public class CascadeAssign
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i, j, k;
// Single line assignment statements
k = 1; // Assigning the same value
j = 1;
i = 1;
// Can be done much quicker like this
i = j = k = 1;
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/02-elem-prog/09-prog-tech/CascadeAssign.java
Write code to exchange the values in the variables a and b:
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
// Code to swap values in a and b
// End result: a = 2, b = 1
}
}
|
Analogy to example the swap programming technique:
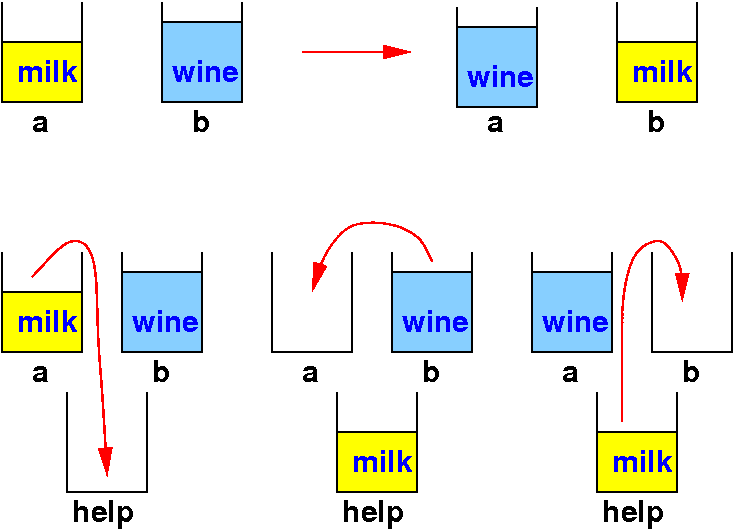
Let's write code using the analogy:
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
// Code to swap values in a and b
// End result: a = 2, b = 1
}
}
|
(1) Define a helper variable (must be of the same data type as the swapping variables)
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
int help; // Helper variable to hold a value
// Code to swap values in a and b
// End result: a = 2, b = 1
}
}
|
(2) Save the value of a in the helper variable:
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
int help; // Helper variable to hold a value
// Code to swap values in a and b
help = a; // Now a is "free"
}
}
|
(3) Save the value of b in the variable a:
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
int help; // Helper variable to hold a value
// Code to swap values in a and b
help = a; // Now a is "free"
a = b; // Perform first half of the swap
}
}
|
(4) Save the value in helper variable help in the variable b:
public class SwapVars
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
int help; // Helper variable to hold a value
// Code to swap values in a and b
help = a; // Now a is "free"
a = b; // Perform first half of the swap
b = help; // Perform second half of the swap
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/02-elem-prog/09-prog-tech/SwapVars.java