- A queueing system consists of:
- An arrival process of
client into a
holding area (queue)
Clients come (enter in) to the queueing system to obtain a certain service
- A queue management process
that organizes the
clients in the queue
The most commonly used queue management processes: FIFO
- A service process that
fullfills the service requests
of clients
After obtaining the service from the server, a client will leave the queueing system
We call this process the departure process
Schematically:
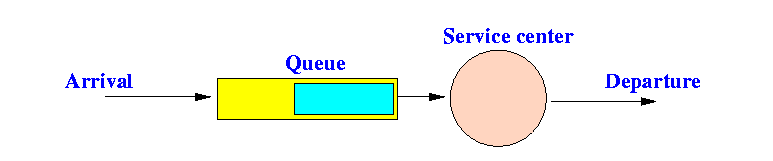
- An arrival process of
client into a
holding area (queue)
- Interesting (relevant) performance measures:
- Average waiting time
inside the queue
I.e., what is the average time that customers must wait before they starts obtaining the service
- Average time spent in system
I.e., what is the average time needed for customers to complete the service
(This is the duration from the arrival of the customer to its departure)
- Average waiting time
inside the queue
- Deterministic process:
- A deterministic process is a process
with a determined schedule of events
We can tell what event will happen next.
Example: sorting algorithm
- A deterministic process is a process
with a determined schedule of events
- Stochastic process:
- A stochastic process is a process
with a probabilistic schedule of events
The next event will occur with a certain probability
Example: post office (when the next cunstomer arrive is a probabilitic event)
- A stochastic process is a process
with a probabilistic schedule of events
- The Poisson process is a
stochastic event where:
1. Ҏ[ one customer arrives in the next time interval Δt ] = &lambda×Δt + o(Δt) ........ (1) 2. Ҏ[ no customer arrives in the next time interval Δt ] = 1 - &lambda×Δt + o(Δt) ........ (2) 3. Ҏ[ ≥ 2 customers arrive in the next time interval Δt ] = o(Δt) ........ (3) 4. The arrivals in non-overlapping time intervals are (probabilistically) independent
Note:
- The notation
Ҏ[x]
means the
probability of the event x
- The parameter
λ is the
arrival rate
I.e., λ = average number of arrivals per time unit
Equation (1):
Ҏ[ one customer arrives in the next time interval Δt ] = &lambda×Δt + o(Δt)
states that the probability of an arrival in the Poisson process is linearly dependent on the arrival rate λ
- The notation
o(Δt)
means:
o(Δt) lim Δt &rarr 0 ------- = 0 ΔtI.e., terms of the order o(Δt) are negligible compared to the term Δt
- The notation
Ҏ[x]
means the
probability of the event x
- The
probabibility density function
of the Poisson arrival process
with arrival rate &lambda is
defined as:
p(k) = Ҏ( k arrivals in an interval T )
Graphically:
k arrival events | | | | V V V V |<--------------------->| T sec
- Computing p(k)
- Divide the interval
into n pieces:
ΔT = T/n <--> |<-->|<-->|<-->|................|<-->| <----------------------------------> T sec
- By Equation (1)
(click here), the
probability that one customer
arrives in the
interval ΔT is:
Ҏ[ 1 arrival in ΔT ] = λ × ΔT + o(ΔT) ~= λ × ΔT = λ × T/n
- The probability that k customers
arrives in the
interval T is a
Binomial trial
with probability of success equal to
λ × ΔT + o(ΔT)
Therefore:
n! Ҏ[ k arrivals in T ] = ----------- (Ҏ[ 1 arrival in ΔT ])k (1 - Ҏ[ 1 arrival in ΔT ])n-k k! (n-k)! n! = lim (n → ∞) ----------- (λ × ΔT)k (1 - λ × ΔT)n-k k! (n-k)!Sub: ΔT = T/n
Move terms that are independent of n out of the limit...
n - x ------- → 1 when n &rarr ∞ for any constant x n
lim (n → ∞) (1 - λT/n)n-k = lim (n → ∞) (1 - λT/n)n × lim (n → ∞) (1 - λT/n)-k = lim (n → ∞) (1 - λT/n)n × (1 - 0)-k = lim (n → ∞) (1 - λT/n)n = e-λT (a well-known Math limit)
Hence: (λT)k Ҏ[ k arrivals in T ] = ------- e-λT ........ (Poisson distribution) k!
- Divide the interval
into n pieces:
- By the definition of expected value:
E[x] = ∑ (all values k) k Ҏ[k] (λT)k = ∑ (k = 0 .. ∞) k × ------ e-λT k! (λT)k = ∑ (k = 1 .. ∞) ------ e-λT (k-1)!Move terms independent of k out of the sum....
Adjust the running index (make k run from 0 &rarr ∞)....
Move one term λT out of the sum...
Well-known Math serie: ∑ (k = 0 .. ∞) xk/k! = ex
- Previously, we found that the
expected value
of a Poisson λ distributed random variable
x is:
E[x] = λT
The random variable x represents the number of arrivals in a time interval of duration T (See: click here )
- Therefore:
- The average (mean) number of arrivals over a time interval of duration T is equal to λ × T
In other words:
- The average number of arrivals
per time unit is:
Avg # arrivals per second = λT/T = λ
- Arrival rate of a Poisson process
- λ is the
arrival rate of
the Poisson arrival process
λ = the average number of arrivals per time unit (sec)
- λ is the
arrival rate of
the Poisson arrival process
- Define:
- y =
the random variable representing the
time between
2 consecutive arrivals
in a Poisson arrival process
( y = the inter-arrival time)
- y =
the random variable representing the
time between
2 consecutive arrivals
in a Poisson arrival process
- Probability density function of y:
Ҏ[ y > t ] = Ҏ[ no arrivals in interval (0..t) ] (λt)0 = ----- e-λt 0! = e-λt
Ҏ[ y ≤ t ] = 1 - Ҏ[ y > t ] = 1 - e-λt .... (Probability distrubution function of y)
- Probability density function of y:
d Q(t) p(t) = ------ ..... (from Probability theory) dt
Qy(t) = 1 - e-λt Therefore: d [1 - e-λt] py(t) = ------------ dt = - e-λt × (-λ) = λ e-λt .....(Probability density function of y)
- Memoryless property:
- A process is
memory-less if it has the following
property:
Ҏ[ no event time within next t sec | event has not happened for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no event time within next t sec ]In other words:
- The likelihood (probability) of when the next event will happen will next be affected by the given knowledge that the event has not happened for some time
- A process is
memory-less if it has the following
property:
- Example of memory-full processes:
- Volcano eruptions:
- The probability that a volcano will not erupt within the next 100 yrs is greatly decreased if we knew that the volcano has not erupted for 1 million years
- Hunger:
- The probability that a person does not become hungry within the next hour is greatly decreased if we knew that the person has not eaten for 6 hours
- Volcano eruptions:
- The Poisson process is memory-less, i.e:
Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec | no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec ]Proof:
Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec | no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec and no arrival for u sec ] = ------------------------------------------------------------------ (def of cond probability) Ҏ[ no arrival for u sec ]
Observe that: |<------ u ------>|<--------- t ------> ------+------------------+---------------------> 0 arrivals 0 arrival Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec and no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival for t+u sec ]
Therefore: Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec | no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival for t+u sec ] = ------------------------------ Ҏ[ no arrival for u sec ] (λ(t+u))0 --------- e-λ(t+u) 0! = -------------------- (λu)0 ----- e-λu 0! e-λ(t+u) = -------- e-λu = e-λt
On the other hand: (λt)0 Ҏ[ no arrivals occurs within next t sec ] = ------ e-λt (# arrivals = 0 !) 0! = e-λt
Therefore: Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec | no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec ] for the Poisson arrival process Hence: the Poisson process is memory-less !