- Number of packets carried by a link:
- Network link:
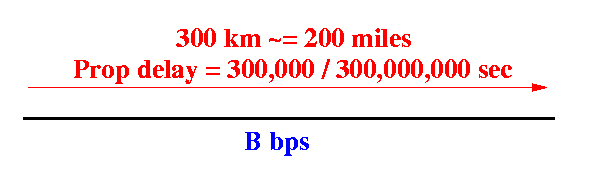
- Propagation delay on
a 300 Km link =
300,000/300,000,000 sec =
10-3 sec
The 300 Km link carries (B × 10-3) bits
- Suppose each packet consists of
10,000 bits (~ 1 Kbytes),
then a 300 Km link carries
approximately
(B × 10-7) packets
Number of packets carried by a 300 Km link:
B = 10 Mbps B = 100 Mbps B = 1 Gbps B = 10 Gbps B = 100 Gbps #packets = 1 #packets = 10 #packets = 100 #packets = 1000 #packets = 10000
- Network link:
- Effect of a high speed link:
- A high speed link acts like
a very large buffer
for packets
- Packets en route (traveling towards) the destination are stored in the high speed link
- A high speed link acts like
a very large buffer
for packets
- Effect of a congested router:
- The queue of a
congested router is
eventually overflow
- The overflowed queue will
drop newly arriving packets
- Effect of high speed link:

Notes:
- Even when the
TCP (sender)
times out and
set CWND = 1,
the arrival rate into
the congested route
will not decrease significantly
- The congested router will
take a very long time to
clear its buffer
- TCP will experience
multiple consecutive timeout
- Consequently: the SSThreh become very small
- Even when the
TCP (sender)
times out and
set CWND = 1,
the arrival rate into
the congested route
will not decrease significantly
- The queue of a
congested router is
eventually overflow
- Example:
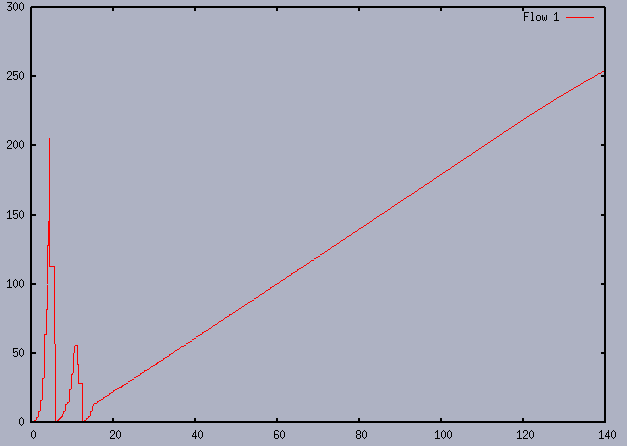
Note:
- When the SSThresh has
become very small,
TCP will take
a very long time
to acquire additional bandwidth
for its transmission use !!!
(Because TCP is in congestion avoidance mode and increases CWND by 1 (one) after every RTT sec)
- When the SSThresh has
become very small,
TCP will take
a very long time
to acquire additional bandwidth
for its transmission use !!!
- CWND update in TCP:
1 new ACK: CWND = CWND + ------ CWND 1 Triple Duplicate ACKs: CWND = CWND - --- CWND 2
- Throughput of TCP:
(using the first order approximation of
the Padhye's result:
(see: click here )
------- 1 / 3 B(p) = ----- \ / ----- RTT \/ 2bpFor the case where b = 1 (no delayed ACK), we have:
------ ------- 1 / 3 1 / 1.5 B(p) = ----- \ / ---- = ----- \ / ----- RTT \/ 2p RTT \/ p 1 1.2 B(p) = ----- * ------- (packets per sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . (1) RTT ---- \/ p
- The
TCP throughput formula (Equation (1))
can tell us that
TCP
cannot achieve
gigabit per second
throughput
- Assume that:
RTT = 0.1 sec Packetsize = 1500 bytes
- The TCP throughput is
equal to:
(See: click here)
1 1.2 B(p) = ----- * ------- (packets per sec) RTT ---- \/ p 1 1.2 = ----- * ------- (packets per sec) 0.1 ---- \/ p 1 1.2 = ----- * ------- * 1500 (bytes per sec) 0.1 ---- \/ p 12 * 1500 * 8 = --------------- bps ---- \/ p 144,000 = --------- bps ---- \/ p - To achieve, says
10 Gbps throughput,
the
packet loss probability p
must be equal to:
144,000 B(p) = --------- = 10,000,000,000 ---- \/ p
---- 144,000 ==> \/ p = --------------- = 0.0000144 10,000,000,000
<==> p = 0.00000000020736 = 2 x 10-10 (in other words: 1 packet loss in every 5,000,000,000 packets !) - Existing
communication networks
cannot achieve
1 packet loss
in every
5,000,000,000 packets sent
- Clarification:
- Fiber optic
has error rate of
1 error in 1010 bits
Probab of bit error in fiber = 10−10
- A packet of 1500 bytes
has 8 * 1500 = 12000 bits
- Every bit have be
received correctly
for the packet to be received
correctly
Therefore:
1 − p = (1 − 10−10)12000 ~= 1 − 12000 × 10−10Packet loss probability for a 1500 byte packet in fiber:
p = 12000 × 10−10 = 1.2 × 10−6
- p is much larger than 2 × 10−10
- Fiber optic
has error rate of
1 error in 1010 bits
- Conclusion:
- Existing technology cannot support giga bit per second throughput with current TCP congestion mechanism because the packet loss requirement is too high !!!
- Classic TCP:
1 Increase: W = W + --- (when new ACK is received) W Decrease: W = W - 0.5 * W (when packet loss is detected by 3 dup ACKs)
1 1.2 Avg TCP Throughput = ----- * ------- (in # packets/sec) RTT --- \/ p p = packet loss probability
- The average CWND
used by (classic) TCP:
- Throughput when using
CWND = k (packets):

What value of CWND used by TCP will yield the average TCP throughput:
1 1.2 Avg TCP Throughput = ----- * ------- (in # packets/sec) RTT --- \/ p
- Throughput when using
CWND = k (packets):
- Relationship:
1.2 Avg. CWND = ------- (in # packets) --- \/ p
- Some explicit values:
Packet Drop Rate P Congestion Window W ------------------ ------------------- 10^-2 12 10^-3 38 10^-4 120 10^-5 379 10^-6 1200 10^-7 3795 10^-8 12000 10^-9 37948 10^-10 120000 Table 2: TCP Response Function for Standard TCP. The average congestion window W in MSS-sized segments (packets) is given as a function of the packet drop rate P. - Observation:
- Packet loss probability on
fiber optic links is
in the order of
p = 10-7
- From the table above, we see that
the (standard) TCP protocol
will
avg. CNWD = 3795
This CWND value is too small not allow TCP to transmit at Giga bits per sec
- Packet loss probability on
fiber optic links is
in the order of
p = 10-7
- Modify TCP:
- We cannot use the
existing TCP congestion mechanism
- We need a modified mechanism with speedier increase in CWND
- We cannot use the
existing TCP congestion mechanism
- Note:
- We should keep using additive increase and multiplicative decrease to achieve a fair throughput equilibrium for competing TCP flows
- A more general
update algorithm
for TCP's CWND
is:
a new ACK: CWND = CWND + ------ CWND 3 dup ACK: CWND = CWND − b * CWND
- The
TCP throughput
is then (approximately):
(see:
click here )
------------ 1 / a (2 - b) B(p) = ----- \ / ---------- (packets/sec) RTT \/ 2bpNotes:
- No proof here -
it's in the paper:
(see:
click here )
- The parameter b
has a
different meaning
then the b
in Padhye's paper.
The parameter b in Padhye's paper relates to delayed ACKs
- The parameter b here
is the
multiplicative decrease factor !!!
(I am using the authors' notation so you can read their paper along side with the class notes with more ease...)
- No proof here -
it's in the paper:
(see:
click here )
- The first attempt to make TCP operate at
Gigabit speed is the work:
-
"HighSpeed TCP for
Large Congestion Windows"
click here
This proposal builds on TCP Reno and is going through the Internet standardization process.
- Another commerically avaialble product is
"FAST-TCP"
(from CalTech):
- "FAST TCP: Motivation, Architecture, ALgorithms and Performance" click here
- A friend of mine is also in the business of designing
high speed TCP protocols:
- "CUBIC: A New TCP-Friendly High Speed TCP variant" click here
- And there are
many other protocols...
too many to cover :-)
- We will therefore cover the first one - that will give you an idea what the other are doing....