- Recall that defining
an array in Java is
a two step process:
Java: 1. Define an array object variable: Example: double[] a; 2. Create the array: Example: a = new double[10];
- Array in C:
- In contrast, defining an array in C is a one step process ------ just like defining ordinary variable !!!
- Syntax to define an
one dimensional array
in C:
DataType varName [ constantSize ] ;
- Example:
double a[10]; // Define an array of 10 variables of type double int b[20]; // Define an array of 20 variables of type int
- This is what will happen inside the computer when
you define an array in C:
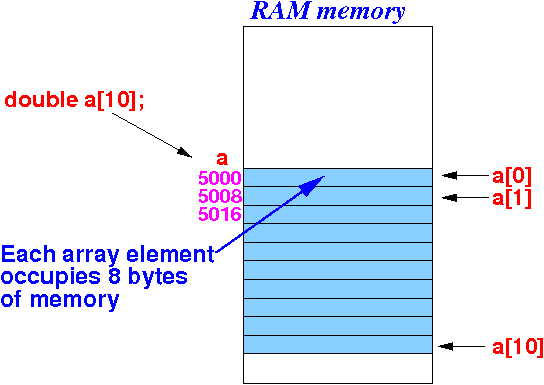
Explanation:
- The computer will reserve
memory cell to store the elements of the
array
- The computer will remember that the
identifier a
is associated with the
first allocated memory cell
of the array
- In the example, the computer will remember that a is located starting at memory location 5000.
- The computer will reserve
memory cell to store the elements of the
array
- Example:
int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) { double a[10]; int i; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) a[i] = i; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf( "a[%d] = %lf\n", i, a[i] ); }Output:
a[0] = 0.000000 a[1] = 1.000000 a[2] = 2.000000 a[3] = 3.000000 a[4] = 4.000000 a[5] = 5.000000 a[6] = 6.000000 a[7] = 7.000000 a[8] = 8.000000 a[9] = 9.000000
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc array1.c
- To run: ./a.out
- In general:
- There are 2 kinds of
arrays that programming languages can provide:
- Static arrays
- The size (number of elements)
associated with the
name of the array variable
cannot be changed
in
static arrays
(After an array is created, the size of the array cannot be changed)
- The size (number of elements)
associated with the
name of the array variable
cannot be changed
in
static arrays
- Dynamic arrays
- The size (number of elements)
associated with the
name of the array variable
can be changed
in
dynamic arrays
(After an array is created, the size of the array can be changed - the array size can grow or shrink)
- The size (number of elements)
associated with the
name of the array variable
can be changed
in
dynamic arrays
- Static arrays
- There are 2 kinds of
arrays that programming languages can provide:
- Static array:
- Static arrays are implemented
using
an (array)
identifier
- The name of the array marks the staring location of the array in memory.
- The array identifier (= name) is
directly associated with the
starting location of the array
as depicted in the following figure:

Explanation:
- When you define an array with
double a[10] ;the compiler will:
- first allocate
memory cells for the array element (say starting at
memory address 5000)
and
- make the symbolic name a equal to the value 5000
- first allocate
memory cells for the array element (say starting at
memory address 5000)
and
- When you define an array with
- When more variables are
created, the static array
will be boxed in
by reserved memory cells
and have no way to expand:

- Static arrays are implemented
using
an (array)
identifier
- Since C's arrays are
static arrays,
you can conclude that:
- The name of an array in C is equal to the starting address of the array
- Proof:
int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) { double a[10]; printf(" a = %u\n", a); // Print array name printf(" &a[0] = %u\n", &a[0]); // Print address of first elem. }Output:
a = 4290768640 &a[0] = 4290768640 (EQUAL !)
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc array-name1.c
- To run: ./a.out
- Dynamic array: (Java !)
- Dynamic arrays are implemented
using
an array object
reference variable
- You first define the
array object reference variable:

- The identifier is
associated with the
array object reference variable !!
- Then in the second step,
you create (allocate space) the
actual array and
store its location
in the
array object reference variable:

- You can expand a
dynamic array by
allocating space else where
in the memory and
make the object reference variable
point to
the new array:

(Remember, you may not be able to expand the old array because it could be boxed in by reserved memory cells.
But you can always try to find a bigger chuck of unreserve memory elsewhere !)
- Dynamic arrays are implemented
using
an array object
reference variable
- Dynamic arrays: (Java !)
- Advantage:
flexibility
- Disadvantage:
slow
- To access an array element
a[i]
(assuming you already know
the index i),
you need
at least 2 memory accesses:
- One memory access to read the
array object reference variable
- A second memory access to access the array element itself
- One memory access to read the
array object reference variable
- To access an array element
a[i]
(assuming you already know
the index i),
you need
at least 2 memory accesses:
- Advantage:
flexibility
- Static arrays: (Most programming languages)
- Advantage:
speed
- To access an array element a[i] (assuming you already know the index i), you only need 1 memory access
- Disadvantage:
inflexible
- You cannot change the size of the (static) array after you have created the array.
- Advantage:
speed
- Fact:
- The more information you maintain on a thing, the more services/capabilities you can provide with that thing.
- Information maintained
on arrays:
- Location (address) of the array in memory
- Number of elements in the array
- Location (address) of the array in memory
Java C
- Consequence:
- Using the length (= number of elements)
information,
the Java compiler can
detect
if the array index is
out of bound
(= too large)
- Because C does not keep any information on the length (= number of elements) of an array, the C compiler cannot detect if an array index is out of bound !!!
- Using the length (= number of elements)
information,
the Java compiler can
detect
if the array index is
out of bound
(= too large)
- Example: Java detects
array index out of bound error
public class array2 { public static void main( String[] args ) { double[] a = new double[10]; int i; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) a[i] = i; for ( i = 0; i < 30; i++ ) System.out.println( "a[" + i + "] = " + a[i] ); } }Result:
a[0] = 0.0 a[1] = 1.0 a[2] = 2.0 a[3] = 3.0 a[4] = 4.0 a[5] = 5.0 a[6] = 6.0 a[7] = 7.0 a[8] = 8.0 a[9] = 9.0 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10 at array2.main(array2.java:14)
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac array2.java
- To run: java array2
- Example: C
cannot detect
array index out of bound error
(insuffience information)
int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) { double a[10]; int i; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) a[i] = i; for ( i = 0; i < 30; i++ ) printf( "a[%d] = %lf\n", i, a[i] ); }Sample output:
a[0] = 0.000000 a[1] = 1.000000 a[2] = 2.000000 a[3] = 3.000000 a[4] = 4.000000 a[5] = 5.000000 a[6] = 6.000000 a[7] = 7.000000 a[8] = 8.000000 a[9] = 9.000000 a[10] = 0.000000 a[11] = 0.000000 a[12] = 0.000000 ... a[22] = -2243494719485605301116825811.... ...
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc array2.c
- To run: ./a.out
- The reason that Java can
detect an
index out of bound error is because:
- Each time a Java program uses an array variable, the Java run time system performs an index out of bound check
These index out of bound checks takes up CPU cycles (uses the CPU)
- That is why:
- C programs are more efficient than Java program (i.e., faster) because C programs not not perform array bound checks at run time
We say that:
- C programs incur less run time overhead....