- Fact:
- The C programming language does not have dynamic array as a language feature
However:
- The C programming language does have sufficient number of powerful features that a C programmer can implement dynamic array (among other things) using these features !!!
- Features in C that
enable you to
implement your own
dynamic array:
- Memory management functions:
malloc( ) (we will use calloc() for arrays) free( )
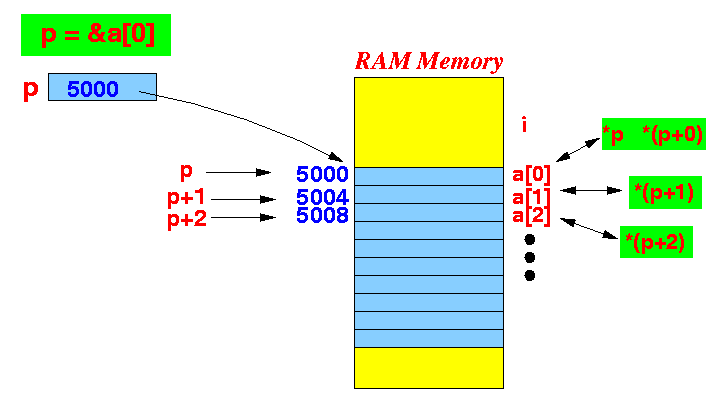
- Pointer arithmetic:
if p points to a[0] then *(p + i) is an alias for a[i]Graphically illustrated:
- Memory management functions:
- Steps to
create a
dynamic array
(of any data type):
- Define a
reference variable
(say p)
of the desired data type
Example: suppose we want to create a dynamic array of double variables
double* p; // reference variable to a double variable
Illustrated:

- Allocate memory cells for
the array elements and
make p
point to the
first array element:

- The array elements
can now be accessed as:
*(p+0) first array element *(p+1) second array element *(p+2) third array element ... *(p+i) ith array element
- Define a
reference variable
(say p)
of the desired data type
- Fact:
- Each computer system has its own
peculiar
memory alignment requirements
- The malloc() function
only alocate memory cells
for one variable:
- malloc(nBytes) will allocates a block of memory cells of at least nBytes bytes that us suitably aligned for any usage.
- Each computer system has its own
peculiar
memory alignment requirements
- To allocate memory cells
for N consecutive variable
(= array),
you must use this function:
calloc( nElems, nBytes ) Example: calloc( 10, 8 ) // Allocate space for 10 elements of size 8 (= array of 10 double)The calloc function:
- The calloc()
function allocates space
for an array
of
nElems
elements
of
size nBytes.
Note:
- The allocated space will alos be initialized to zeros.
- The calloc()
function allocates space
for an array
of
nElems
elements
of
size nBytes.
- We have now learn everything
we will need to
build our own
dynamic array
in C
- C program that illustrates a
dynamic array of
double variables:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; double* p; // We uses this reference variable to access // dynamically created array elements p = calloc(10, sizeof(double) ); // Make double array of 10 elements for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) *(p + i) = i; // put value i in array element i for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("*(p + %d) = %lf\n", i, *(p+i) ); free(p); // Un-reserve the first array putchar('\n'); p = calloc(4, sizeof(double) ); // Make a NEW double array of 4 elements // ***** Notice that the array size has CHANGED !!! **** for ( i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) *(p + i) = i*i; // put value i*i in array element i for ( i = 0; i < 4; i++ ) printf("*(p + %d) = %lf\n", i, *(p+i) ); free(p); // Un-reserve the second array }Output:
*(p + 0) = 0.000000 *(p + 1) = 1.000000 *(p + 2) = 2.000000 *(p + 3) = 3.000000 *(p + 4) = 4.000000 *(p + 5) = 5.000000 *(p + 6) = 6.000000 *(p + 7) = 7.000000 *(p + 8) = 8.000000 *(p + 9) = 9.000000 *(p + 0) = 0.000000 *(p + 1) = 1.000000 *(p + 2) = 4.000000 *(p + 3) = 9.000000
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc dyn-array1.c
- To run: ./a.out