- A string is
a sequence of characters
enclosed between the
double quotes "..."
Example:
"abc123" "Hello World" "Hello, what is your name ?"
- Each character in a string is of the type char and uses the Unicode as encoding method
- The String data type is the
first data type that we learn that is
not built-in
into the programming labugae Java
- Primitive data types of
built-in data types of Java:
- double
- float
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- char
- boolean (we will learn this soon)
- The Java language (and most programming languages)
does not provide
the String data type
- However: the Java language does provide the char data type
The String data type is a class that is constructed using the char data type:
- A data type has:
- information
- operations
(Example: the integer data type contains a value (= information) and operations such as: +, -, etc.)
- Implementing the String
data type in Java:
- The information of the String data type is stored using a number of char typed variables
- The operations on String data are implemented by a number of methods (= computer programs)
- The documentation of the class String (you can find a list of the methods) can be found here: click here
- Note:
- At this moment,
we do not have
enough knowledge on
Java to explain
how the String data type
is constructed
(It uses advanced program language knowledge)
- We will learn about this later in the course.
- At this moment,
we do not have
enough knowledge on
Java to explain
how the String data type
is constructed
- For now, we will only learn how to use the String data type
- We write string literals between
double quotes "..." (as discussed above)
Example:
"Hello World"
- Escape character:
- Escape character =
a special character that
allow Java to
change the meaning
of the
next character
- \ (backslash) = the
escape character for
strings
- The escape character is usually used to express "unprintable" characters
- Escape character =
a special character that
allow Java to
change the meaning
of the
next character
- Escape sequence:
- Escape sequence =
the escape character \ followed
by one character
Example:
\n
- A escape sequence
denotes
one character
The character denoted by an escape sequence is usually one that you cannot type in with the keyboard
- Escape sequence =
the escape character \ followed
by one character
- Commonly used escape sequences:
Escape sequence Denoted character Example \t Tab "\t" (string with a TAB character) \n New line (NL) "\n" (string with a NL character) \\ Backslash (\) "\\" (string with a \) \" Double quote (") "\"" (string with a ")
- Example:
public class Escape01 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("He said \t \"Hello\" \nI said \" \\ \" \n"); } }Output:
He said "Hello" I said " \ "
- Syntax to define a
String typed variable:
String NameOfVariable ;Notes:
- The class String announces the variable definition clause
- The NameOfVariable is an identifier which is the name of the variable.
- The variable definition clause is
must be ended with a
semi-colon ";"
- A String typed variable can store the location (address) of a sequence characters (string)
- Example: defining and
using a
String typed variable
public class String01 { public static void main(String[] args) { String a; a = "Hello World"; // a = location of "Hello World" System.out.println(a); // Print the string at a } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String01.java
- To run: java String01
- Challenge to
store strings:
- Strings have
variable lengths !!!
Example:
"Hello" contains 5 characters "Good-bye" contains 8 characters - Conclusion:
- You cannot store a string in a fixed sized variable !!!
- Strings have
variable lengths !!!
- There are 2
techniques
in Computer Science for storing
strings:
- The location + length method
- The location + sentinel method
- The location + length method
- The location + length method:
- The characters of string is
stored
(using Unicode encoding)
somewhere consecutively inside the
RAM memory
- A string variable
contains:
- the location of the first character of the string
- the length of the string (total number of characters in the string)
- The characters of string is
stored
(using Unicode encoding)
somewhere consecutively inside the
RAM memory
- Example: storing strings "abc" and "12" using
location + length

Explanation:
- The string "abc" is
stored beginning at
memory location 984 in
RAM memory
- The length of this
string is 3 characters
- The string variable that
helps us find the
string "abc" contains:
- The address 984
- The length 3
- Another string variable that
helps us find the
string "12" contains:
- The address 520 which is the first location of the string "12"
- The length 2
- The string "abc" is
stored beginning at
memory location 984 in
RAM memory
- Sentinel
- Sentinel =
a special character (symbol)
that denotes the
end of a string
- The sentinel used in programming languages to denote the end of a string is usually the NULL character with Unicode value 0.
- Sentinel =
a special character (symbol)
that denotes the
end of a string
- The location + sentinel method:
- The characters of string is
stored
(using Unicode encoding)
somewhere consecutively inside the
RAM memory
- The sentinel (NULL character)
is added
after the
last character of the string
- A string variable
contains:
- the location of
the first character
of the string
(The end of the string is marked by the sentinel)
- the location of
the first character
of the string
- The characters of string is
stored
(using Unicode encoding)
somewhere consecutively inside the
RAM memory
- Example: storing strings "abc" and "12"
using
location + sentinel

Explanation:
- The string "abc" is
stored beginning at
memory location 984 in
RAM memory
- The sentinel NULL
(with Unicode value 0) is
added after the
string
- The string variable that
helps us find the
string "abc" contains:
- The address 984
(We trace down the memory until we find the sentinel to find the end of the string)
- The address 984
- Another string variable that
helps us find the
string "12" contains:
- The address 520 which is
the first location of the
string "12"
(We trace down the memory until we find the sentinel to find the end of this string)
- The address 520 which is
the first location of the
string "12"
- The string "abc" is
stored beginning at
memory location 984 in
RAM memory
- According to an
article, the
location + length method
is much more efficient
- Article: click here
- String representation in Java:
- Java uses the location + length method to store String typed data
- Obtaining the
length information of strings in Java:
- Let a be
a String typed variable
- The expression a.length() returns the length of the string stored in the string variable a
- Let a be
a String typed variable
- Example:
public class String02 { public static void main(String[] args) { String a; a = "abc"; // a = location + length of "abc" System.out.println(a); // Print the string at a System.out.println(a.length()); // Print the length of the string at a } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String02.java
- To run: java String02
- Numeric string:
- Numeric string =
a string containing
only
numbers in Unicode
that represent digits
- Numeric string uses the Unicode encoding method !
- Numeric string =
a string containing
only
numbers in Unicode
that represent digits
- (Integer) Numbers:
- Numbers uses the binary number system as encoding method !!!
- Important fact:
- Integer numbers and
numeric strings
look
visually alike in
a computer program:
What you see in a Java program What's stored inside computer -------------------------------- ------------------------------------- 12 (integer number) 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001100 (12) "12" (numeric string) 00000000 00110001 00000000 00110010 ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ Unicode for '1' Unicode for '2' - Notice that:
- What is stored
inside the computer
are
complete different
(because they use different representation (encoding) techniques)
- What is stored
inside the computer
are
complete different
- Integer numbers and
numeric strings
look
visually alike in
a computer program:
- Quiz for class:
- Do you still remember how the computer decide what encoding method it must use to interpret a number ?
Answer:
- Based on the
data type information
The data type is the necessary context information that the computer need to decide which encoding method it will use.
- We saw that
the integer 12 is
stored using
Binary number system as
the following
binary number:
000...00001100 || |+--------------> 22 = 4 +---------------> 23 = 8 ----- 12On the other hand, the string "12" is stored using the Unicode scheme as:
00000000 00110001 (code for '1') 00000000 00110010 (code for '2')
Conclusion:
- We need a conversion mechanism to change the representation between numbers and strings
- Converting
an integer representation
to the string representation:
- Converting numbers into
strings is
an advanced programming problem
- The algorithm to convert an integer representation to the string representation will be discussed in CS255
- Here, I will only show you how to do this in Java:
- Converting numbers into
strings is
an advanced programming problem
- How to convert:
int
⇒
String
String a; int x; a = Integer.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the integer value in variable x
- How to convert:
double
⇒
String
String a; double x; a = Double.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the double value in variable x
- Converting:
float
⇒
String
String a; float x; a = Float.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the float value in variable x
- Example:
public class String04 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1, s2; // Strings int x = 12; double y = 3.1415; System.out.print("x + y = "); System.out.println( x + y ); // Add numbers s1 = Integer.toString(x); s2 = Double.toString(y); System.out.print("s1 + s2 = "); System.out.println( s1 + s2 ); // + on String is concatenation } }Output:
x + y = 15.1415 s1 + s2 = 123.1415 (Concatenation of Strings !)
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String04.java
- To run: java String04
- There is only
one operator
(the + operator)
defined for
the String data type:
- string1 + string2 = concatenate the strings string1 and string2
Example:
"abc" + "12" returns the string: "abc12"
- Example Java program with
4 string concatenation operations:
public class String03 { public static void main(String[] args) { String a, b, c; a = "abc"; b = "12"; c = a + b; // String concatenation System.out.println("a = " + a); // String concatenation !! System.out.println("b = " + b); // String concatenation !! System.out.println("c = " + c); // String concatenation !! } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String03.java
- To run: java String03
- Recall that
the integer 12 is
stored using
Binary number system as
the following
binary number:
00001100 || |+--------------> 22 = 4 +---------------> 23 = 8 ----- 12On the other hand, the string "12" is stored using the Unicode scheme as 2 binary numbers:
00110001 (code for '1') 00110010 (code for '2')
- Converting
an integer representation
to the string representation:
- Converting numbers into
strings is
an advanced programming problem
- The algorithm to
convert
an integer representation
to the string representation
will be discussed in
CS255
- Here, I will only show you how to do this in Java:
- Converting numbers into
strings is
an advanced programming problem
- Converting:
int
⇔
String
String s; int x; s = Integer.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the integer value in variable x x = Integer.parseInt(s) ; // Returns the binary number representation // for the numeric string in variable s
- Converting:
double
⇔
String
String s; double x; s = Double.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the double value in variable x x = Double.parseDouble(s) ; // Returns the IEEE 754 double // precision number representation // for the numeric string in variable s
- Converting:
float
⇔
String
String a; float x; s = Float.toString(x) ; // Returns the String representation // for the float value in variable x x = Float.parseFloat(s) ; // Returns the IEEE 754 single // precision number representation // for the numeric string in variable s
- Example:
public class String04 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1, s2; // Strings int x = 12; double y = 3.1415; System.out.print("x + y = "); System.out.println( x + y ); // Add numbers s1 = Integer.toString(x); s2 = Double.toString(y); System.out.print("s1 + s2 = "); System.out.println( s1 + s2 ); // + on String is concatenation } }Output:
x + y = 15.1415 s1 + s2 = 123.1415 (Concatenation of Strings !)
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String04.java
- To run: java String04
- Java provides an
automatic conversion feature
when the
+ operator
is used
between:
- a number typed data and a string typed data
Java's automatic conversion rule for number ⇒ string:
- When the + operator
is used
between
- a number and
- a string
Then:
- the number
is automatically converted
to a string
- The + operator is then applied on 2 strings (i.e., the + operator is a concatenation !)
- Example:
public class String05 { public static void main(String[] args) { String a, b; int x; a = "abc"; x = -12; b = a + x; System.out.println(b); // Prints "abc-12" b = x + a; System.out.println(b); // Prints "-12abc" } }Explanation:
a = "abc"; x = -12; b = a + x; is executed as follows: a + x = "abc" + (-12) convert number to string = "abc" + "-12" concatenate 2 strings = "abc-12" b = x + a; is executed as follows: x + a = (-12) + "abc" convert number to string = "-12" + "abc" concatenate 2 strings = "-12abc"
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String05.java
- To run: java String05
- What is printed
by the following Java program:
public class String06 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println( "a" + 1 + 2 ); System.out.println( 1 + 2 + "a" ); } }Solution:
"a" + 1 + 2 = "a" + 1 + 2 (+ is left associative !) = "a" + "1" + 2 (convert 1 to "1") = "a1" + 2 = "a1" + "2" (convert 2 to "2") = "a12"
1 + 2 + "a" = 1 + 2 + "a" (+ is left associative !) = 3 + "a" (This + is an integer addition !) = "3" + "a" = "3a"
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String06.java
- To run: java String06
- There are
many other operations
defined on the
String data type.
However, these operations are available as instance methods (that we will learn later)
Here, I will just give you a little taste of these operations without explaining the details
- charAt(i): return the
character at
position i in the string.
Example:
01234567890 <---- Character position String s = "Hello World"; char x; x = s.charAt(0); // x = 'H'; x = s.charAt(1); // x = 'e'; x = s.charAt(2); // x = 'l';
- substring(i, j): return the
substring consisting of the
characters between
positions i and j-1
in the string.
Example:
01234567890 <---- Character position String s = "Hello World"; char x; y = s.substring(0,1); // y = "H" y = s.substring(2,4); // y = "ll"
- Jave program showing the effects:
public class String07 { public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "Hello World"; char x; String y; x = s.charAt(0); System.out.println("s.charAt(0) = " + x); x = s.charAt(2); System.out.println("s.charAt(2) = " + x); y = s.substring(0,1); System.out.println("s.substring(0,1) = " + y); y = s.substring(2,4); System.out.println("s.substring(2,4) = " + y); } }Output:
s.charAt(0) = H s.charAt(2) = l s.substring(0,1) = H s.substring(2,4) = ll
- Example Program:
(Run it yourself !)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac String07.java
- To run: java String07
- Previously discussed:
- Procedure to read in a
floating point number from
keyboard:
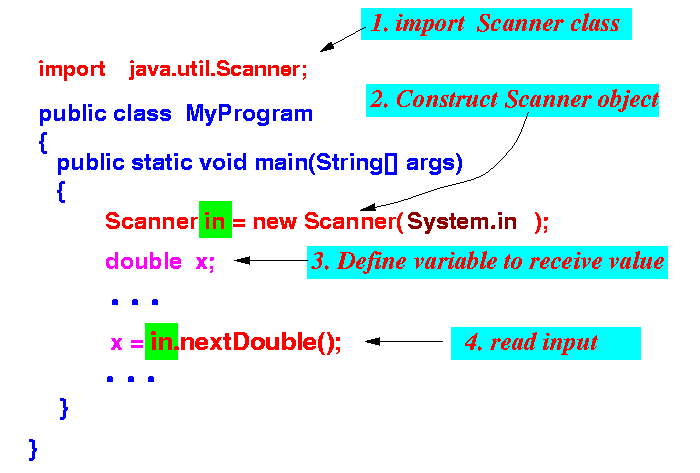
The procedure to read other types of inputs from the keyboard is similar to the one above.
The only different is that we need to use a different method in the Scanner class that read the correct type of data.
- Procedure to read in a
floating point number from
keyboard:
- Reading a string (word)
from the keyboard:
use next()

Note: in this case, you need to use a String typed variable to store a string !!!
- Can you replace
the highlighted statements
by one statement:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Quiz1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int i; String s; s = in.next(); i = Integer.parseInt(); } }What effect does these 2 highlighted statements have ?
What have you learned that does the same thing ?
- Answer:
s = in.next(); // Read in a string i = Integer.parseInt(); // Converts to binary number (integer) // representation Total effect: read in a "integer numeric string" as a binary number Replaced by: i = in.nextInt();