|
|
Demo program used in explaining the program control flow in a method invocation:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x, y, z;
x = 3;
y = 7;
z = max(x,y);
}
public static int max(int a, int b)
{
int result;
if ( a > b )
result = a;
else
result = b;
return result;
}
|
DEMO: demo/06-methods/02-method/Max.java
Step in BlueJ --- Show variable content of main( ) while stopped in max( )
Detailed explanation: when a Java program starts, it will call the main( ):

The program starts execution at the first statement in the main( ) method. |
When the program invokes/calls the max( ) method, program control is transfered to the called method max:
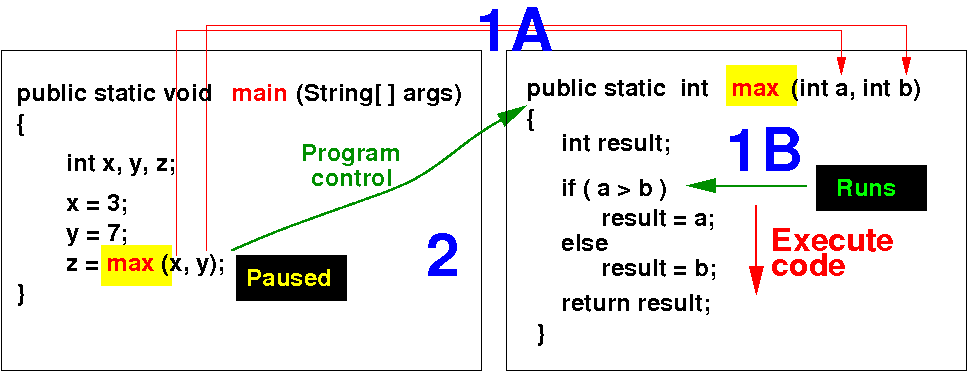
(1A) The method call passes (=copies) the actual parameters to the formal parameters (1B) Program control is transfered to max (2) The method that makes the call is paused at the call statement method |
When the called method executes a return statement, program control is returned to the calling method:
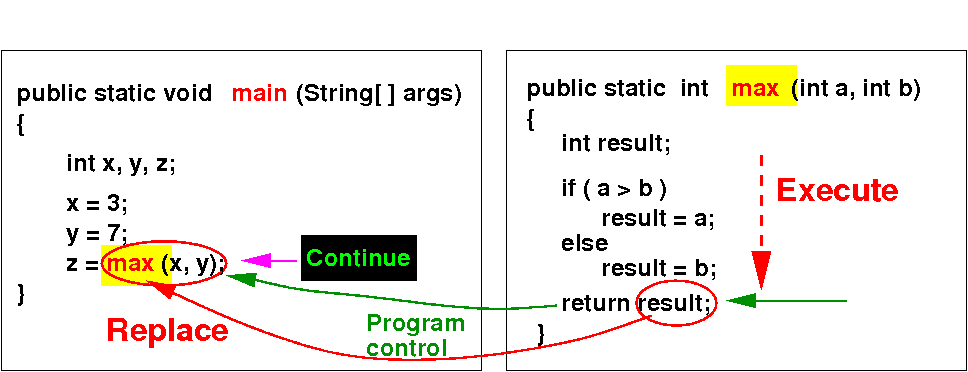
The method call is replaced by the return value
|
Each time a method is invoked, Java creates an activation record that stores parameters and variables:

The activation record is placed in an area of memory known as a call stack. A call stack is also known as an execution stack, runtime stack, or machine stack, and it is often shortened to just "the stack". |
The activation record remains on the stack as long as the method is active (= has not returned):
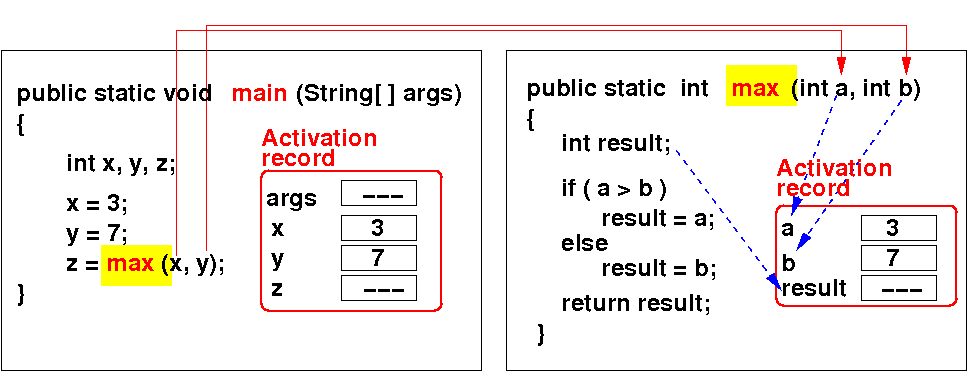
main( ) is active when max( ) is being run ! main( ) also has an activation record ! Show in BlueJ !!! |
The activation record is deleted when a method returns :
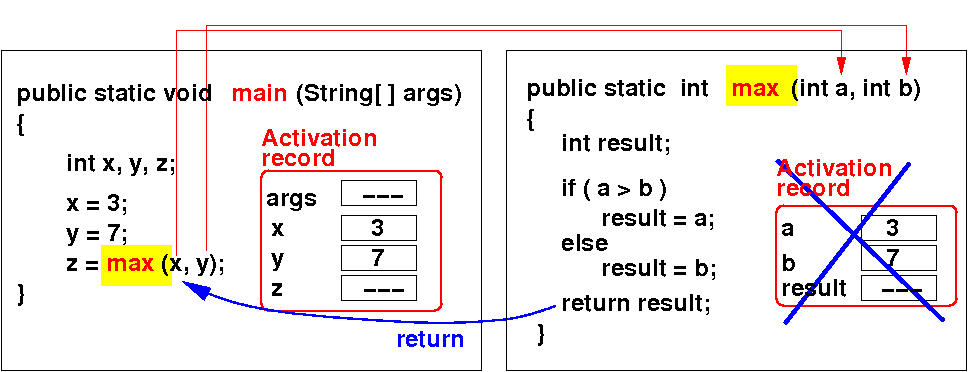
The activation record of max is gone in BlueJ when method returns |