- When mobile host roam (travel),
it will cross the coverage area
of different APs:
- When a node changes
coverage, it must
contact the new AP to
exchange vital information
Example:
- The PN code for the CDMA transmission scheme
- IEEE 802.11 defines
rules (protocol)
that enable a nomadic host to
change APs.
- There are 2 protocols defined:
- Active Scanning
- Passive Scanning
- In active scanning,
the nomadic node
takes the
inititive in searching for APs
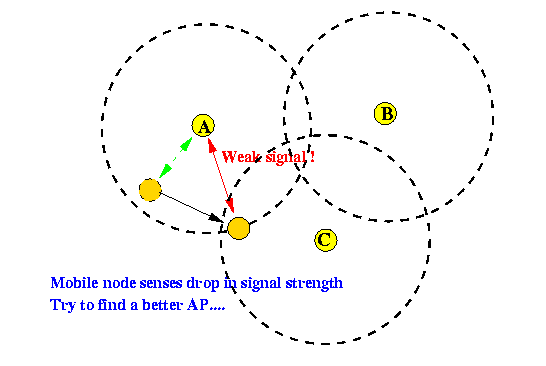
- The search for a suitable AP
is usually triggered by
a drop
in signal strength
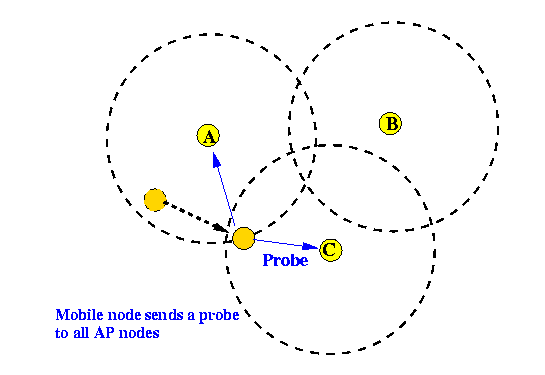
- A node that detects that the
signal level
drop below a certain level
broadcasts a
probe message
to all AP nodes
(a special "All AP" address identifier is reserved):
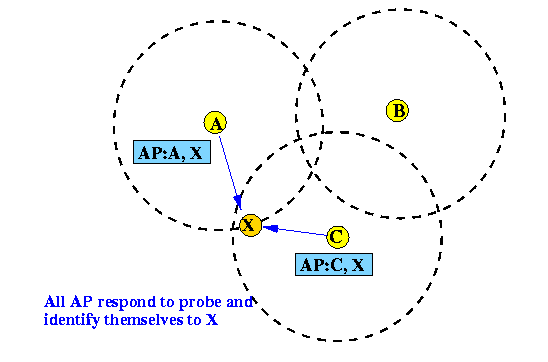
- When an AP receives the probe, it transmits a response to the requester to identify itself:
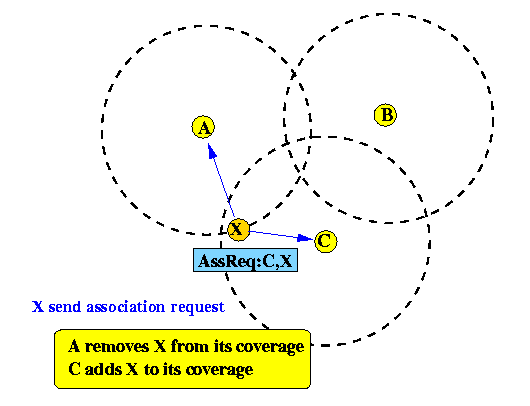
- The requester node associates itself with the AP whose signal strength is the highest by sending an Association Request:
- When an AP receives the probe, it transmits a response to the requester to identify itself:
- In passive scanning,
the nomadic node
(passively) scans
for capacity reports
transmitted by APs
In this mode, each AP periodically broadcasts a capacity report message to enable nomadic node to "find the best AP":
- When a node finds a
better AP,
it will transmit the
Association Request message:

- Associations with AP has an
expiration time
- If a node is not heard of for longer than the expiration time, the AP will remove the node