- The probability
of an event A is the
likelihood
of the occurring
of that event.
Concretely:
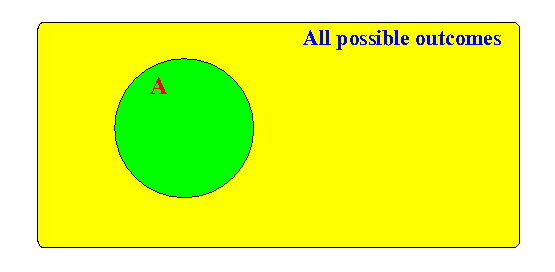
Probability of an event A:
# outcomes A Ҏ [ event A ] = ------------------------ # posible outcomes
- The probability mass/density function:
- p(k) = Probab[ event x = k ]
I.e.: p(k) = the probability that the outcome x is equal to k
(x is called a random variable)
- p(k) = Probab[ event x = k ]
- Cumulative probability distribution function:
Discrete p(x): Q(k) = Ҏ[ x ≤ k ] = &sum x ≤ k p(x)
Continuous p(x): Q(k) = Ҏ[ x ≤ k ] = &int x ≤ k p(x) Note that: d Q(x) p(x) = ------ dxProperty of every cumulative probability distribution function:
lim (x → ∞) Q(x) = 1
- Mathematical definition of expected value:
E[x] = ∑(all values k) k Ҏ[k] (discrete x) E[x] = ∫(all values k) x p(x) dx (continuous x)
Conditional Probability Ҏ[A | B]:
Ҏ[A &cap B]
Ҏ[A | B] = ----------
Ҏ[B]
|
- Law of Total Probability
- Let
B1, B2, ...
BN
finite (or countably infinite)
partition of a probability space
Then:
Ҏ[ A ] = Ҏ[ A | B1 ] × Ҏ[ B1 ] + Ҏ[ A | B2 ] × Ҏ[ B2 ] + ... + Ҏ[ A | BN ] × Ҏ[ BN ]
- Let
B1, B2, ...
BN
finite (or countably infinite)
partition of a probability space
- The Poisson process is a
stochastic event where:
1. Ҏ[ one customer arrives in the next time interval Δt ] = &lambda×Δt + o(Δt) ........ (1) 2. Ҏ[ no customer arrives in the next time interval Δt ] = 1 - &lambda×Δt + o(Δt) ........ (2) 3. Ҏ[ ≥ 2 customers arrive in the next time interval Δt ] = o(Δt) ........ (3) 4. The arrivals in non-overlapping time intervals are (probabilistically) independent
- Poisson PDF:
(λT)k Ҏ[ k arrivals in interval of T sec ] = ------- e-λT k!
E[x] = λT (avg. # arrivals in interval of T sec) |
- Arrival rate:
Avg # arrivals per second = λT/T = λ
- Ҏ[ y ≤ t ] = probability that
the inter-arrival time is
less that t:
Ҏ[ y ≤ t ] = 1 - e-λt
- Memoryless property:
u sec t sec |<---------------->|<-------------------->| Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec | no arrival for u sec ] = Ҏ[ no arrival occurs within next t sec ] - Allows us to compute transition probabilities in Markov chains easily...
- One-step transition probability:
Pij = Ҏ[ X(t+1) = j | X(t) = i ]
- One-step transition probability matrix:
+- -+ | P11 P12 P13 ... P1N | | P21 P22 P23 ... P2N | P = | .. .. .. .. | | .. .. .. .. | | PN1 PN2 PN3 ... PNN | +- -+
- n-step transition probability matrix:
Pn = P × P × P × .... × P
- Finding the stationary (steady state)
state probability π for
a Markov chain:
π = π × P (with: &pi1 + &pi2 + ... + &pin = 1)
- Birth-death process only has transitions to its
immediate neighbor:

- Poisson birth/death process:
- Ҏ[ an arrival occurs in time interval Δt ] = λ × Δt
-
Ҏ[
a departure
occurs in time interval Δt
] =
μ × Δt
- λ = arrival rate (see: click here )
- μ = departure rate
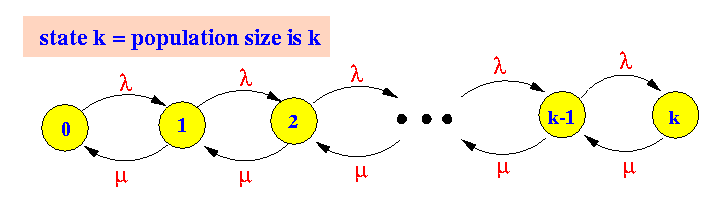
- State transition diagram for a Poisson birth/death process:

- Steady state probability distribution
of a Poisson birth/death
process with arrival rate λ and departure rate μ:
p0 = (λ/μ)0 × (1-(λ/μ)) p1 = (λ/μ)1 × (1-(λ/μ)) p2 = (λ/μ)2 × (1-(λ/μ)) p3 = (λ/μ)3 × (1-(λ/μ)) ....
Or: p0 = ρ0 × (1 - ρ) p1 = ρ1 × (1 - ρ) p2 = ρ2 × (1 - ρ) p3 = ρ3 × (1 - ρ) .... Or:Ҏ[ k customers in system ] = pk = ρk × (1 - ρ)
- The rate transition diagram
for the M/M/1 queueing system is:
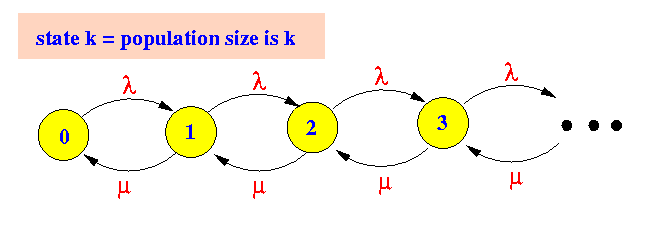
- The rate transition diagram
for the M/M/2 system is:
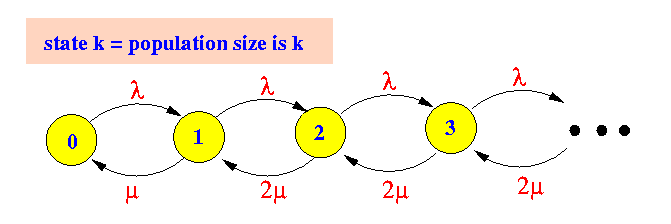
- The rate transition diagram
for the M/M/k system is:
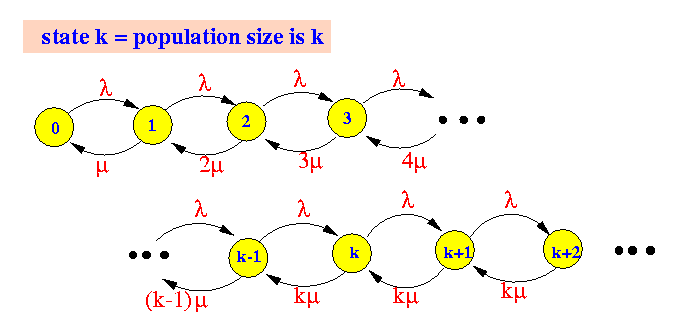
- The rate transition diagram
for the M/M/1/k
(finite buffer)
queueing system is:
- Average queue length:
N = mean (expected) number of customer = 0 × Ҏ[ k customers in system] + 1 × Ҏ[ 1 customer in system] + 2 × Ҏ[ 2 customers in system] + .... = ∑ {k = 0, 1, .., ∞} k × Ҏ[ k customers in system] (definition of "expected value") = ∑ {k = 0, 1, .., ∞} k × pk
- Average delay:
the Little's formula:
T = N / λ (Little's formula in another form)