Physical organization of a computer
- What a
computer
looks like
physically:
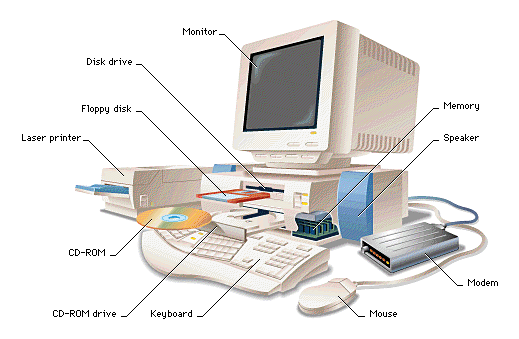
|
Logical (functional)
organization of a computer
- What a
computer
looks like
logically (= functionally):
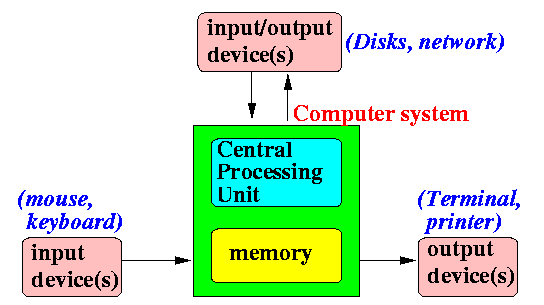
|
Components of a computer
A computer consists of
4 types of
components:
- Central Processing Unit
(= CPU) = "brain" of
a computer
- Main memory
(= RAM) = storage space of
a computer
- Input devices =
devices used to
receive data into the computer
- Output devices =
devices used to
output data from the computer

|
We take a closer look at the
computer (main) memory component
next
Computer memory
(a.k.a.: Random Access Memory or RAM)
- The main memory
or RAM consists of
many
memory cells:

- Each
memory cell
is uniquely
identified
by a
memory address
(which is an
integer number)
-
Note:
memory addresses always
starts at
the number zero (0)
|
- Each
memory cell
can store a
small number
|
Analogy to help you
understand a computer memory
- The main memory
or RAM is
similar to
a collection of
mail boxes:

- Each
mail box
is uniquely
identified
by an integer
mail box number
-
Imagine that:
each mail box contains
a (small) slip of paper !!
|
- Each
memory cell's
slip of paper
can store a
small number
|
Operations
that a computer can perform on the main memory
- The computer can perform
2 operations
on
the main memory:
-
Write
operation: the computer
stores
a number
into
one or more
memory cells
at a specific
memory address
-
Read
operation: the computer
retrieves
the number
from
one or more
memory cells
at a specific
memory address
|

|
Analogy to help you understand the
write and
read operations to a computer memory
- The
write operation
and
the
read operation to
the computer memory is
similar to the
store
and
recall
operations
of a
calculator:

|
How does the computer store information using
just numbers ?
How can a computer tell the meaning of
a number ?
Problem description:
How can a computer tell the meaning of
a number ?
Answer to the
representation conundrum:
- The
meaning of
a
code
(like the number 0)
can only be determined when
the
context is
known/given:
- When the computer is
examining some
marital status
data,
the number 0 means:
single
- When the computer is
executing
a computer instruction,
the number 0 means:
the add instruction
|
- Analogy to
help you understand
the concept of
context:
- Make a correct
English sentence that begins with:
You is ....
|
|
The context of the word
You
- When you use the word
You as
a
personal pronoun
(which is the common case), you
must use
You are ...
Example:
- You can
use the word
You as
a
noun !
Example:
|
❮
❯




