Linking information between
tables
Linking information between
tables
Linking information between
tables using SQL
Sample queries using join
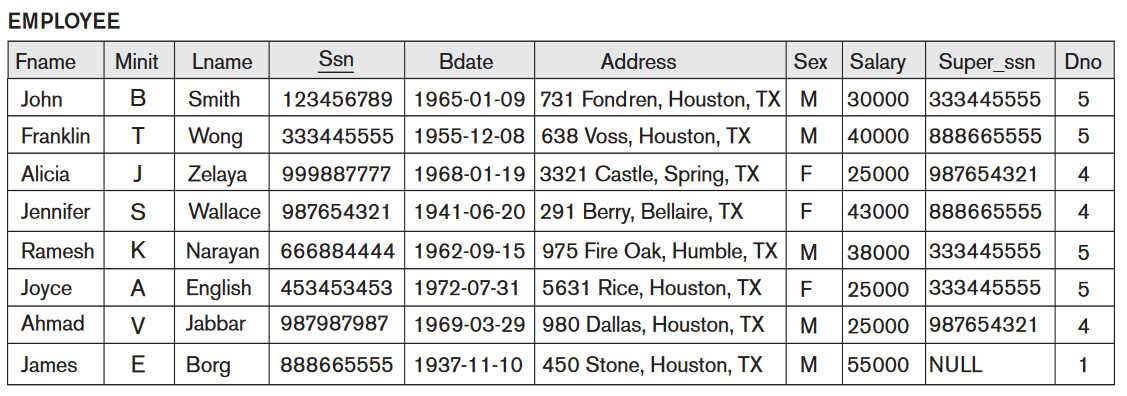
Use the
company database
when formulating the following
queries:
- Find fname, lname of
employees in the
Research department
- Find the name of the department
where John Smith works
- For each employee, list
the fname, lname of the
employee and
the name of all his/her
dependents
- List the names of
the dependents of
the employee
John Smith
|
Ambiguous attribute names
Resolving
ambiguous attribute names
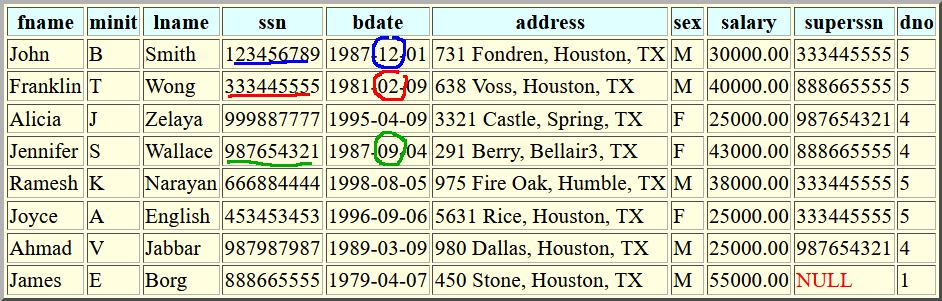
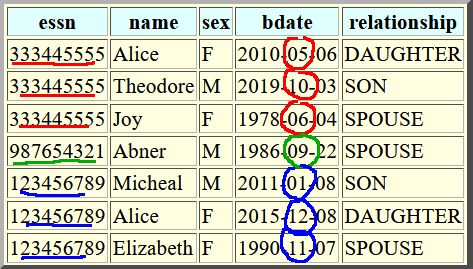
Try this (pretty tough) query
- Find fname, lname of
employees who has
a dependent born
in the same month as
the employee
Employee:
|
Dependent:
|
|
Ambiguous relation names
- Some queries
will require the
use of the same
relation
more than once
- Example:
- List the fname, lname of
all employee
along with the
fname, lname of their
supervisor
(for only employees who has a supervisor)
|
|
Resolving
ambiguous relation names:
aliasing
Resolving
ambiguous relation names:
aliasing
❮
❯