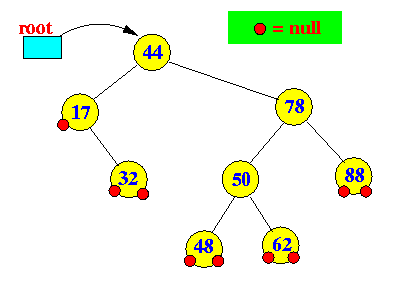
- Example binary search tree:
- Example: insert entry 46:
- Search for the location to contain
46:

- Insert entry
46:

- Search for the location to contain
46:
- Note:
- A newly insert node is always a leaf node (with no children nodes) of the binary search tree
- Sample AVL tree:

- Inserting an
entry (node) can
cause an AVL tree to
become height imbalanced:

(The resulting tree is no longer an AVL tree !!)
- The two effects of
inserting a node in
an AVL tree:
- Effect 1:
- Inserting a node will change the height (increase by ≤ 1) of nodes on the path from the root to the newly inserted node only
Example:

Therefore:
- Only nodes on the path from the root to the newly inserted node can become height imbalanced
- Effect 2:
- If there are
some nodes that
have become
height imbalanced,
then the
difference between
the heights of
the left and right trees
is exactly = 2
- Also: the larger value of the height is found in the nodes on the path from the newly inserted node to the root
Example:

(Because before the insertion, the difference between the heights was ≤ 1.
The insertion increased the height of one of the sub tree by ONE.
The difference between the heights is ≤ 2)
- If there are
some nodes that
have become
height imbalanced,
then the
difference between
the heights of
the left and right trees
is exactly = 2
- Effect 1:
- Re-balance:
- Re-balance =
re-organize the
nodes in an
out-of-balanced AVL tree so that
the resulting tree will
satisfy the height constraint
of an AVL tree
(I.e., the result of the re-balance operation is an AVL tree
- Re-balance =
re-organize the
nodes in an
out-of-balanced AVL tree so that
the resulting tree will
satisfy the height constraint
of an AVL tree
- Example:
- AVL tree before
inserting node 78:

- AVL tree after
inserting node 78:

- The AVL tree is now
out-of-balance because there are
nodes in the tree with
(height(left tree) - height(right tree)) =
2 :

- We can re-arrange the
shaded subtree as follows:
Before re-arranging nodes in shaded subtree After re-arranging nodes in shaded subtree 

Notice that:
- The node re-arrangement
must
preserve the
properties of
a Binary Search Tree:
- All keys in the
left subtree must be
smaller than the
top node
- All keys in the right subtree must be greater than the top node
- All keys in the
left subtree must be
smaller than the
top node
- After the node re-arrangement, the resulting tree is an AVL tree !!!!
- The node re-arrangement
must
preserve the
properties of
a Binary Search Tree:
- AVL tree before
inserting node 78:
- In what follows, I will explain the
"node re-arrangement" operation
that can
re-balance an
out-of-balance AVL tree
This "node re-arrangement" operation is called tri-node reconstruction operation (by Goodrich).
(BTW, the classic way to do re-balancing is with a bunch of "left-rotation", "right-rotation", "right-left-rotation", "right-right-rotation", etc..)
- Consider the following sub tree
of a binary tree:

- From their relative positions
of the nodes
x,
y and
z
, and the subtrees
T0,
T1,
T2 and
T3
in the AVL (binary) tree, we can conclude that:
- keys(T0) < z < keys(T1) < y < keys(T2) < x < keys(T3)
- In the node re-arrangement operation,
we will
always
make a tree that look like this:

To preserve the property of a Binary Search Tree (left subtree with smaller keys and right subtree with larger keys), we must attach the subtrees T0, T1, T2 and T3 to the nodes x, y and z as follows:

This is the first tri-node reconstruction operation:

- Note:
- There are 4 different
tri-node reconstruction operation
(depending on the
relative positions of
the nodes
x,
y and
z)
Here are the 4 different relative positions of the nodes x, y and z:

- There are 4 different
tri-node reconstruction operation
(depending on the
relative positions of
the nodes
x,
y and
z)
- Teaching note:
- Each configuration
has its own
tri-node reconstration operation
- I have listed
all 4
tri-node reconstration operations
below if
you want to take look at them:
click here
- I don't want to present the details of all 4 tri-node reconstration operations (because they are similar and you will hear the same story 4 times --- some of you will bored to death...)
- I have listed
all 4
tri-node reconstration operations
below if
you want to take look at them:
click here
- So I will discuss the details of the first tri-node reconstration operation only
- Each configuration
has its own
tri-node reconstration operation
- How to use
a tri-node reconfiguration operation
to re-balance an
AVL tree:
- If after an insertion,
the AVL tree is
still balanced:
- We are done :)
(If it ain't broken, don't fix it !!!)
- We are done :)
- If after an insertion,
the AVL tree becomes
imbalanced:
- Find the first imbalanced node
from the point of insertion
(Recall that only node from inserted node ⇒ root can become imbalanced):

- Apply the (appropriate for that configuration))
tri-node reconstruction operation
on the tree rooted at the
first imbalanced node = x:

The resulting tree will become balanced (i.e., an AVL tree !!!)
- Find the first imbalanced node
from the point of insertion
- If after an insertion,
the AVL tree is
still balanced:
- A concrete example:
- After inserting node
46,
the AVL tree
becomes
imbalanced:

Starting at the inserted node (46), traverse up the tree and find the first imbalanced node:
- We find node 78 (this is the first node with | height(left tree) − height(right tree) | > 1
- The AVL tree will become
balanced again after
we performed the
(approriate) tri-node restructuring
operation:

Procedure summary:
- I did the example using configuration 1
The other configurations are similar
- Precedure for re-balancing an AVL tree after
insertion
- Starting at the inserted node,
traverse up the tree
to find the first node
- If not found, then
done
- Otherwsie: apply the (appropriate) tri-node restructuring operation using x as the first imbalanced node
- Starting at the inserted node,
traverse up the tree
to find the first node
- After inserting node
46,
the AVL tree
becomes
imbalanced:
- $64,000 question:
- Will this procedure
guarantee that
the resulting tree is an
AVL tree ???
(If you can believe that without proof, I have a bridge in Brooklyn for sale :-))
- Will this procedure
guarantee that
the resulting tree is an
AVL tree ???
- Proposition:
- The tri-node restructuring operation will always be able to re-balance an out-of-balance AVL tree due to insertion
- Proof:
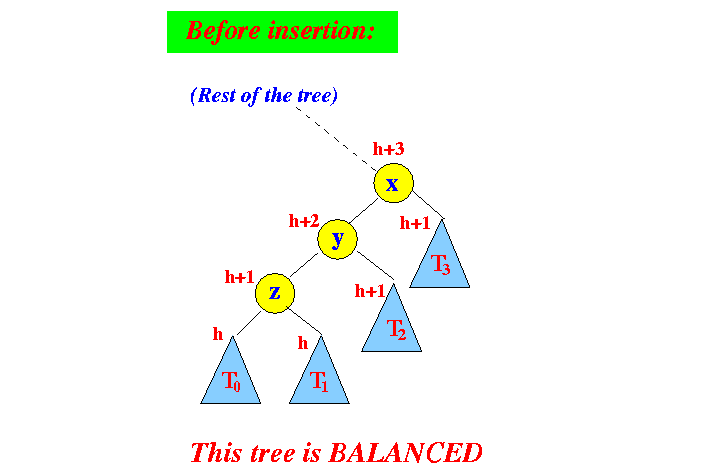
- Suppose the AVL tree becomes
imbalanced
after we inserted a node w:

Since the node x is the first imbalanced node, its height must have increased by 1 !!!
The increase in height of node x can only be caused by a height increase in node y (and in node z)
- Let's figure out what are the value of all the
? in the figure are first.
Because the tree was balanced before the insertion of w, we have that:

The height of T1 can only be h−1 or h because the difference in height (with subtree T0) is at most 1
(BTW, height of T1 cannot be h+1, because otherwise node z will have height = h+2 !!!)
- Then because
node x is the
first imbalanced node,
we can conclude that:

The height of T1 must be equal to h (otherwies, node z will be an earlier imbalanced node)
The height of T2 must be equal to h+1 (otherwies, node y will be an earlier imbalanced node)
The height of T3 must be equal to h+1 (otherwies, node x will be an balanced node)
- We now know the exact height
before the
insert operation:
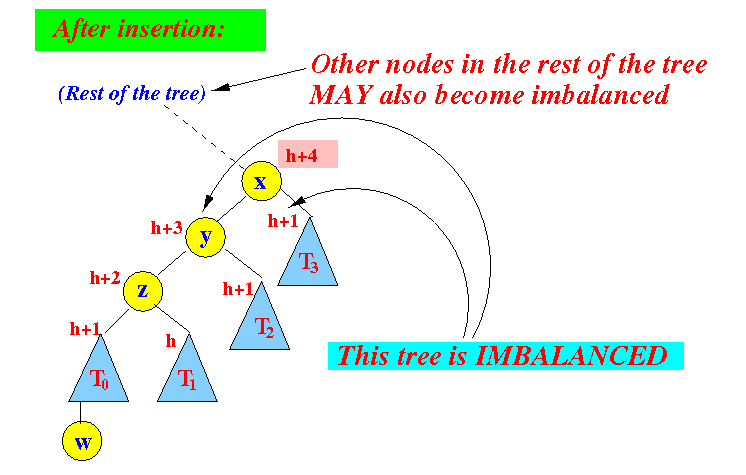
- After the
insert operation, the tree is:
- After the
tri-node reconstruction operation,
the tree is:

We can see the tri-node reconstruction operation has fixed the height violation in node x
- Question that remains:
- Did the tri-node reconstruction operation fix the height violation in the rest of the tree ???
Answer: yes because the height of the root node of the subtree after the tri-node reconstruction operation is the same as the original tree !!!
See:
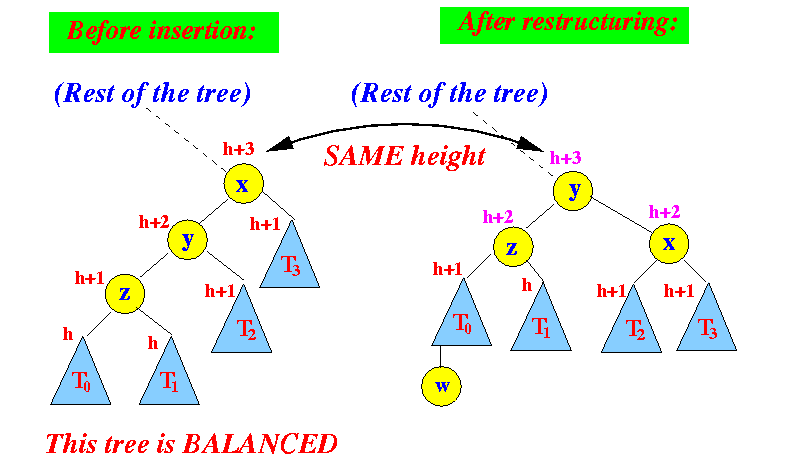
Since the rest of the tree was balanced when the subtree had height = h+3, therefore, the rest of the tree will be balanced because the subtree still has height = h+3 !!!
Conclusion:
- The entire tree is re-balanced after the tri-node reconstruction operation !!!
- Suppose the AVL tree becomes
imbalanced
after we inserted a node w:
- Notations:
- w =
the newly inserted node in
the AVL tree
- x =
the first node in
the (previously) AVL tree on the
path from w to the root
that is imbalanced
- y =
the child node of
x in
the (previously) AVL tree on the
path from w to the root
- z = the child node of y in the (previously) AVL tree on the path from w to the root
Graphically:

- w =
the newly inserted node in
the AVL tree
- There are 4 possible
parent/child relations
between the nodes
x, y and
z:

The configurations can be characterized as follows:
- Left-left configuration: y is left child of x and z is left child of y
- Left-right configuration:
y is left child of x
and
z is right child of y
- Right-left configuration: y is right child of x and z is right child of y
- Right-right configuration: y is right child of x and z is left child of y
Remember that:
- Node x is always the first imbalanced node from the inserted node to the root !!!
- Examples:
- An insert that
results in configurtaion 1:

- An insert that
results in
configurtaion 2:

- An insert that
results in configurtaion 1:
- Fact:
- For each kind of configuration,
there is a
corresponding tri-node operation
that re-balance the height
of an imbalanced AVL tree !!!
- Recall the 4 kinds of
configurations:

- For each kind of configuration,
there is a
corresponding tri-node operation
that re-balance the height
of an imbalanced AVL tree !!!
- If you want to discover the
4 different
tri-node reconstruction operations
yourself,
you can do so by
applying
the following property:
- keys(T0) < z < keys(T1) < y < keys(T2) < x < keys(T3)
I have spare you the discovery.... here are the 4 different tri-node reconstruction operations
- Notation:
- Because a
tri-node reconstruction operation
will always
make the one of
the following
4 configuration (of 3 nodes):

it is useful (especially when we write the code) to fix the different node with labels.
- Labelling scheme:
- The root node is labeled with b
- The left child node is labeled with a
- The right root node is labeled with c
In other words (or picture):

- Because a
tri-node reconstruction operation
will always
make the one of
the following
4 configuration (of 3 nodes):
- The 4
tri-node reconstruction operations:
- Configuration 1:

- Remember that the
reconstruction operation
must produce a
Binary Search Tree.
- In other words, you must preserve the property that the left subtree contains smaller key values and the right subtree contains larger key values !!!
- Remember that the
reconstruction operation
must produce a
Binary Search Tree.
- Configuration 2:

Correspondence of node: a = y b = z c = x
- Configuration 3:

Correspondence of node: a = x b = y c = z
- Configuration 4:

Correspondence of node: a = x b = z c = y
- Configuration 1:
- Peusdo code:
Let x = first imbalanced node Let y = child node of imbalance node x (on the way to the inserted node) Let z = grand child of imbalance node x (on the way to the inserted node) (1) Identify the configuration; which node is a ? which node is b ? which node is c ? where is subtree T0 (= root of subtree T0) ? where is subtree T1 (= root of subtree T1) ? where is subtree T2 (= root of subtree T2) ? where is subtree T3 (= root of subtree T3) ? (2) Make the links according to the tri-node reconstruction operation (build from the top first) (2.a) Make b the root of the new subtree x's parent must now point to b ! (Be careful: if x is the root node, b will become the new root !) (2.b) Now make these links: b / \ Note: don't forget the PARENT links !!! a c (2.c) Then these links: b / \ a c / \ T0 T1 (2.d) And finally these links: b / \ a c / \ T2 T3 Recompute the heights of a, c, b and all nodes from b to root. Done.
- Tri-node restructuring algorithm in Java (my own version):
(Goodrich's code is Chinese to me... took me a while to figure out what he was trying to do, ain't not way in hell I'm using it to teach.....)
/* ======================================================= tri_node_restructure(x, y, z): x = parent(y) y = parent(z) ======================================================= */ public void tri_node_restructure( BSTEntry x, BSTEntry y, BSTEntry z) { /* ******************************************************************* Determine the parent child relationships between (y,z) and (x,y)) ******************************************************************* */ /* ======================================================= Determine the node configuration: find out which nodes are in positions a, b and c given in the following legend: b / \ a c / \ / \ T0 T1 T2 T3 ======================================================= */ BSTEntry a, b, c; BSTEntry T0, T1, T2, T3; boolean zIsLeftChild = (z == y.left); boolean yIsLeftChild = (y == x.left); if (zIsLeftChild && yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration 1 */ a = z; // x=c b = y; // / \ c = x; // y=b T3 T0 = a.left; // / \ T1 = a.right; // z=a T2 T2 = b.right; // / \ T3 = c.right; // T0 T1 } else if (!zIsLeftChild && yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration 2 */ a = y; // x=c b = z; // / \ c = x; // y=a T3 T0 = a.left; // / \ T1 = b.left; // T0 z=b T2 = b.right; // / \ T3 = c.right; // T1 T2 } else if (zIsLeftChild && !yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration 4 */ a = x; // x=a b = z; // / \ c = y; // T0 y=c T0 = a.left; // / \ T1 = b.left; // z=b T3 T2 = b.right; // / \ T3 = c.right; // T1 T2 } else { /* Configuration 3 */ a = x; // x=a b = y; // / \ c = z; // T0 y=b T0 = a.left; // / \ T1 = b.left; // T1 z=c T2 = c.left; // / \ T3 = c.right; // T2 T3 } /* ------------------------------------------------------------------ Old Tree: New tree: x's parent x's parent | | x b Put b at x's place ------------------------------------------------------------------ */ if ( x == root ) { /* If x is the root node, handle the replacement differently.... */ root = b; // Need to update root ! b.parent = null; } else { BSTEntry xParent; xParent = x.parent; // Find x's parent if ( x == xParent.left ) { /* Link b to the left branch of x's parent */ b.parent = xParent; xParent.left = b; } else { /* Link b to the right branch of x's parent */ b.parent = xParent; xParent.right = b; } } /* ====================================================== Now we can make the REST of the tree (from b down) b / \ a c / \ / \ T0 T1 T2 T3 ======================================================= */ /* ------------------ Make: b / \ a c ------------------ */ b.left = a; a.parent = b; b.right = c; c.parent = b; /* ------------------ Make: b / \ a c / \ T0 T1 ------------------ */ a.left = T0; if ( T0 != null ) T0.parent = a; a.right = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = a; /* ------------------ Make: b / \ a c / \ T2 T3 ------------------ */ c.left = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent= c; c.right= T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent= c; /* ====================================== Recompute the heights of the nodes ====================================== */ recompHeight(a); recompHeight(c); }
- It is now very
straightforward to write
the put()/insert method
for an AVL tree:
public void put(String k, Integer v) { insert (k,v) using the ordinary BST put(k,v) algorithm; (I leave the code out for brevity) /* -------------------------------------------- Recompute the height of all parent nodes... -------------------------------------------- */ recompHeight(p); /* -------------------------------------------------------- Check for height violation starting at insert location -------------------------------------------------------- */ BSTEntry x, y, z; x = y = z = q; // Start search at q (new node) while ( x != null ) // Traverse all the way up to the root node.... { if ( diffHeight(x.left, x.right) <= 1 ) { /* ============================================= No violation --> continue to the next level ============================================= */ z = y; // Go up the tree one level y = x; x = x.parent; } else { break; // Found the first violation } } if ( x != null ) { tri_node_restructure( x, y, z ); // Re-balance the AVL tree } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BSTEntry.java Prog file: click here
- The AVL_BST.java Prog file:
click here
- The test program TestAVL.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestAVL.java
- To run: java TestAVL
- Output of TestAVL: