The Relational Database
- Database:
- A collection of
data that can be
accessed
electronically (through a
computer system
|
- Relational Database:
- A collection of
data that are
organized as a
set of tables
(and can be
accessed
electronically through a
computer system)
- Relational databases are
accessed using
the Structured Query Language,
a.k.a.:
SQL
|
|
The most popular database systems in
2022
- The most popular
database systems today ranked:
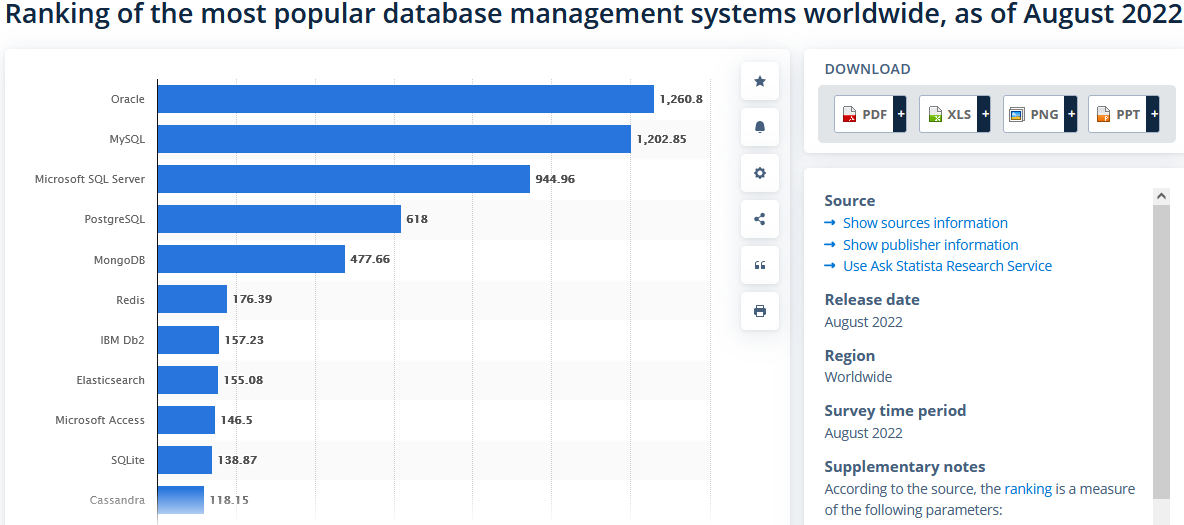
- The most popular
database used
today is the
Relational Database !!
Supporting data:
www.statista.com
|
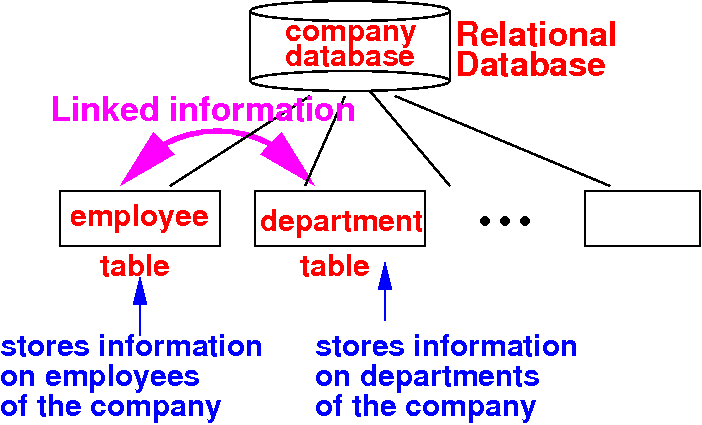
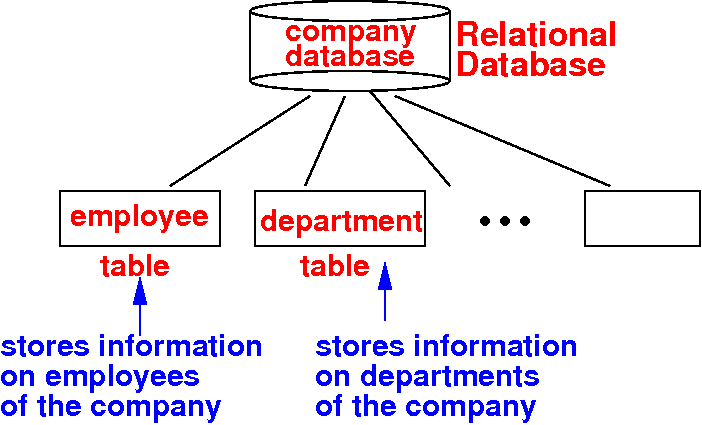
Structure of a relational database
- A relational database consist of
a number of
relations (a.k.a.: tables)
- A table stores
information on
one type of
entity
- Example database on
a company:
|
Relational Database Table (a.k.a. a
relation)
Relational Database Table (a.k.a. a
relation)
Linking information in different tables
though a key
The meaning of the information in a relation
- The meaning of the
data in a
relation must be
described
externally
- Attribute names are
usually chosen to
convey the
meaning
Example:
- fname =
name of the employee
- minit =
middle initial of the employee
- ...
- super_ssn =
the SSN of the
supervisor of the employee
- dno =
the department number of the
department that the employee
is working in.
|
|
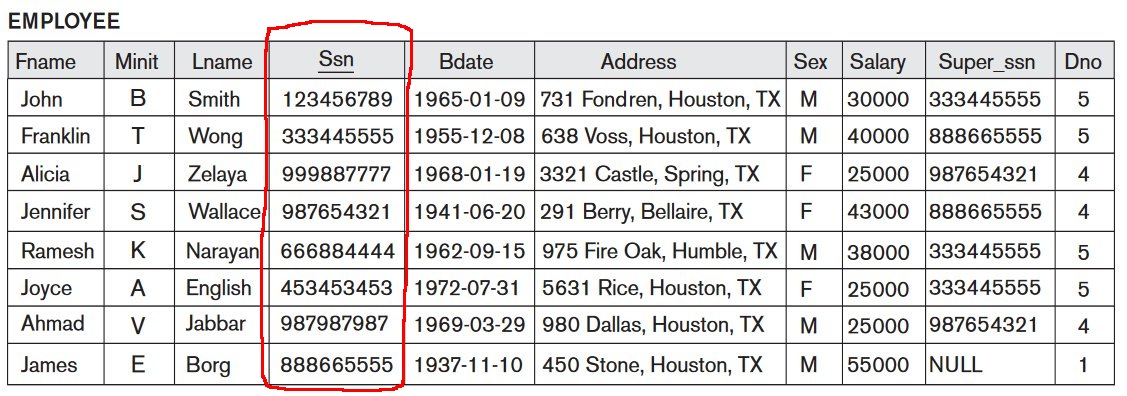
Interpreting the information in a relation
Can you find the
address of
the employee whose SSN
is 123456789 ?
- Employee relation:
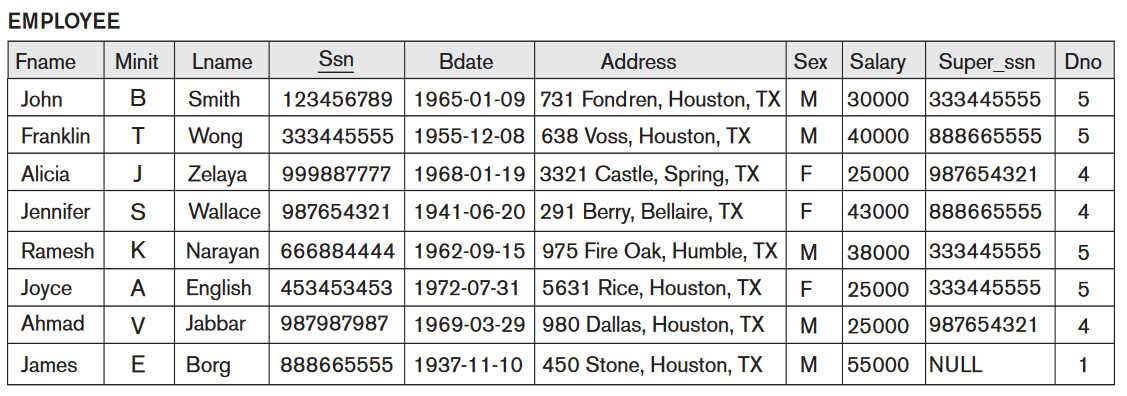
- Answer:
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
Can you find the
address of
the employee whose SSN
is 123456789 ?
- Employee relation:
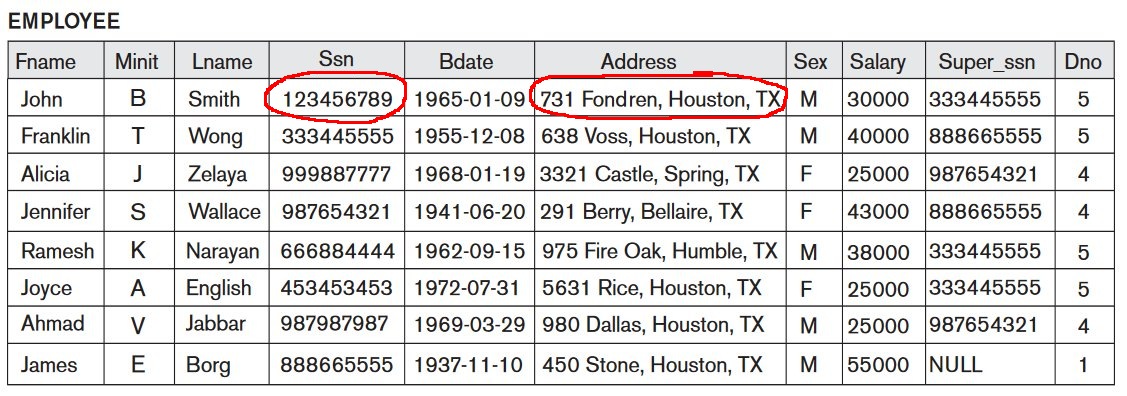
- Answer:
731 Fondren, Houston, TX
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
Can you find the
Birthdate of
the employee Jennifer Wallace ?
- Employee relation:

- Answer:
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
Can you find the
Birthdate of
the employee Jennifer Wallace ?
- Employee relation:
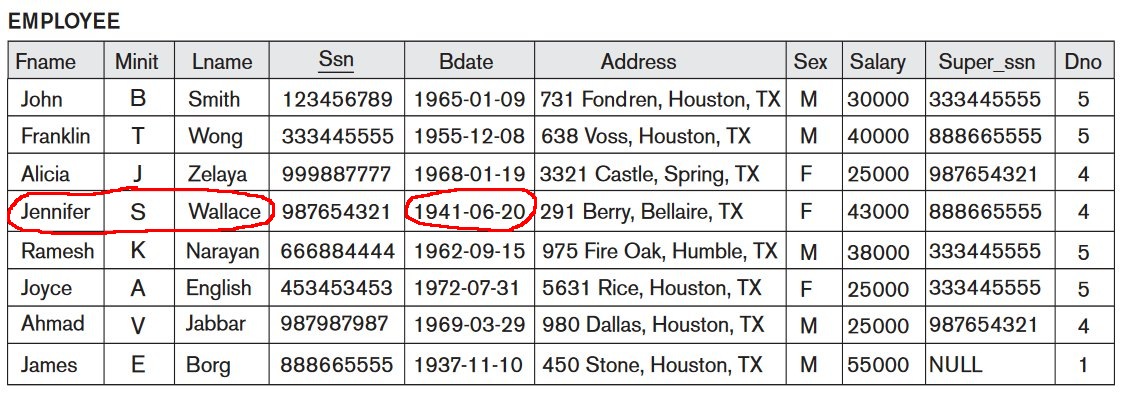
- Answer:
1941-06-20
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
What is the
name of
the supervisor of employee
Jennifer Wallace ?
- Employee relation:

- Answer:
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
What is the
name of
the supervisor of employee
Jennifer Wallace ?
- Employee relation:
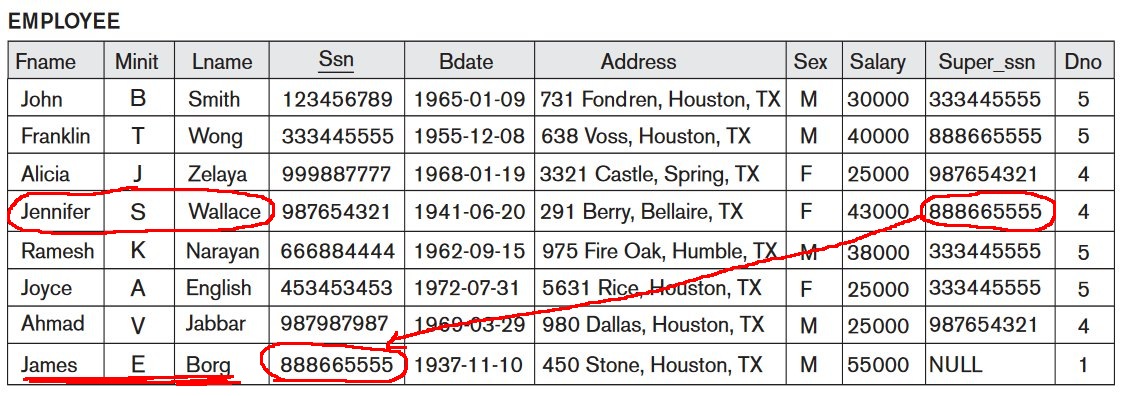
- Answer:
James Borg
(Notice that you have
used a key that
links information)
|
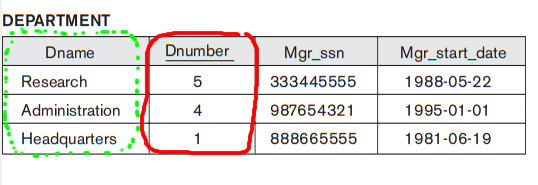
Interpreting the information in a relation
Who work
in the Research department ?
- Employee relation:

- Department relation:
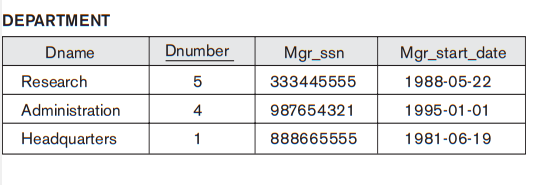
- Answer:
|
Interpreting the information in a relation
Who work
in the Research department ?
- Employee relation:
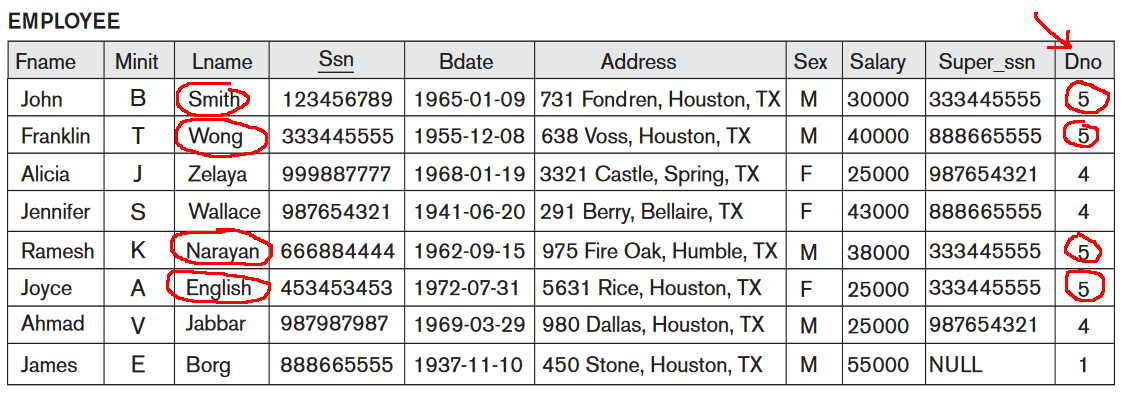
- Department relation:
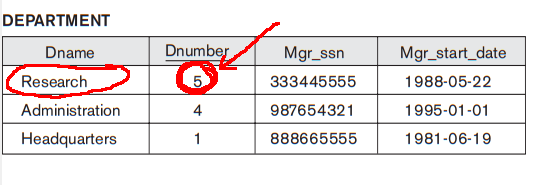
- Answer:
Smith,
Wang,
Narayan and
English
(Information linking !)
|
Database Management System (DBMS)
- Database Management System
(DBMS) =
computer software (program)
that is dedicated to
process
access requests to
a database
- Relational DBMS
(RDBMS) =
computer software (program)
that is dedicated to
process
access requests to
a
relational database
- Popular
RDBMS:
- I am using
MySQL
for this course.
|
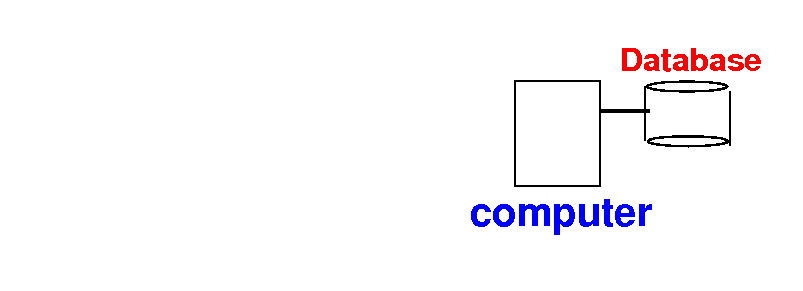
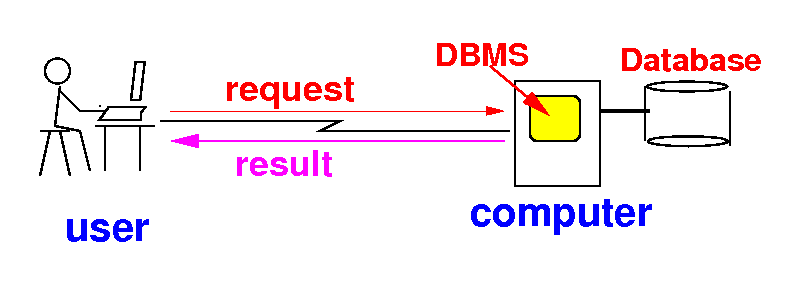
How to access a database
- The database is
stored on
some computer:
|
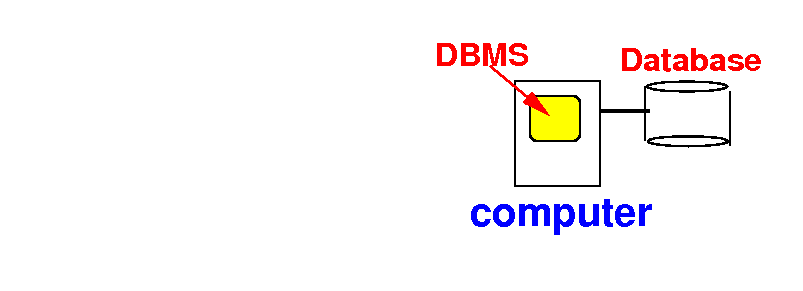
How to access a database
- The DBMS (program) runs
on the computer an
manages the
database:
|
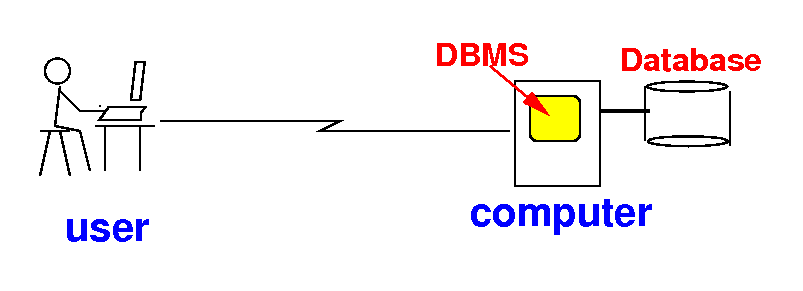
How to access a database
- Users are
connected to the
database system through the
Internet:
|
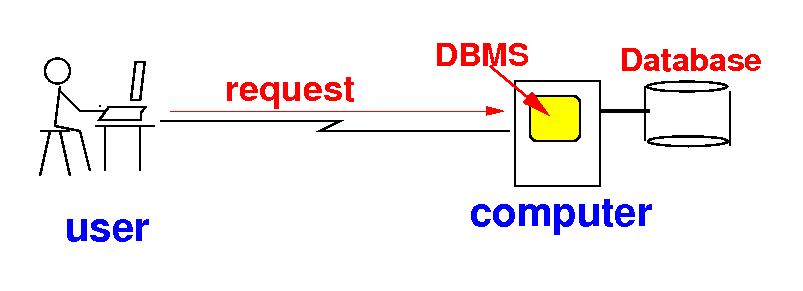
How to access a database
- Users can
send requests
to the DMBS:
|
How to access a database
- The DBMS processes
the request
and
sends the
result back to
the user:
|
How to access a relational database
- A
relational
DBMS is
accessed using
the
SQL
(programming) language:
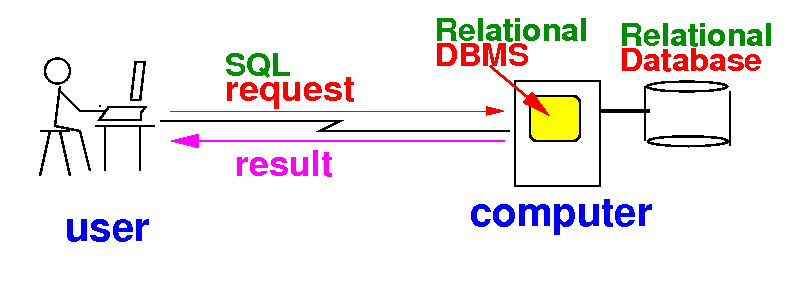
- SQL is
widely used in
the corporate world to
manage
sales,
order and
employee
information !
|
Example: accessing a
relational DBMS
- Open this URL in
your browser:
|
❮
❯