a
recursive solution
- If you are not very skilled in
dynamic programming,
you will have a hard time
finding the
tabular solution
directly...
- General technique on
how to convert memoization code
into
tabular dynamic programming
- Define a table (= array)
- You can use the same variable as the one used in the memoization technique
(e.g.: L[ ][ ])
- Initialize the
base cases in the
table
Example:
for (i = 0; i < m; i++ ) L[i][0] = 0;
- Compute all values in the
table
(e.g.: L[ ][ ])
starting
from the smaller indices towards
larger indices
using the
memoization program statements
- Define a table (= array)
- Example: Fibonacci numbers
fn = fn−1 + fn−2 f0 = 1 f1 = 1Recursive solution:
int fib(int n) { int sol1, sol2, mySol; /* ============================= Base cases ============================= */ if ( n == 0 ) { return 1; // f0 = 1 } else if ( n == 1 ) { return 1; // f1 = 1 } else /* Recursive solver */ { sol1 = fib( n-1 ); // Solve smaller problem 1 sol2 = fib( n-2 ); // Solve smaller problem 2 mySol = sol1 + sol2; // Use solution to solve orig. proble, return ( mySol ); // Claim credit... } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Fib0.java
- To run:
java Fib0
It will run slowly for n ~= 40
- Inefficiency in the
recursive solution:
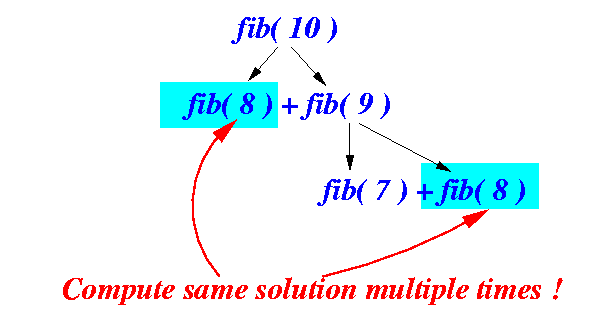
Inefficiency caused by:
- The same problem is solved multiple times !!!
- Memoization solution:
int fib(int n) { int sol1, sol2, mySol; /* ============================= Base cases ============================= */ if ( n == 0 ) { return 1; // f0 = 1 } else if ( n == 1 ) { return 1; // f1 = 1 } else /* Recursive solver */ { if ( F[n] >= 0 ) return (F[n]); // Return solution if you have it /* ======================== No solution: compute it ========================= */ sol1 = fib( n-1 ); // Solve smaller problem 1 sol2 = fib( n-2 ); // Solve smaller problem 2 mySol = sol1 + sol2; // Use solution to solve orig. proble, F[n] = mySol; // Save it ! return ( mySol ); // Claim credit... } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Fib1.java
- To run:
java Fib1
It will run fast even for n ~= 40
- Converting to
tabular dynamic programming:
- Look at how
F[n]
is computed:
sol1 = fib( n-1 ); // fib(n-1) will be stored in F[n-1] sol2 = fib( n-2 ); // fib(n-2) will be stored in F[n-2] mySol = sol1 + sol2; // mySol = F[n-1] + F[n-2] F[n] = mySol; // Save it !
In other words: F[n] = F[n-1] + F[n-2]
- The recursive solver
(with memoization) computes the
solutions in the
following order:
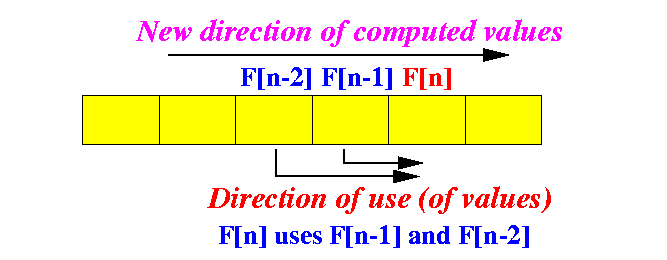
F[n] F[n-1] F[n-2] ... and so on.You can see the sequence in the following invocation sequence:

- Problem is:
- In order to compute F[n], we need the values of F[n-1] and F[n-2]:
See:
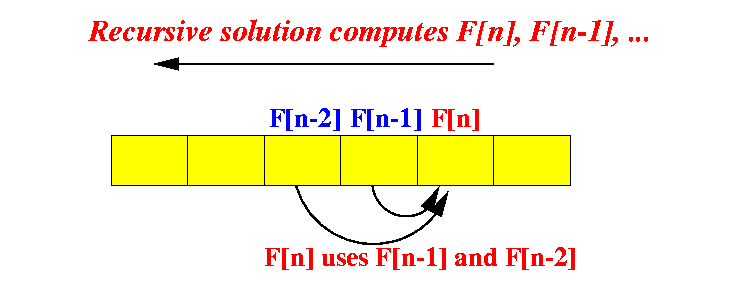
Observe that:
- The direction of
computed values
is opposite to the
direction
of use:
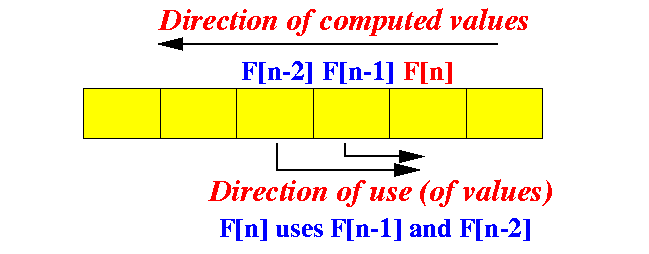
- If we reverse the
direction of
computed values:
Then:
- We do not need to
use recursion !!!
(Because at the time that we are computing the value F[n], the values of F[n-1] and F[n-2] are available)
(BTW, in the recursive solution, the call fib(n) is waiting for fib(n-1) and fib(n-2) to finish because these values were not available !!!)
- We do not need to
use recursion !!!
- Look at how
F[n]
is computed:
- The dynamic programming solution
for Fibonacci numbers:
public static int fib(int n) { int k; /* ================= Base cases ================= */ F[0] = 1; F[1] = 1; /* ========================================================== Compute direction: F[2], F[3], ..., F[n-2], F[n-1]. F[n] ========================================================== */ for ( k = 2; k <= n; k++ ) { F[k] = F[k-1] + F[k-2]; // Dyn. prog } return ( F[n] ); }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Fib2.java
- To run: java Fib2
- Observe
how the
values of
L[i][j] are
computed:
int L[][]; // L[i][j] = Saved output of LCS(i,j) ********** int LCS( int i, int j, String x, String y ) { int sol1, sol2, sol3; /* ======================================== Base cases ======================================== */ if ( i == 0 || j == 0 ) { /* ------------------------------------------ One of the strings has 0 character => no match possible Longest common subsequence = 0 characters ------------------------------------------- */ return(0); // I.e.: L[0][..] = 0 and L[..][0] = 0 } /* ------------------------------------------------- Check if we have a Memoized solution ********* ------------------------------------------------- */ if ( L[i][j] >= 0 ) { return( L[i][j] ); // Return stored solution !!! } /* ------------------------------------------------------ We will only run the recursive solver if we don't have the solution LCS(i,j) stored... ------------------------------------------------------ */ if ( x[i-1] == y[i-1] ) { sol1 = LCS(i-1, j-1, x, y); L[i][j] = sol1 + 1; // I.e.: L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1] + 1 return( sol1 + 1 ); } else { sol2 = LCS(i-1, j, x, y); sol3 = LCS(i, j-1, x, y); if ( sol2 >= sol3 ) { L[i][j] = sol2; // sol2 = LCS(i-1, j, x, y) return(sol2); } else { L[i][j] = sol3; // sol3 = LCS(i, j-1, x, y) return(sol3); } // I.e.: L[i][j] = max( L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1] ) } }The direction of flow of data used in the computation is as follows:
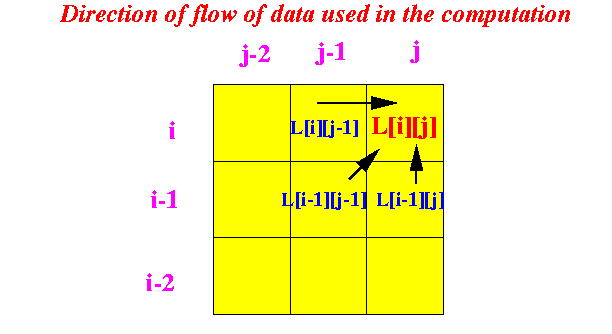
Therefore, our loop index should run as follows:
for ( i = ..; i < m; i++ ) for ( j = ..; j < n; j++ ) L[i][j] = .... ; // Compute L[i][j]So that when L[i][j] is computed, all the values of:
- L[i-1][j-1]
- L[i][j-1]
- L[i-1][j]
will be available !!!
OK, let's write the dynamic programming code !!!
- The base cases:
for (i = 0; i < x.length()+1; i++) L[i][0] = 0; // y = "" ===> LCS = 0 for (j = 0; j < y.length()+1; j++) L[0][j] = 0; // x = "" ===> LCS = 0 - How to compute
L[i][j] according to
the memoization code:
if ( x[i-1] == y[j-1] ) { L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1] + 1; } else { if ( L[i-1][j] >= L[i][j-1] ) { L[i][j] = L[i-1][j]; } else { L[i][j] = L[i][j-1]; } }We must compute L[i][j] in this order:
for ( i = ..; i < m; i++ ) for ( j = ..; j < n; j++ ) L[i][j] = .... ; // Compute L[i][j]
- The tabular (bottom-up)
dynamic programming
solution for LCS:
public static int solveLCS(String x, String y) { int i, j; /* =============================================== Initialize the base cases =============================================== */ for (i = 0; i < x.length()+1; i++) L[i][0] = 0; // y = "" ===> LCS = 0 for (j = 0; j < y.length()+1; j++) L[0][j] = 0; // x = "" ===> LCS = 0 /* ===================================================== Bottom-up (smaller to larger) computation of L[][j] ===================================================== */ for (i = 1; i < x.length()+1; i++) { for (j = 1; j < y.length()+1; j++) { if ( x.charAt(i-1) == y.charAt(j-1) ) { L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1] + 1; } else { if ( L[i-1][j] >= L[i][j-1] ) { L[i][j] = L[i-1][j]; } else { L[i][j] = L[i][j-1]; } /* =================================================== Note: we can replace the above if-statement with: L[i][j] = max ( L[i-1][j] , L[i][j-1] ); =================================================== */ } } } return( L[x.length()][y.length()] ); // This is LCS(x,y) }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file:
click here
- Sample input:
x = CACAB y = BCA Max length = 2 L[][]: 0 1 2 3 ================================== 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 2 0 0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 4 0 0 1 2 5 0 1 1 2
- Prog file:
click here
- Running time =
O(n × m)
(quite obvious if you look at the size of the matrix)
n = length of string x
m = length of string y