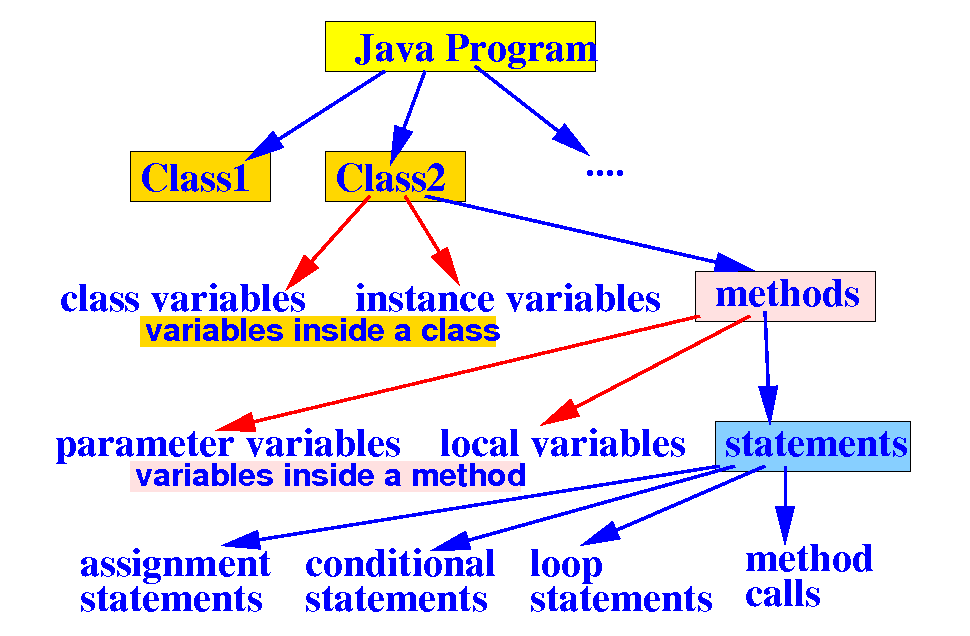
Structure of a Java Program
|
Your first Java program
|
DEMO: 01-basics/02-hello/hello.java (in ~/c/OutSchool/CS/AP-CS/demo/)
How to
define a
class
|
Show the structure of the hello class with slide 1
Adding comments to the codes in your Java program
|
Example comments in a Java program
/* ----------------------------------------------------
This is your first Java program
---------------------------------------------------- */
public class hello // The name of this class is hello
{
// There are no variables defined in the class
/* ------------------------------------------------------
A Java program starts executing with the method "main"
------------------------------------------------------ */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello World"); // Prints "Hello World"
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/01-basics/03-comment/hello.java