- Consider the following 2 class definitions
ClassA ClassB public class ClassA { public double var1 = 3.14; public void method1() { System.out.println("Hi.."); } }public class ClassB { // Completely empty... }Notice that:
- The class ClassA contains:
- An instance variable var1
- An instance method method1
- The class ClassB contains:
- No instance variables
- No instance methods
- The class ClassA contains:
- Consider the following program that
tries to use
the instance variable
var1 and
the instance method
method1 in
a ClassB object:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassB b = new ClassB(); System.out.println( b.var1 ); b.method1(); } }Because the instance variable var1 and the instance method method1 are not defined inside a ClassB object, the Java compiler will report these "identifier undefined" errors:
> javac Test.java Test.java:7: cannot find symbol symbol : variable var1 location: class ClassB System.out.println( b.var1 ); ^ Test.java:9: cannot find symbol symbol : method method1() location: class ClassB b.method1(); ^ 2 errors
(The Java compiler can not find variable var1 and method method1() inside the object b)
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Test.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassB.java Prog file: click here
How to do the experiment:
- Right click on links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Test.java
- Now,
consider the following 2 class definitions
ClassA ClassB public class ClassA { public double var1 = 3.14; public void method1() { System.out.println("Hi.."); } }public class ClassB extends ClassA { // Completely empty... }Notice that:
- The content of the classes
ClassA and
ClassB are
unchanged
- But, we have
added this clause to
ClassB:
extends ClassAThis clause tells the Java compiler to inherit from ClassB
- The extends ClassA clause tells the Java compiler that we want to build further using the class ClassA as starting point.
- The content of the classes
ClassA and
ClassB are
unchanged
- Let me first
show you the
effect of the
extends clause...
(And explain it later)
- Consider
the following program that
tries to use
the instance variable
var1 and
the instance method
method1 in
a ClassB object:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassB b = new ClassB(); System.out.println( b.var1 ); b.method1(); } }(Recall that ClassB is empty !!!)
The Java compiler will report no errors !!!
- Furthermore, you will get the
following output:
3.14 Hi, I'm method1 in ClassA
Wait a minute... 3.14 ???
Isn't that the value of the variable var1 defined inside ClassA ???And b.method1() prints the same message as the method1() inside ClassA ???
Hmmmm....
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Test.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassA.java Prog file: click here
- The ClassB.java Prog file: click here
How to do the experiment:
- Right click on links and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac Test.java
- To run: java Test
- Inheritance:
- Inherit =
receive something from
someone else by
succession
(Well, in a Java program, nothing has to die to inherit :-))
- Inheritance in
a class =
to receive the
instance variables and
instance methods
from a "parent" class
(The inheritance mechanism is not applicable to class (i.e., static) variables and methods).
- Inherit =
receive something from
someone else by
succession
- The extends clause:
inheritance mechanism in Java
- The syntax of the
extends clause
is as follows:
public class ClassB extends ClassA { *** Nothing changed inside the method *** It will contain variables and method definitions }
- The effect of the
extends ClassA clause
to inherit
the instance variables and
instance methods
from the
class ClassA:
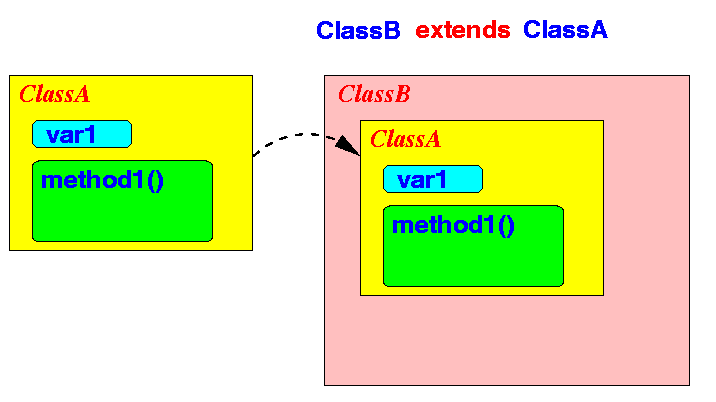
- The syntax of the
extends clause
is as follows:
- Purpose:
- The inheritance mechanism is
let the programmer
re-use some
existing program (= class)
for a
new programming project.
- Instead of writing a class
from scratch
(= starting with an empty class
with no variables and methods),
he can start with
some existing program (= class)
- Note:
- The inheritance mechanism
will only be applicable
if the programmer can
find a suitable class
that contains
methods that he
can re-use in his new project.
- If he cannot find a suitable class, then inheritance will not be helpful to his project.
- The inheritance mechanism
will only be applicable
if the programmer can
find a suitable class
that contains
methods that he
can re-use in his new project.
- The inheritance mechanism is
let the programmer
re-use some
existing program (= class)
for a
new programming project.
- Terminology:
- When a class ClassB
inherits from a class
ClassA:

We call:
- ClassA is the base class
- ClassB is the derived class
- Other terminologies that are
commonly used are:
- ClassA is the parent class
- ClassB is the child class
and:
- ClassA is the super class
- ClassB is the sub class
Summary:

Note:
- The terms are
coupled.
- You cannot say:
- ClassA is the base class and ClassB is the child class....
- You must used the coupled term:
- ClassA is the base class and ClassB is the derived class.
- When a class ClassB
inherits from a class
ClassA:
- The inheritance mechanism is
not useful
to inherit
class variables (and
class methods) because:
- There is only one copy of
a class variable
- When ClassB inherits
a static (class) variable x
from the parent class
ClassA, then:
ClassB.x will refer to the variable ClassA.xIn other words: we made an alias (aliases should be avoided if possible; can make debugging programs very difficult !)
- There is only one copy of
a class variable
- Example:
public class ClassA { public static double var1 = 3.14; public static void method1() { System.out.println("Hi, I'm the STATIC method1 in ClassA"); } } public class ClassB extends ClassA { // Completely empty... }
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { ClassB.var1 = 777; System.out.println( ClassA.var1 ); // Prints 777.0 } }The output is:
777.0
So: ClassB.var1 and ClassA.var1 are different names for the same variable (alias !)