- Another way to share a broadcast medium:
- regulated transmissions...
- The use (= transmission)
of the LAN is
regulated
by well-defined rules.
Because nodes do not content (compete) for access, this type protocol are called "contention-free".
- regulated transmissions...
- Right to use (= transmit):
- The right to use
is conveyed in a
special messages
from one node
to another
- The right is
passed
in a round robin manner
(for fairness reasons).
- The special message is called a token
- The right to use
is conveyed in a
special messages
from one node
to another
- There are 2 types of
contention-free MAC protocols:
- Token ring (IEEE 802.5)
- Token bus (IEEE 802.4)
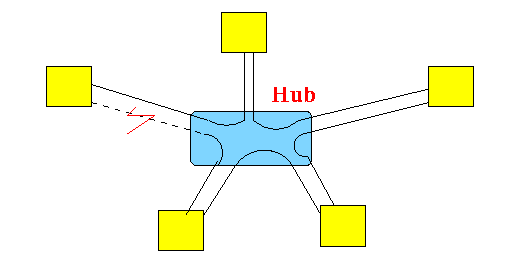
- Architecture:
- Computers are organized into a
physical ring:
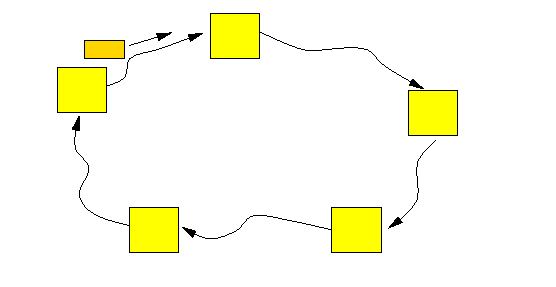
- Messages
are circulated through the
ring network:
- Computers are organized into a
physical ring:
- Preliminaries:
- The "token"
is nothing more
than a bit
in the
message header
When this special bit is set (= 1), the message is a token.
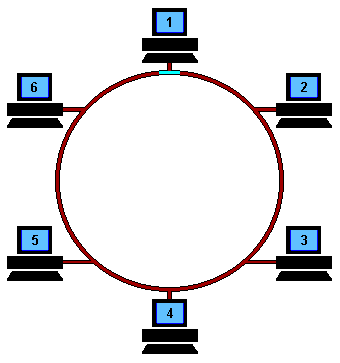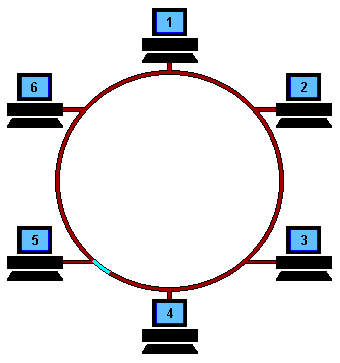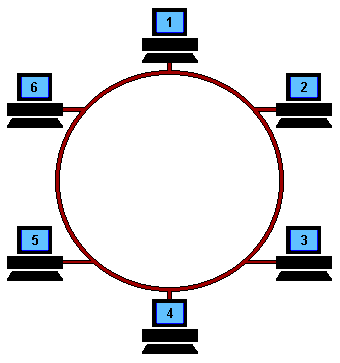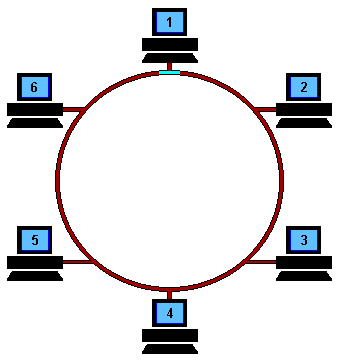
- The node that has
received a
token message is
called the
token holder
- The token holder
is permitted to transmit
only one message
- A transmitted messages
will circulated through the entire ring
and returned back to
the sender
- The "token"
is nothing more
than a bit
in the
message header
- Reliability protocol in IEEE 802.5 token ring:
- The header of the message
also has an
ACK bit
- Initially, the
ACK bit is
reset (0)
When the intended destination received the message, it sets (= 1) the ACK bit
- When the message returns to the sender, it can detect whether the message was received
- The header of the message
also has an
ACK bit
- The Token ring protocol:
- Graphically:
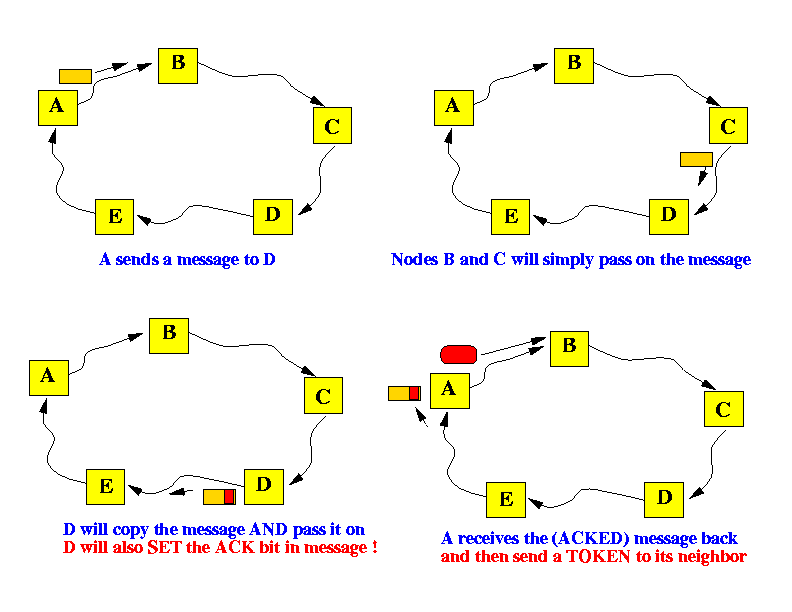
- When a node has a messages to send, it waits for the token.
- The node removes the token from the ring - this way,
other nodes in the network will not start a transmission.
(Easy: the node simply do not forward the token further)
- When the node receives the token, it transmits the messages.
- The nodes waits for the message to return
back !!
- After the messages returns, the node "issues" a new token on the ring.
- When a node has a messages to send, it waits for the token.
- Graphically:
- Weaknesses:
- Poor performance
in lightly loaded situation:
- When most nodes are idle, the token will circulate by many nodes "in vain"
- Addition and
deletion of
nodes (computers)
from the token ring
is very labor intensive
- Cable breakage
will cause the
entire network to fail...
(Because the ring is severed....)

NOTE:
- Locating the section of the cable that had the disruption is not easy...
- Poor performance
in lightly loaded situation:
- Strengths:
- Good performance
in highly loaded situation
- Built-in
ACK scheme
(Since the packet has to come back to the sender before the sender can release the token, the message frame might as well take on the role of an ACK frame...)
- Good performance
in highly loaded situation
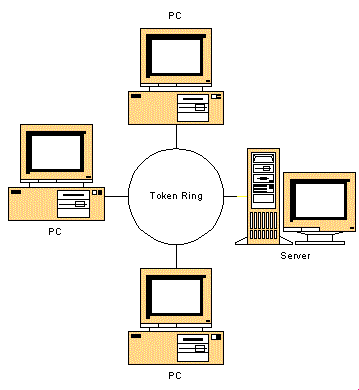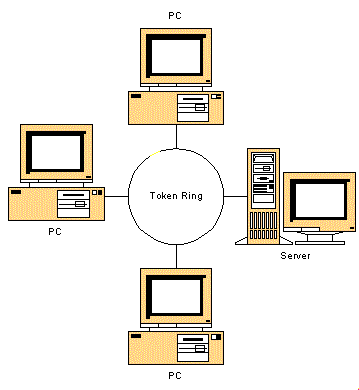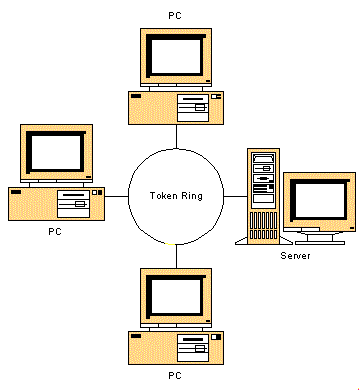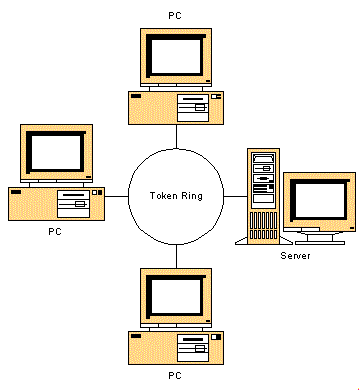
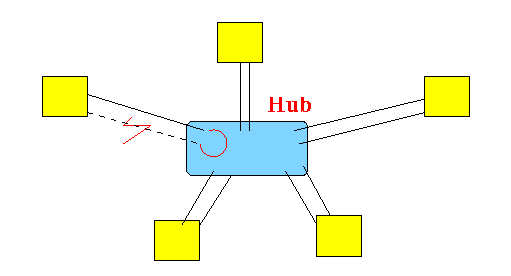
- The star-shaped ring
topology was proposed to
overcome the
cable failure problem:
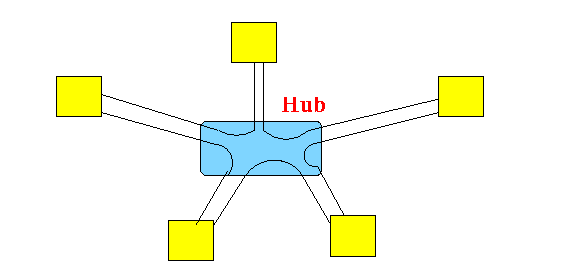
The actual shape of the hub or concentrator is a box:
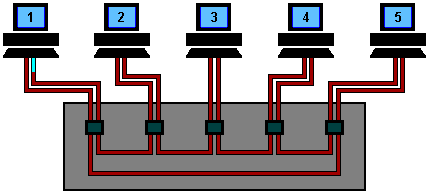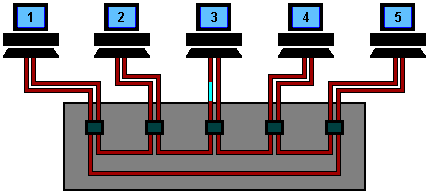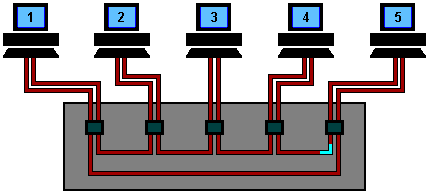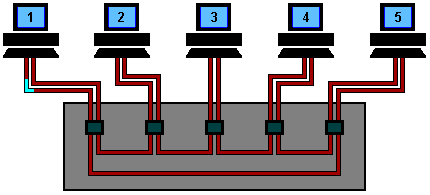
The connection forms a physical ring !!!
- Suppose a section of the
Token Ring
was disrupted:
Locating the cable disruption is now relatively easy:
- Just find the 2 end points that
does not
for a closed loop:
Fixing the token ring is also relatively easy:
- Omit
the disconnected segment:
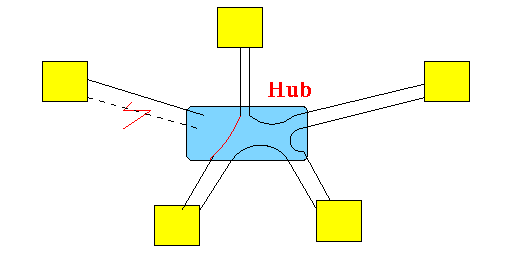
- Just find the 2 end points that
does not
for a closed loop: