Value ranges
of Java
Primitive types and
type conversion
- Value ranges of
Java
primitive
data types:
double: -1.7976931348623157E+308 --- +1.7976931348623157E+308
float: -3.4028235E+38 --- +3.4028235E+38
long: -9223372036854775808 --- 9223372036854775807
int: -2147483648 --- 2147483647
short: -32768 --- 32767
byte: -128 --- 127
double contains all values in float, long, int, short and byte
float contains all values in long, int, short and byte
long contains all values in int, short and byte
int contains all values in short and byte
short contains all values in byte
|
- The computer has
circuitry that
can
convert
a value of
any
primitive
data type to
any other
primitive
data type
|
Problem:
assigning/converting different
data types
Assigning/converting
a value in a
float to
a double:
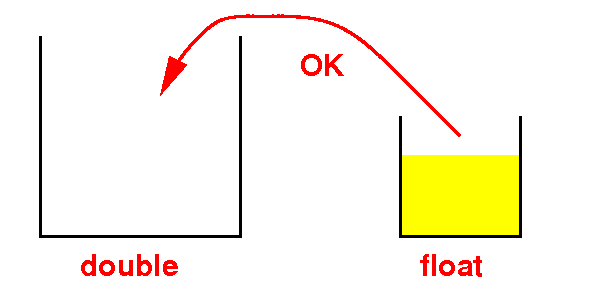
It will always "fit" because double contains all values in float
Therefore:
Assigning/converting a value in a float to a double can never
result in "overflow" error
|
Problem:
assigning/converting different
data types
Assigning/converting
a value in a
double to
a float:
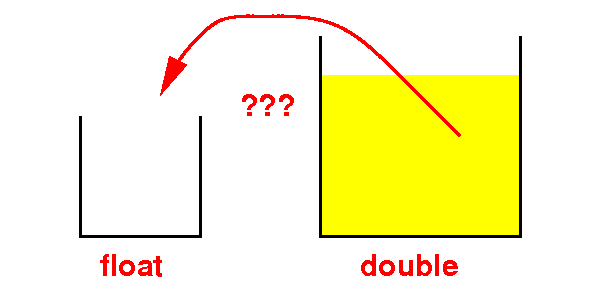
It may result in overflow because some double are not in float !!!
Example:
1.0E300 (10300) is a double value
But this value cannot be stored as a float
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/StoreFloat.java
Programming rule for the
assignment statement
b = a in Java
- The assignment
is
only
allowed if:
- The value range of
data type of b
contains
the value range
of
data type of a
|
Examples:
short a;
int b;
float c;
double d;
d = a; // Allowed
c = b; // Allowed
a = d; // Disallowed
b = c; // Disallowed
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/DemoAssignment.java
Casting:
converting one data type
to another data type
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/Casting.java
Rounding
float and
double to
integers
- When you
assign/convert
a float or
double to an
integer, the
decimal part will be
truncated
Example:
public class FloatToInt
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x;
x = (int) 3.14; // x = 3 (0.14 is truncated)
x = (int) 6.99; // x = 6 (0.99 is truncated)
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/FloatToInt.java
Rounding
float and
double to
integers
- If you want to
round a
float or
double
values
to an
integer,
first
add 0.5
and
then
cast
Example:
public class RoundFloatToInt
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x;
x = (int) (3.14+0.5); // = 3.54, cut off --> x = 3
x = (int) (6.99+0.5); // = 7.49, cut off --> x = 7
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/RoundFloatToInt.java
Background information:
Computer can
only add, subtract, multiple, divide with
same type of values
- Computer circuitry can
only perform
operations on
2 values of
the
same
data type
Examples:
double + double double - double double * double double / double
float + float float - float float * float float / float
long + long long - long long * long long / long
int + int int - int int * int int / int
short + short short - short short * short short / short
byte + byte byte - byte byte * byte byte / byte
|
-
Mixed
data type
operations:
- Java
will
first perform
one or more
convert (=cast)
operation(s) to
make operands into
the
same
data type
- and
then
perform the
operation
|
|
Data type promotion in
Java in
mixed type operations
- When Java performs
an arithmetic operation on
different
data types,
the "smaller"
data type is
converted ("promoted")
to the "larger"
data type
-
Data type
promotion
in arithmetic operations
in
Java when
using different
data types:
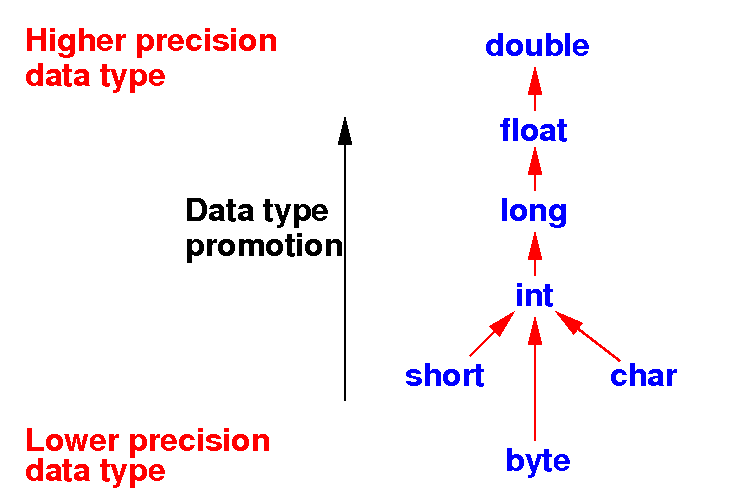
-
Additional rule:
- In Java,
integer operations are
always
performed (= converted) in
int
|
|
Example 1
of data type promotion in
Java
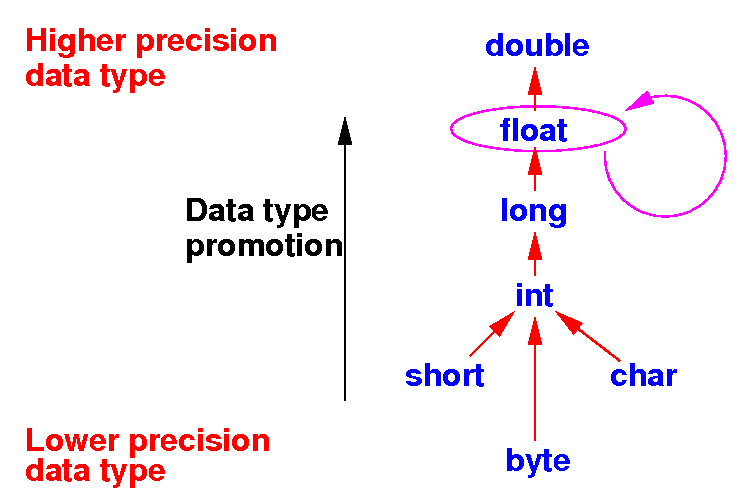
- Example 1:
Evaluate: How Java evaluates a + b
float a; (float) a + (float) b // No promotion necessary
float b;
a + b Result is a float
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/TypePromo1.java
Example 2
of data type promotion in
Java
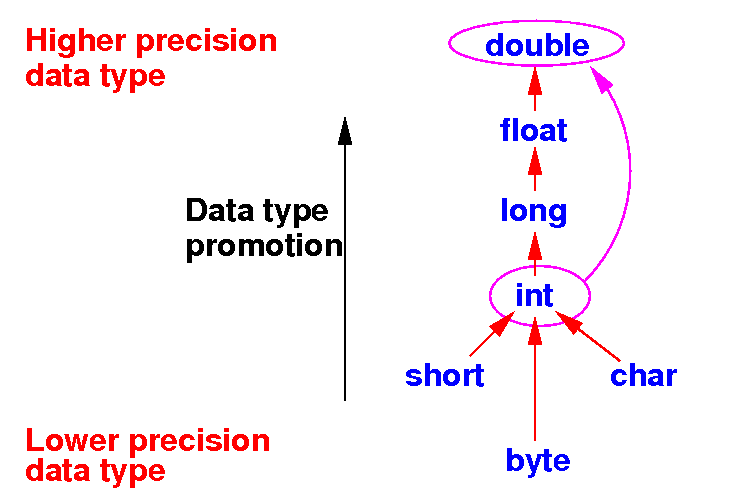
- Example 2:
Evaluate: How Java evaluates a + b
double a; (int) a + (double) b // Promote a to double
int b; (double) a + (double) b
a + b Result is a double
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/TypePromo1.java
Example 3
of data type promotion in
Java
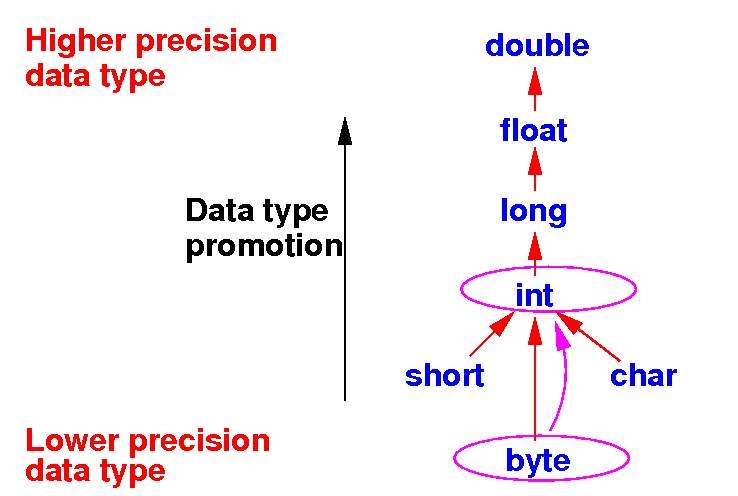
- Example 3:
Evaluate: How Java evaluates a + b
byte a; (byte) a + (byte) b // Promote a and b to int
byte b; (int) a + (int) b
a + b Result is a int
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/TypePromo1.java
Combining assignment with
mixed data type operations
-
Rule:
the assignment:
x = value from a mixed data type operation
|
is
only
allowed if:
- The value range of
data type of x
contains
the value range
of
result of the
mixed data type operation
|
Examples:
byte a = 1;
int b = 2;
float c = 3;
double d = 4;
d = a + c; // Allowed (a + c is a float)
a = a + 1; // Disallowed (a + 1 is an int)
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/AssignMixed.java
Mixed type operation:
---- more practice
- For each of the
assignment statement:
- State if the
assignment statement has
an error
(explain why)
- If no error,
give the
value stored in the
destination
variable
|
Program:
public class Quiz
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double answer1 = 3.0 * 5 / 3;
double answer2 = 3.0 + 5 / 3; // Tricky !
double answer3 = 5.0 / 3 * 3.0;
double answer4 = 5 / 3 * 3.0; // Tricky !
int answer5 = 1 + 2.0 + 3;
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/Quiz.java
Mixed type operation:
Fahrenheit --> Celsius
Google:
Fahrenheit to Celcius (to find conversion formula)
Fix the
error(s)
in the program
below:
public class FtoC
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double F = 70.0;
double C; // Answer should be: 21.11111
C = 5 / 9 * ( F - 32 );
}
}
|
DEMO:
demo/02-elem-prog/07-mixed-datatype/FtoC.java
❮
❯





