- Recall that:
- A byte is a
memory cell consisting of
8 switches and
can store
a binary number
(See: click here )

- Although the computer stores
binary numbers,
we can interpret then
as decimal number through
a conversion operation:

- The computer can
combine adjacent bytes in
the RAM memory to form
larger memory cells

- Although
a computer memory
can only
store numbers,
we can use an
encoding scheme
to
represent
any kind of information
(E.g.: marital status information: 0 = single, 1 = married, and so on...
gender information: 0 = male, 1 = female) - We must have
context information to
interpret
a number that is stored in
the RAM memory
(E.g., we cannot interpret the number 0 stored in RAM memory unless we know kind of information it is.)
- A byte is a
memory cell consisting of
8 switches and
can store
a binary number
(See: click here )
- A Java computer program
uses variables to
store information
- There are different kinds
(types) of
variables
- In this webnote, we will study the floating point variables
- Variable in Java
- A variable in a
computer program is in fact
a memory cell
A memory cell can store a number
- A variable in a computer program stores a number
- Each variable
in Java has a
data type
The data type allows the computer program to use the appropriate encoding (interpretation) scheme to interpret the number stored in the variable
- A variable in a
computer program is in fact
a memory cell
- Analogy of a variable
- A variable
(in Computer Science) is like
a piece of paper
with a tag attached to it.

- The tag represents the
data type of the variable
(the value of the tag cannot be changed)
- You can only write
one (binary) number on the piece of paper.
- You can erase the number and write a new number on the paper; but you can never write more than one number on the paper at any time.
- A variable
(in Computer Science) is like
a piece of paper
with a tag attached to it.
- A floating point value
(in decimal)
can be expressed using one of the following
form:
- x..x.x..x
- x..x.x..xex..x
where x..x represent a sequence of (decimal) digits
-
Examples:
3.1415 0.31415e1 (= 0.31415×101 = 3.1415) 31.415e-1 (= 31.415×10-1 = 3.1415)
- A double precision
floating point variable is
a variable that:
- uses 8 consecutive bytes of
memory as a single 64 bit memory cell
- uses a modified
binary number system
as encoding scheme
- For more details on the floating point encoding method, please take CS255
- It can hold an floating number of about 16 (decimal) digits accuracy
(I used a double precision floating point variable to avoid explaining casting)
- uses 8 consecutive bytes of
memory as a single 64 bit memory cell
- Every variable in Java
must be defined
-
This rule applies to a
floating point variable.
Also, you must use the correct syntax construct to write a variable definition
-
Syntax to define an
floating point variable:
double NameOfVariable ;Notes:
- The keyword double announces the variable definition clause
- The NameOfVariable is an identifier which is the name of the variable.
- The variable definition clause is must be ended with a semi-colon ";"
- Example:
public class Var01 { public static void main(String[] args) { double x; // Define floating point variable with name "x" System.out.println("Hello Class"); System.out.println(" The variable x contains this number:"); System.out.println(x); // Print variable "x" } }Notes:
- The name of the Java program
is Var01
Therefore, the UNIX filename that contain this Java program must be: Var01.java
- The statement "System.out.println(x);" will print the content of the variable x to the terminal
- The name of the Java program
is Var01
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
If you compile the program, you will get an error:
Var01.java:11: variable x might not have been initialized System.out.println(x); // Print the content in variable "x" ^This is because the variable x does not have a value yet.
- Assignment statement:
- The assignment statement in the Java programming language instructs the computer to update the value stored in a variable
- Syntax of an assignment statement:
VariableName = Value ;
Notes:
- The symbol = is used
to tell the computer to
assign some value to
a variable
The symbol = is called the assignment operator in Java
- The item on left-hand-side of
the = operator is
the receiving variable
- The item on right-hand-side of
the = operator is
the value that
is assigned to the
receiving variable
- The assignment statement must be ended with a semi-colon ";"
- The symbol = is used
to tell the computer to
assign some value to
a variable
- Example:
public class Var02 { public static void main(String[] args) { double x; // Define floating point variable with name "x" x = 0.31415e1; // Assign 3.1415 to x System.out.println("Hello Class"); System.out.println(" The variable x contains this number:"); System.out.println(x); // Print variable "x" } }Notes:
- The name of the Java program
is now Var02
Therefore, the UNIX filename that contain this Java program must be: Var02.java
(I will not make this comment anymore from this point on...)
- The name of the Java program
is now Var02
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Var02.java
- To run: java Var02
Output:
Hello Class The variable x contains this number: 3.1415
- Floating point operators are
arithmetic operators that
manipulate (operate on)
floating point values
- A floating point operator
only operates on
2 floating point values
- The result of an integer operator is always a floating point value
All of the floating point (arithmetic) operators should look familiar to you...
- A floating point operator
only operates on
2 floating point values
- Floating point arithmetic operators:
Operator symbol Operation + addition - subtraction * multiplication / division
- Example:
Result of the integer operation 5.0 + 3.0 is 8.0 Result of the integer operation 5.0 - 3.0 is 2.0 Result of the integer operation 5.0 * 3.0 is 15.0 Result of the integer operation 5.0 / 3.0 is 1.666666666666...
- An Floating point expression is
a (legal) combination of
- Floating point values
- Floating point variables and
- Floating point operators
- Locations in a Java program
where you can define
variables:
- Variables can be defined
inside a method
- Variables can be defined outside any method
Schematically:
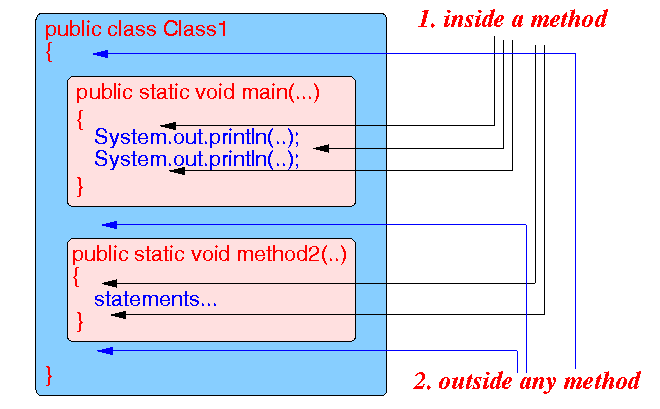
- Variables can be defined
inside a method
- Warning:
- Where you define a variable will affect where you can access the information stored in that variable !!!
- Types of data:
- Each type of data is
given a unique type name
- Different types of data are represented in different ways inside a computer
- Each type of data is
given a unique type name
- Built-in data types
- Every computer has
2 built-in types:
- Integer number type
- Floating point number type
- In other words:
- A computer contain built-in circuitry that can manipulate representations of integer numbers and of floating point numbers
- Every computer has
2 built-in types:
- Examples:
- The integer number 1 is represented inside the computer by the byte (= 8 bits) 00000001
- The integer number 2 is
represented inside the computer by the byte (= 8 bits)
00000010
- The computer also knows how to add, subtract, multiply and divide binary numbers.
- We don't need to learn about how the computer does it in this course. It will be explained in other courses.
- Recall that:
- The smallest memory element in
a computer RAM memory is
a byte
(= 8 bits)
- The computer can combine adjacent bytes (memory cells) and use it as a larger memory cell
- The smallest memory element in
a computer RAM memory is
a byte
(= 8 bits)
- Practically speaking, the integer value 1 can be
represented inside the computer using:
- There is a trade-off between
- Although the computer
can only work with 2 data types
(integers and
floating numbers),
a programming language
can uses
these two data types
to represent
any number of data types
All it takes is a bit of imagination
- The way a programming language
represents a
new data type
is as follows:
- Define a new context
- Define an encoding for the new context
(Context: remember the example of "you is a word" and "you are a student" ?)
- The context information
is called type information
in Computer Science
- Very important facts:
- Every value stored used
inside a program is a
(binary) number
- Every value stored used
inside a program has a
type
- The type information provides the context to interpret the given value
Example:
- We will write the type next
to the value in the examples
- 0 (integer) represents 0 (numeric)
- 1 (integer)
represents 1 (numeric)
- 0 (logical) represents false
- 1 (logical) represents true
- Every value stored used
inside a program is a
(binary) number
- In this course, we will be
studying the programming language named
Java
- It is important to understand
- Every modern programming language provides the
following pre-defined data types
- The names of the
built-in data types as usually:
- int: Integer type
- float: Floating point number type
- char: Alpha-numeric (characters) type
- boolean: Logic value type
- Recall that a
computer can process
2 types of data representations:
- integer numbers
- floating point numbers
- The int data type in a programming language uses the same representation as the integers in
- Example: how a programming language
represent logic information
Logic value Value used to encode the logic value true 1 (integer) false 0 (integer) In other words:
- The computer has the
built-in integer type
- The programming language uses the integer value 1 to represent the
- The computer has the
built-in integer type